IdentityHashMap
-
It is exactly same as HashMap (including methods&constructors) except following diffrences
-
In the case of Normal HashMap JVM will use .equals() method to identify Duplicate keys, which is ment for Content comparision
-
But, In the case of IdentityHashMap JVM will use == operator to identify Duplicate keys, which is ment for reference comparision or address comparision
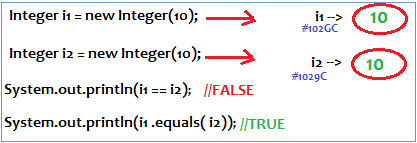
== is for reference comparision or address comparision
.equals () is for content comparision
HashMap Example
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] a) {
HashMap m = new HashMap();
m.put(new Integer(10), "Satya");
m.put(new Integer(10), "Surya");
System.out.println(m);
// {10=Surya}
}
}
---------------
{10=Surya}
IdentityHashMap Example
public class IdentityHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
IdentityHashMap m = new IdentityHashMap();
m.put(new Integer(10), "Satya");
m.put(new Integer(10), "Surya");
System.out.println(m);
// {10=Satya, 10=Surya}
}
}
-----------
{10=Satya, 10=Surya}
PREVIOUSTreeMap
NEXTWeakHashMap