HashSet – Internal implementation
-
The underlying data structure is Hashtable, internally uses HashMap
-
Duplicate Objects are Not Allowed
-
Insertion Order is Not preserved & it is based hash code of Objects
-
Null Insertion is possible (Only once), Heterogeneous Objects are allowed
-
Implements Serializable & Clonable but not RandomAccess Interface
-
HashSet is the Best Choice for Search Operation
-
In HashSet Duplicates are not allowed. If we are trying to insert duplicates then it won’t get any Compile time or Runtime Error and add() method simply returns FALSE
Constructors
-
HashSet h = new HashSet ()//16 capacity, Def. fill ratio = 0.75 Creates an empty Object with def. initial capacity 16 & def. fill ratio 0.75 -
HashSet h = new HashSet (int intialcapacity)// Def. fill ratio = 0.75 -
HashSet h = new HashSet (int intialcapacity, float fillRatio) -
HashSet h = new HashSet (Collection c)
Implementation
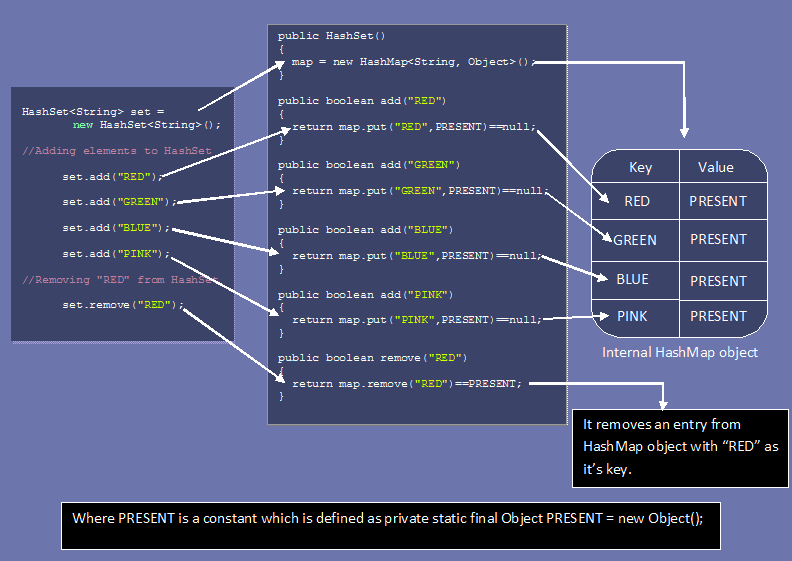
1.HashSet uses HashMap internally to store it’s objects. Whenever you create a HashSet object, one HashMap object associated with it is also created.
public HashSet()
{
map = new HashMap<>(); //Creating internally backing HashMap object
}
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
{
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
2.The elements you add into HashSet are stored as keys of this HashMap object. The value associated with those keys will be a constant(PRESENT).
Add Method
- add() method of HashSet class internally calls put() method of
backing HashMap object by passing the element you have specified as a
key and constant -PRESENT” as it’s value.
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; } -
Here hash function is calculated using value we are trying to insert.that is why only unique values are stored in the HashSet.
- When element is added to HashSet using add(E e) method internally HashSet calls put() method of the HashMap where the value passed in the add method becomes key in the put() method. A dummy value -PRESENT” is passed as value in the put() method.
public class HashSetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet h = new HashSet();
h.add("A");
h.add("B");
h.add("C");
h.add(10);
h.add(null);
System.out.println(h.add("A"));//False
System.out.println(h);
}
}
--------------------
false
[null, A, B, C, 10]