What is Thread
A thread is a lightweight sub process, a smallest unit of processing. It is a separate path of execution. Threads are independent, shares a common memory area. if there occurs exception in one thread, it doesn’t affect other threads.
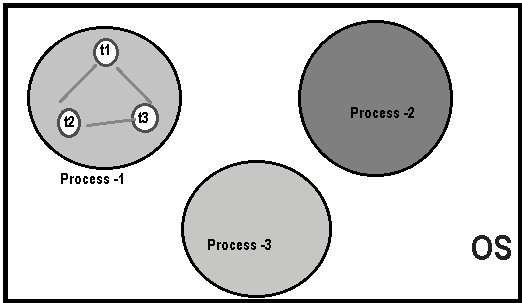
As shown in the above figure, thread is executed inside the process. There is context-switching between the threads. There can be multiple processes inside the OS and one process can have multiple threads
At a time one thread is executed only.
Thread Life Cycles (Thread States)
See below picture which compares Interview process & Thread Execution process.
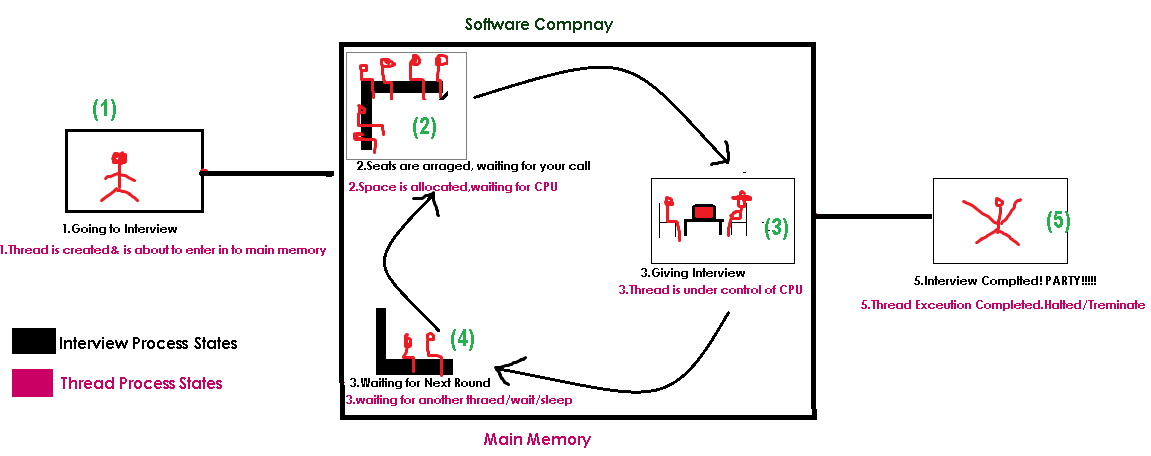
Based on the process of execution of thread, people said there are 5 states of a
thread
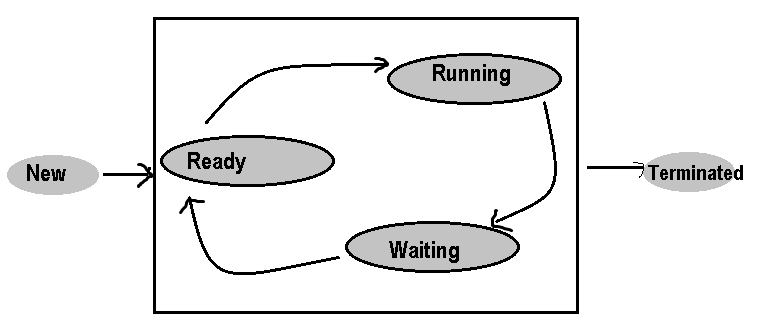
1. New: Thread is created and about to enter into main memory. i.e., New Thread Object is created but before the invocation of start() method.
2. Ready/Runnable: thread memory space allocated and it is waiting for CPU for executing. i.e., after invocation of start() method, but the thread scheduler has not selected
3. Running: thread is under the control of CPU. i.e., thread scheduler has selected (run() executing).
4. Waiting: This is the state when the thread is still alive, but is currently not eligible to run. Thread is waiting because of the following factors:
-
For the repeating CPU burst time of the thread
-
Make the thread to sleep for some specified amount of time.
-
Make the thread to suspend.
-
Make the thread to wait for a period of time.
-
Make the thread to wait without specifying waiting time.
5. Terminated: thread has completed its total execution. i.e., Exit form run () method
We have two ways of creating Thread,
- by extending java.lang.Thread class
- By implementing java.lang.Runnable interface.
In multi-threading we get only one exception known as
java.lang.InterruptedException.