LinkedHashMap – Internal implementation
-
LinkedHashMap is just an extension of HashMap , internally uses HashTable+DoublyLinkedList
-
It has two references head and **tail **which will keep track of the latest object inserted and the first object inserted
1.Each node in a LinkedHashMap needs to have information about previous node and next node as the order in which they are accessed in important. The structure is as follows.

class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
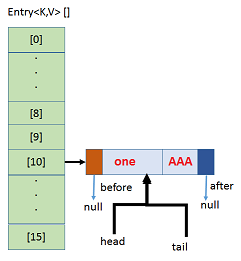
2.After inserting map.put(“one”, “AAA”);,Bucket with 16 capacity is created, hashcode & index will be caluculated.Here one is added, head and tail will refer to it.
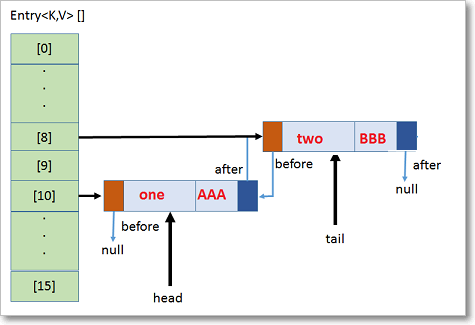
3.On adding map.put(“two”, “BBB”);, inserted in 8th bucket & it is next to -one”, so head one, tail two, before & after will linked, like this all elements will be added & Insertion order will be marinated.
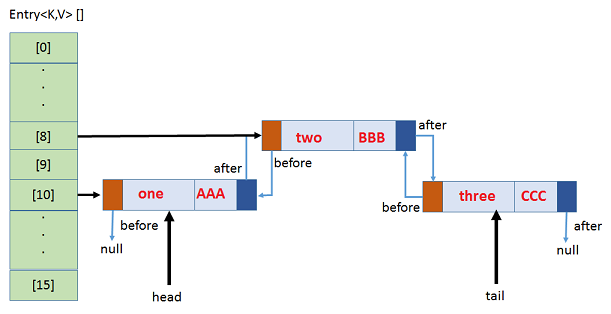
4.If any collision, new element will be added in same Bucket location with LinkedList& points to next.
public class HashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put("one", "AAA"); //7 -> []
map.put("two", "BBB"); //
map.put("two", "ZZZ");
map.put("three", "CCC");
map.put("four", "DDD");
map.put(null, "XXX");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
{one=AAA, two=ZZZ, three=CCC, four=DDD, null=XXX}
So here Insertion Order is preserved, elements the order they added, same order they will store
public class LinkedHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap h = new LinkedHashMap();
h.put("one", "Satya");
h.put("two", "Ravi");
h.put("three", "Rakesh");
h.put("four", "Surya");
System.out.println(h);// Insertion Order Preserved
System.out.println("adding exsting key:" + h.put("two", "Madhu"));
System.out.println("All keys : " + h.keySet());
System.out.println("All Values : " + h.values());
System.out.println("Both Key-Values\n---------");
Set s = h.entrySet();
Iterator it = s.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry) it.next();
System.out.println(m.getKey() + "\t : " + m.getValue());
}
}
}
{one=Satya, two=Ravi, three=Rakesh, four=Surya}
adding exsting key:Ravi
All keys : [one, two, three, four]
All Values : [Satya, Madhu, Rakesh, Surya]
Both Key-Values
---------
one : Satya
two : Madhu
three : Rakesh