Legacy Classes on Map
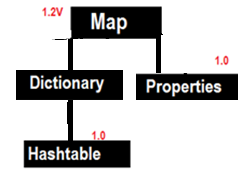
The Dictionary class is the abstract parent of any class, such as Hashtable, which maps keys to values. Every key and every value is an object.
1.Hashtable
-
Underlying D.S Hashtable for is Hashtable
-
Insertion order is not preserved & it is based on Hashcode of keys
-
DUPLICATE keys are NOT allowed & Values can be duplicated
-
Hertogenious objects are allowed for both keys&values
-
Null is NOT allowed for both key& value.otherwise we will get NullPointerException at runtime
-
It implements Serializable, Clonable interfaces but not RandomAccess
-
All methods are Synchronized, so Hashtable is Thread-Safe
-
Hashtable is best choice for Search Operation
1. Hashtable h = new Hashtable () //16 capacity, Def. fill ratio = 0.75
Creates an empty Object with def. initial capacity 11 & def. fill ratio 0.75
2. Hashtable h = new Hashtable (int intialcapacity) // Def. fill ratio = 0.75
3. Hashtable h = new Hashtable (int intialcapacity, float fillRatio)
4. Hashtable h = new Hashtable (Map m)
class Test {
int i;
Test(int i) {
this.i = i;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return i;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return i + "";
}
}
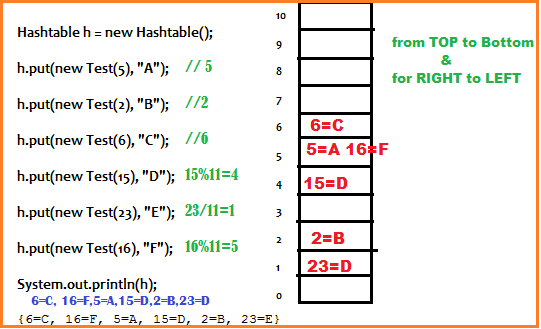
public class HashtableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable h = new Hashtable();
h.put(new Test(5), "A");
h.put(new Test(2), "B");
h.put(new Test(6), "C");
h.put(new Test(15), "D");
h.put(new Test(23), "E");
h.put(new Test(16), "F");
System.out.println(h);
}
}
---------------------------
{6=C, 16=F, 5=A, 15=D, 2=B, 23=E}
By default HashMap is non-synchronized but we can get Sychronized version of
HashMap by usinh synchronizedMap () of collections class
HashMap m = new HashMap()
Map m1 = Collections.synchronizedMap(m)
2.Properties
In our if anything which changes frequently like Database names, username, password etc we use properties file to store those & java programe used to read properties file
1. Properties p = new Properties ()
KEY & Values must be String type
Methods
-
String getProperty(String name);
-
String setProperty(String name, value);
-
Enumaration propertyNames();
-
void load(InputStream is)
Load properties from properties file into java properties Object -
void store(OutputStream is, String commet)
Store java properties Object into properties file
////abc.properties
uname=satya
port=8080
---------------------------------
public class PropertiesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Properties p = new Properties();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("abc.properties");
p.load(fis);
System.out.println(p);
System.out.println("Uname : "+p.getProperty("uname"));
p.setProperty("port", "8080");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("abc.properties");
p.store(fos, "Port Number comment added");
}
}
-----------------------
#Port Number comment added //abc.properties After
#Mon Sep 12 20:38:33 IST 2016
uname=satya
port=8080
pwd=smlcodes
Multiple values in java.util.Properties
foo=1,2
String[] foos = properties.getProperty("foo").split(",");