Quick Sort
Quick sort is based on the divide-and-conquer approach based on the idea of choosing one element as a pivot element(normally height index value) and partitioning the array around it such that:
-
Left side of pivot contains all the elements that are less than the pivot element
-
Right side contains all elements greater than the pivot
For example: In the array {52, 37, 63, 14, 17, 8, 6, 25}, we take 25 as pivot. So after the first pass, the list will be changed like this.
{6 8 17 14 25 63 37 52}
Hence after the first pass, pivot will be set at its position, with all the elements smaller to it on its left and all the elements larger than to its right. Now 6 8 17 14 and 63 37 52 are considered as two separate subarrays, and same recursive logic will be applied on them, and we will keep doing this until the complete array is sorted.
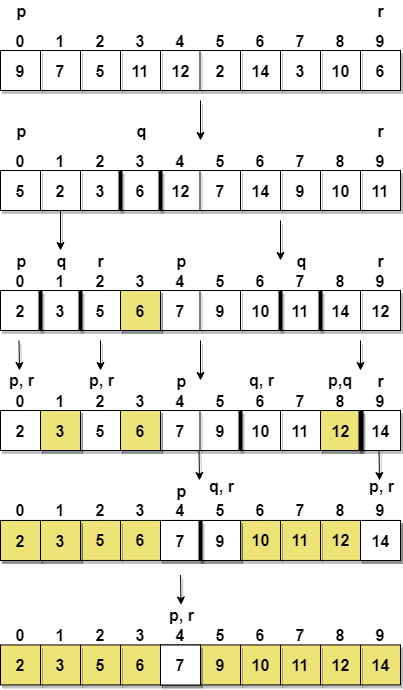
Step 1 − Choose the highest index value has pivot
Step 2 − Take two variables to point left and right of the list excluding pivot
Step 3 − left points to the low index
Step 4 − right points to the high
Step 5 − while value at left is less than pivot move right
Step 6 − while value at right is greater than pivot move left
Step 7 − if both step 5 and step 6 does not match swap left and right
Step 8 − if left ≥ right, the point where they met is new pivot