4.CyclicBrarrier
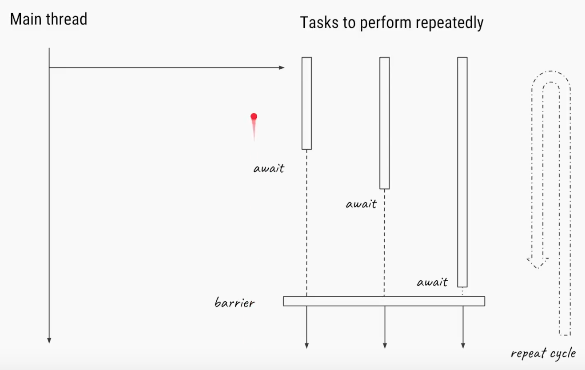
CyclicBrarrier is a synchronization mechanisum that allows a set of threads to all wait for each other to reach a common barrier point.
First a new instance of a CyclicBarriers is created specifying the number of threads that the barriers should wait upon.
CyclicBarrier newBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(numberOfThreads);
Methods- await()
Each and every thread does some computation and after completing it s execution, calls await() methods as shown:
public void run()
{
// thread does the computation
newBarrier.await();
}
Once the number of threads that called await() equals numberOfThreads, the barrier then gives a way for the waiting threads. The CyclicBarrier can also be initialized with some action that is performed once all the threads have reached the barrier. This action can combine/utilize the result of computation of individual thread waiting in the barrier.
Runnable action = ...
//action to be performed when all threads reach the barrier;
CyclicBarrier newBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(numberOfThreads, action);
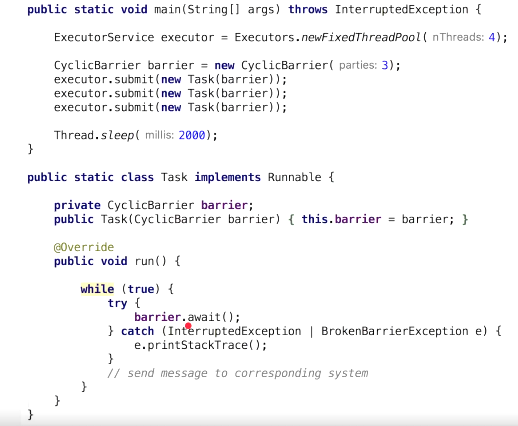
class Task implements Runnable {
private CyclicBarrier barrier;
public Task(CyclicBarrier barrier) {
this.barrier = barrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " is waiting on barrier");
barrier.await();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " COMPLETED");
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
} catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
}
public class CyclicBarrierExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// creating CyclicBarrier with 3 Threads which, meet at this point
final CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier(3, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// This task will be executed once all thread reaches barrier
System.out.println("================================");
System.out.println("All parties are arrived at barrier, lets play");
System.out.println("================================");
}
});
// starting each of thread
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Task(cb), "Thread 1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Task(cb), "Thread 2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(new Task(cb), "Thread 3");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
Thread 1 is waiting on barrier
Thread 3 is waiting on barrier
Thread 2 is waiting on barrier
================================
All parties are arrived at barrier, lets play
================================
Thread 2 COMPLETED
Thread 3 COMPLETED
Thread 1 COMPLETED
PREVIOUSCountDownLatch
NEXTPhaser