Constructor
At the time of Object Creation some peace of code will execute automatically to perform initialization that peace of code is nothing but -Constructor”. Hence the main Objective of constructor is to perform initialization.
Rules for writing Constructor
-
The name of the constructor and name of the class must be same.
- The only allowed modifiers for the constructors are
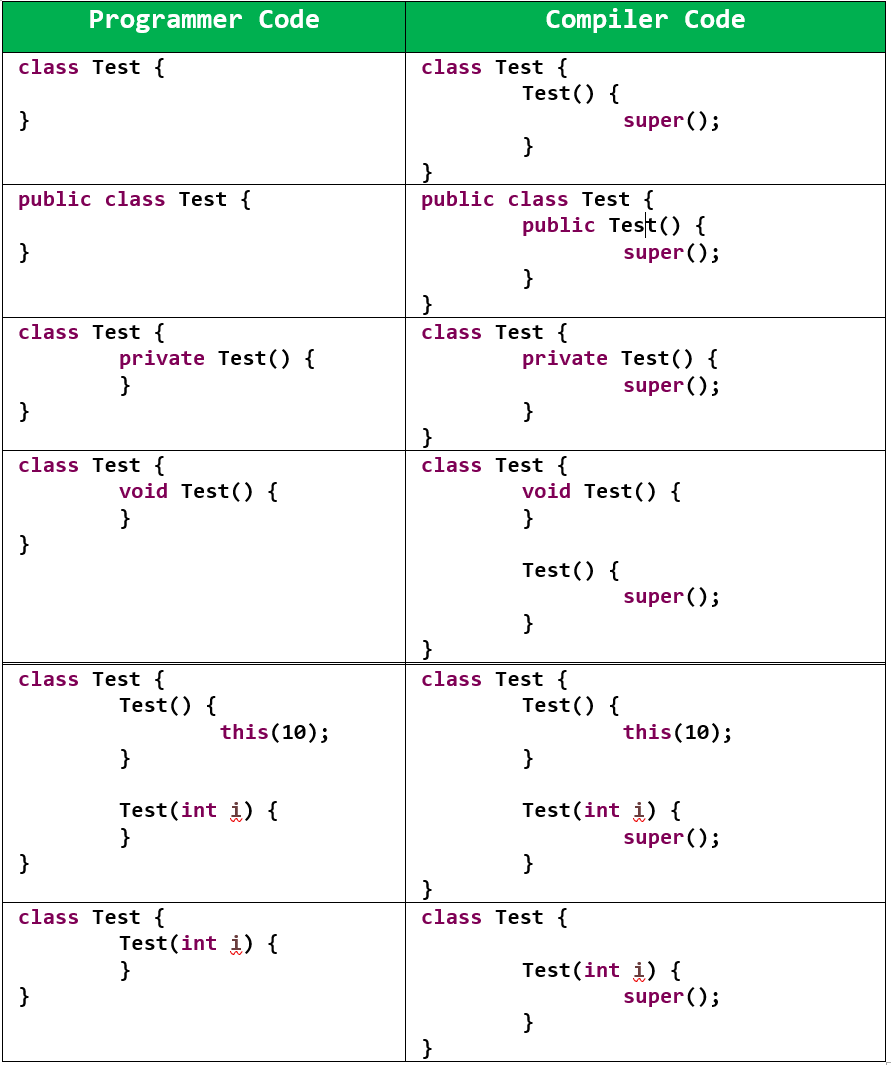
public, private,protected, <default>. If we are using any other modifier we will getC.E(Compiler Error).class Test { static Test(){ ---- } } C.E:- modifier static not allowed here. -
returntype is not allowed for the constructors evenvoidalso. If we are declaring return type, then the compiler treats it as a method and hence there is no C.E and R.E(RuntimeError).class Test { void Test(){ System.out.println("Hai ....."); } public static void main(String arg[]){ Test t = new Test(); } } -
If we are not writing any constructor, then the compiler always generate default constructor.
-
If we are writing at least one constructor, then the compiler won’t generate any constructor. Hence every class contains either programmer written constructor or compiler generated default constructor but not both simultaneously.
-
super() & this() in constructor
-
we should use as first statement in constructor.
-
We can use either
superorthisbut not both simultaneously. -
we can invoke a constructor directly from another constructor only
-
-
Inheritance concept is not applicable for constructor, so overriding is also not applicable
- Recursive Constructor invocation leads to Compile-time Exception.
class Test { Test() { this(10); } Test(int i) { this(); } } --------------------------------------- Test.java:6: error: recursive constructor invocation Test(int i) { ^ 1 error -
whenever we are writing parameterized constructor, it is recomended to provide no-arument constructor as well. If parent class contains parameterized constructor, then while writing child class constructor we should take a bit care
- If the parent class constructor throws checked exception, Compulsory the
child class constructor should throw the same checked exception or it’s
parent other wise we will get compile time error
class p { p() throws IOException {} } class c extends p { c() { super(); } } Test.java:10: error: unreported exception IOException; must be caught or declared to be thrown super(); ^ - If the parent class constructor throws unchecked exception, then child class constructor not required to throw that exception.