Conditions
A java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition interface provides a thread ability to
suspend its execution, until the given condition is true.
Alternative for
wait & notify
We can Create Condition object by
using ReentrantLock & ReentrantReadWriteLock Which are implementation
classes of Lock interface. You can create condition variable by
calling lock.newCondtion() method
Methods
-
await():The current thread suspends its execution until it is signalled or interrupted.
-
await(long time, TimeUnit unit) :The current thread suspends its execution until it is signalled, interrupted, or the specified amount of time elapses.
-
awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) :The current thread suspends its execution until it is signalled, interrupted, or the specified amount of time elapses.
-
awaitUninterruptibly() :The current thread suspends its execution until it is signalled (cannot be interrupted).
-
await(long time, TimeUnit unit) :The current thread suspends its execution until it is signalled, interrupted, or the specified deadline elapses.
-
signal(): This method wakes a single thread which is waiting for a longtime on this condition.
-
signalAll(): This method wakes all threads waiting on this condition.
Condition variables are instance of java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition class, which provides inter thread communication methods similar to wait, notify and notifyAll e.g. await(), signal() and signalAll().
if one thread is waiting on a condition by calling condition.await() then once that condition changes, second thread can call condition.signal() or condition.signalAll() method to notify that its time to wake-up.
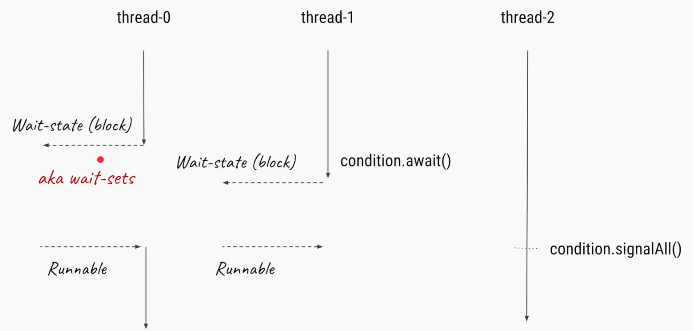
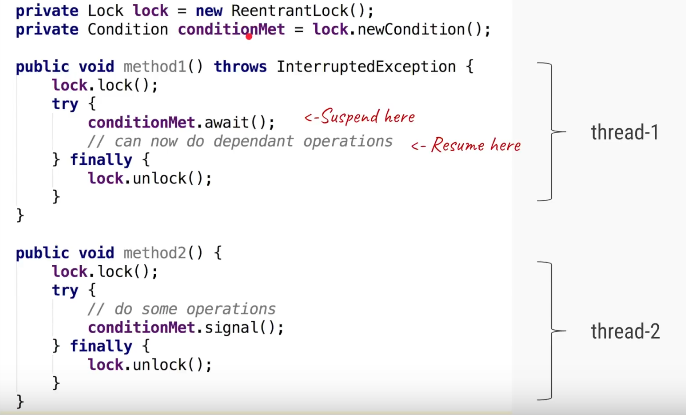
Locks are used for Sychronization.We will use Lock and Condition variables for solving classic Producer Consumer problem.
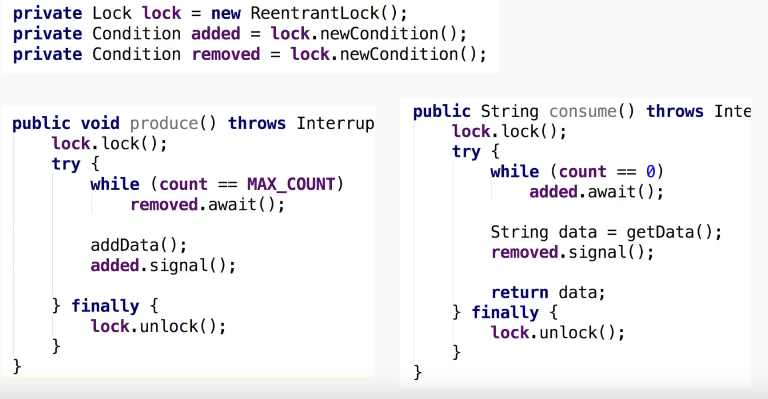
Example : solving classic Producer Consumer problem. //Not Imp
public class ProducerConsumerSolutionUsingLock {
public static void main(String[] arg) {
// Object on which producer and consumer thread will operate.
ProducerConsumerImpl sharedObject = new ProducerConsumerImpl();
// creating producer and consumer threads.
Productor p = new Productor(sharedObject);
Consumer c = new Consumer(sharedObject);
// starting producer and consumer threads.
p.start();
c.start();
}
}
class ProducerConsumerImpl {
// Productor consumer problem data.
private static final int CAPACITY = 10;
private final Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
private final Random theRandom = new Random();
// Lock and condition variables.
private final Lock aLock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition bufferNotFull = aLock.newCondition();
private final Condition bufferNotEmpty = aLock.newCondition();
public void put() throws InterruptedException {
aLock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == CAPACITY) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Buffer is full, waiting.");
bufferNotEmpty.await();
}
int number = theRandom.nextInt();
boolean isAdded = queue.offer(number);
if (isAdded) {
System.out.printf("%s added %d into queue %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), number);
// signal consumer thread that, buffer has element now
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Signalling that buffer is no more empty now.");
bufferNotFull.signalAll();
}
} finally {
aLock.unlock();
}
}
public void get() throws InterruptedException {
aLock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Buffer is empty, waiting.");
bufferNotFull.await();
}
Integer value = (Integer) queue.poll();
if (value != null) {
System.out.printf("%s consumed %d from queue %n ", Thread.currentThread().getName(), value);
// Signal producer thread that, buffer me be empty now
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Signalling that buffer may be empty now.");
bufferNotEmpty.signalAll();
}
} finally {
aLock.unlock();
}
}
}
class Productor extends Thread {
ProducerConsumerImpl producerConsumer;
public Productor(ProducerConsumerImpl sharedObject) {
super("PRODUCER");
this.producerConsumer = sharedObject;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
producerConsumer.put();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
ProducerConsumerImpl producerConsumer;
public Consumer(ProducerConsumerImpl sharedObject) {
super("CONSUMER");
this.producerConsumer = sharedObject;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
producerConsumer.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}