Swing Components
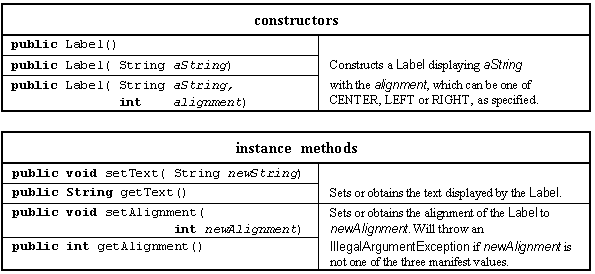
1. Label
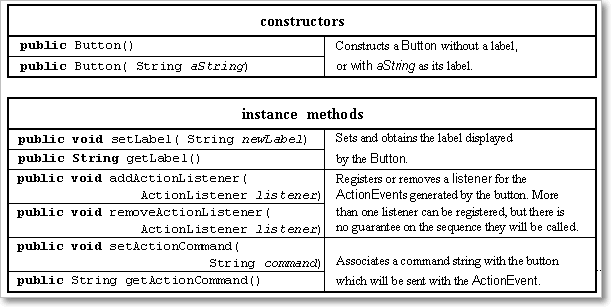
2. Button
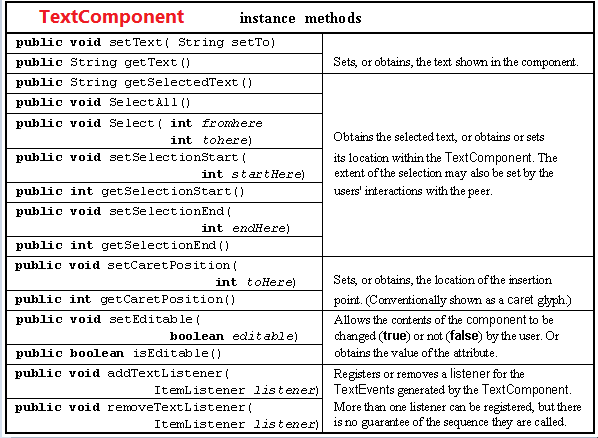
3.TextComponet
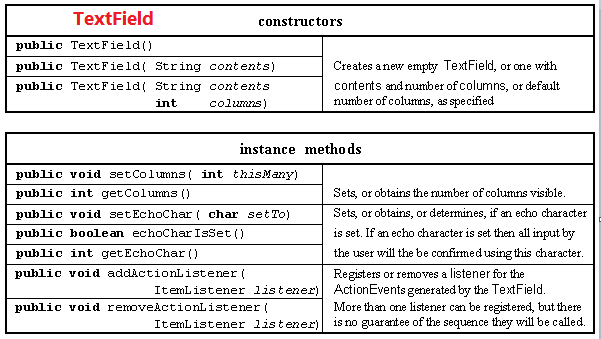
4. TextField
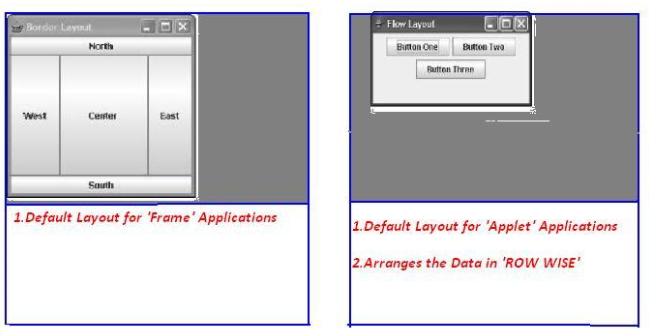
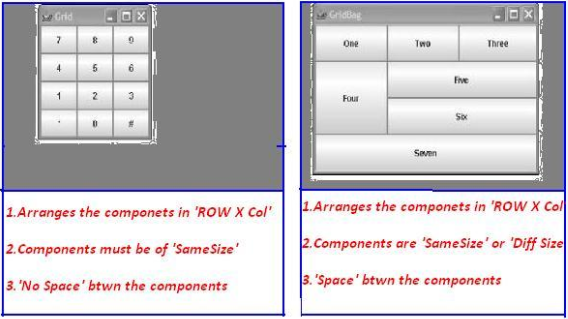
5. Layout Managers

Steps for developing awt program:
-
Import the appropriate packages.
-
Choose the appropriate class and it must extend java.awt.Frame and implements appropriate Listener if required.
-
Identify & declare components as data members in the top of the class.
-
Set the title for the window.
-
Set the size of the window.
-
Create Objects of the components in the Constructor which are identified in step 3.
-
Add the created components to container.
-
Register the events of the appropriate interactive component with appropriate Listener.
-
Make the components to be visible (setvisible(true)).
-
Define the undefined methods in the current class which is coming from appropriate Listener.
-
Write functionality to GUI component in that method
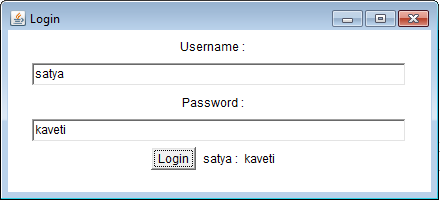
Example
public class LoginDemo extends Frame implements ActionListener {
// 1. Decalring components
Label l1, l2, status;
TextField t1, t2;
Button login;
public LoginDemo() {
// 4,5 Setting title & Size
setSize(200, 200);
setTitle("Login");
// 6.creating Component Objects
l1 = new Label("Username : ");
l2 = new Label("Password : ");
status = new Label("Status");
t1 = new TextField(50);
t2 = new TextField(50);
login = new Button("Login");
// 7.adding componets to container
add(l1);
add(t1);
add(l2);
add(t2);
add(login);
add(status);
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
// 8.reister with Listener
login.addActionListener(this);
setVisible(true);// 9.setvisble
}
@Override // 10
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if (e.getSource() == login) {
// 11.implemeting Logic
status.setText(t1.getText() + " : " + t2.getText());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new LoginDemo();
}
}
Similarly we have no.of components but the process of each one is similar.
Combined steps to develop FRAME and APPLET applications
-
Import appropriate packages for GUI components (java.awt.*) providing functionality to GUI components (java.awt.event.*) and for applet development (java.applet.Applet).
-
Every user defined class must extend either Frame or Applet and it must implement appropriate Listener if required.
-
Identify which components are required to develop a GUI application.
-
Use life cycle methods (init, start, destroy) in the case of applet, use default Constructor in the case of Frame for creating the components, adding the components, registering the components, etc.
-
Set the title of the window.
-
Set the size of the window.
-
Set the layout if required.
-
Create those components which are identified.
-
Add the created components to container.
-
Every interactive component must be registered with appropriate Listener.
-
Make the components to be visible in the case of Frame only.
-
Implement or define the abstract method which is coming from appropriate Listener.