ReadWriteLock interface
In addition to Lock interface,we have a ReadWriteLock interface which maintains a pair of locks, one for read-only operations, and one for the write operation.
ReentrantReadWriteLock class
ReentrantReadWriteLock class is implementation of it
-
Lock readLock()– returns the lock that’s used for reading -
Lock writeLock()– returns the lock that’s used for writing
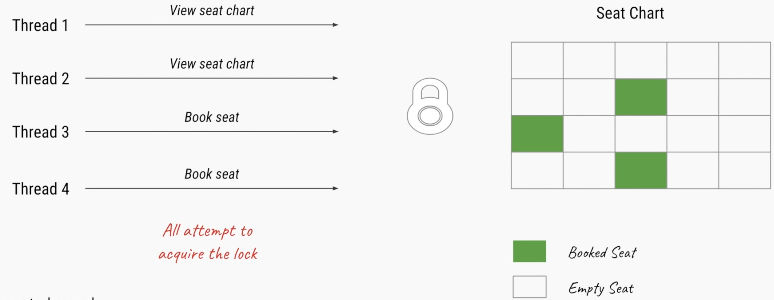
public class ReadWriteLockDemo implements Runnable {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
ReadWriteLock rwlock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(true);
Lock readLock = rwlock.readLock();
Lock writeLock = rwlock.writeLock();
public void write() {
writeLock.lock();
int ele = 100;
list.add(ele);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : Write : " + ele);
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
writeLock.unlock();
}
public void read() {
if (readLock.tryLock()) {
int index = list.size();
int ele = (int) list.get(index - 1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : Read : " + ele);
readLock.lock();
} else {
S.O.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": Write Lock Not avaialble");
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
String thname = Thread.currentThread().getName();
if (thname.contains("write")) {
write();
} else {
read();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReadWriteLockDemo ob = new ReadWriteLockDemo();
new Thread(ob, "write1").start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
new Thread(ob, "read1").start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
new Thread(ob, "read2").start();
}
}
---------------------------
write1 : Write : 100
read1: Write Lock Not avaialble
read2 : Read : 100

PREVIOUSSynchronization VS Locks
NEXTConditions