5.Phaser
Phaser is like a collection of advantages of CountDownLatch and CyclicBarrierClasses
The CountDownLatch is :
-
Created with a fixed number of threads
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3); -
Cannot be reset
-
Allows threads to wait (await()) or continue with its execution once count becomes 0 countDown()
the CyclicBarrier :
-
Can be reset.
-
Does not a provide a method for the threads to advance. The threads have to wait till all the threads arrive.
-
Created with fixed number of threads.
Now, the Phaser has following properties
-
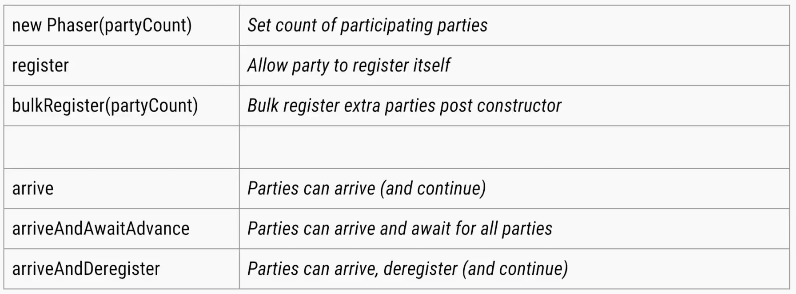
Number of threads need not be known at Phaser creation time. Threads can be added dynamically.
-
Can be reset and hence is, reusable.
-
Allows threads to wait(Phaser#arriveAndAwaitAdvance()) or continue with its execution(Phaser#arrive()).
-
Supports multiple Phases(, hence the name phaser).
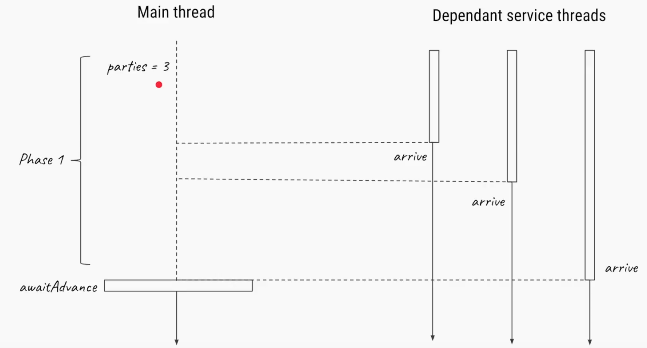
We will try to understand how the Phaser Class can be used with an example. In this example, we are creating a three threads, which will wait for the arrival all the threads being created.
Once all the threads have arrived(marked by arriveAndAwaitAdvance() method) the Phaser allows them through the barrier.
Methods
-
awaitAdvance()
-
arrive()
Scenario
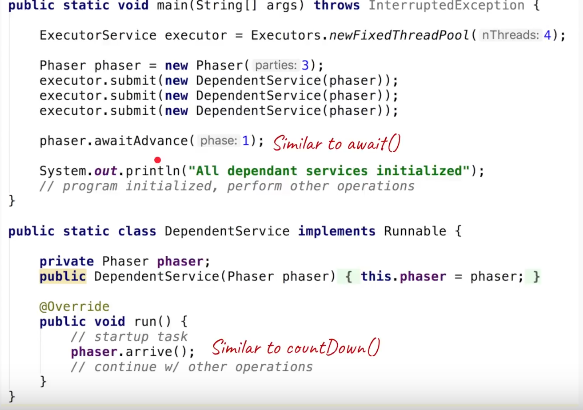
public class PhaserExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Phaser phaser = new Phaser();
phaser.register();// register self... phaser waiting for 1 party (thread)
int phasecount = phaser.getPhase();
System.out.println("Phasecount is " + phasecount);
new PhaserExample().testPhaser(phaser, 2000);// phaser waiting for 2 parties
new PhaserExample().testPhaser(phaser, 4000);// phaser waiting for 3 parties
new PhaserExample().testPhaser(phaser, 6000);// phaser waiting for 4 parties
// now that all threads are initiated, we will de-register main thread
// so that the barrier condition of 3 thread arrival is meet.
phaser.arriveAndDeregister();
Thread.sleep(10000);
phasecount = phaser.getPhase();
System.out.println("Phasecount is " + phasecount);
}
private void testPhaser(final Phaser phaser, final int sleepTime) {
phaser.register();
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " arrived");
phaser.arriveAndAwaitAdvance();// threads register arrival to the phaser.
Thread.sleep(sleepTime);
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " after passing barrier");
}
}.start();
}
}