java.io package
For dealing with input & Output Operations in java we have java.io.* package
In java we will write two types of programs
1. volatile programs : whose result are stored in main Memory (RAM),Temporally (Ex. Console Applications)
2. Non-Volatile programs : whose results are saved permanently in secondary memory like Drives,Harddisks, Databases & files.
Stream : flow of data/bites/bytes from source to destination
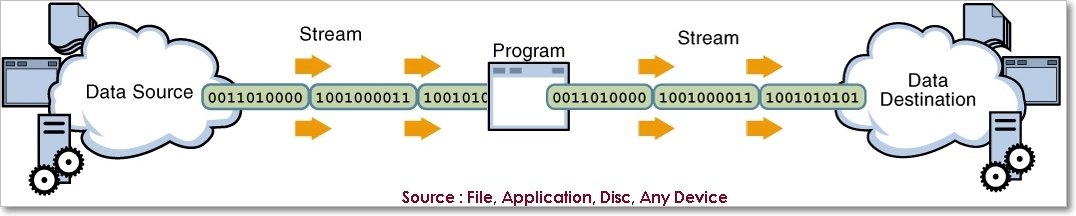
We have following types of streams to handle IO operations.
1. Byte Streams : perform input and output of 8-bit bytes. (FileInputStream & FileOutputStream)
2. Character Streams : I/O of character data, automatically handling translation to and from the local character set (FileReader and FileWriter)
3. Buffered Streams : Above are unbuffered I/O. This means each read or write request is handled directly by the underlying OS. Buffered input streams read data from a memory area known as a buffer; the native input API is called only when the buffer is empty. Similarly, buffered output streams write data to a buffer, and the native output API is called only when the buffer is full (BufferedInputStream and BufferedOutputStream)
4. Data Streams handle I/O of primitive data type and String values. ( DataInputStream & DataOutputStream.)
5. Object Streams : handle binary I/O of objects. (ObjectInputStream and ObjectOutputStream)
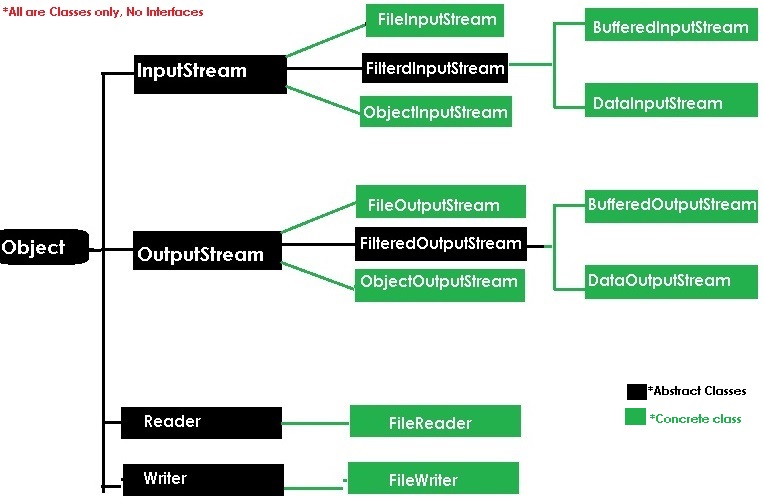
InputStream, OutputStream methods can be used by all their child classes for performing IO operations
1. InputStream : read Data from File/Source
-
public int read ();
-
public int length (); // total size of the file
-
public int available (); // available number of bytes only
-
public void close ();
2.OutputStream : Write data to file/Destination
-
public void write (int);
-
public int length ();
-
public void available ();
-
public void close ();
In java End of file (EOF) is indicated by -1