Threads
Introduction to Multi-threading
If a program contains multiple flow of controls for achieving concurrent execution, then that program is known as multi-threaded program
The languages like C, C++ comes under single threaded modeling languages, since there exists single flow of controls whereas the languages like JAVA, .NET are treated as multi-threaded modeling languages, since there is a possibility of creating multiple flow of controls
When we write any JAVA program there exist two threads they are
1.fore ground thread (main Thread)
2.Back ground thread.
1. Fore ground threads are those which are executing user defined sub-programs. There is a possibility of creating ‘n’ number of fore ground threads
2. Back ground threads are those which are monitoring the status of fore ground thread. And always there exist single back ground thread.
In information technology we can develop two types of applications. They are process based applications and thread based applications.
Context Switch
Context Switch in Process
Single flow of Execution is process. Each and every process has Process Control
Block(PCB), the state of the process is represented in PCB by the operating
system.
Whenever CPU want to execute the another process it will save the State of current process in PCB(Process Control Block) with their PID, and loads the new process to execute.
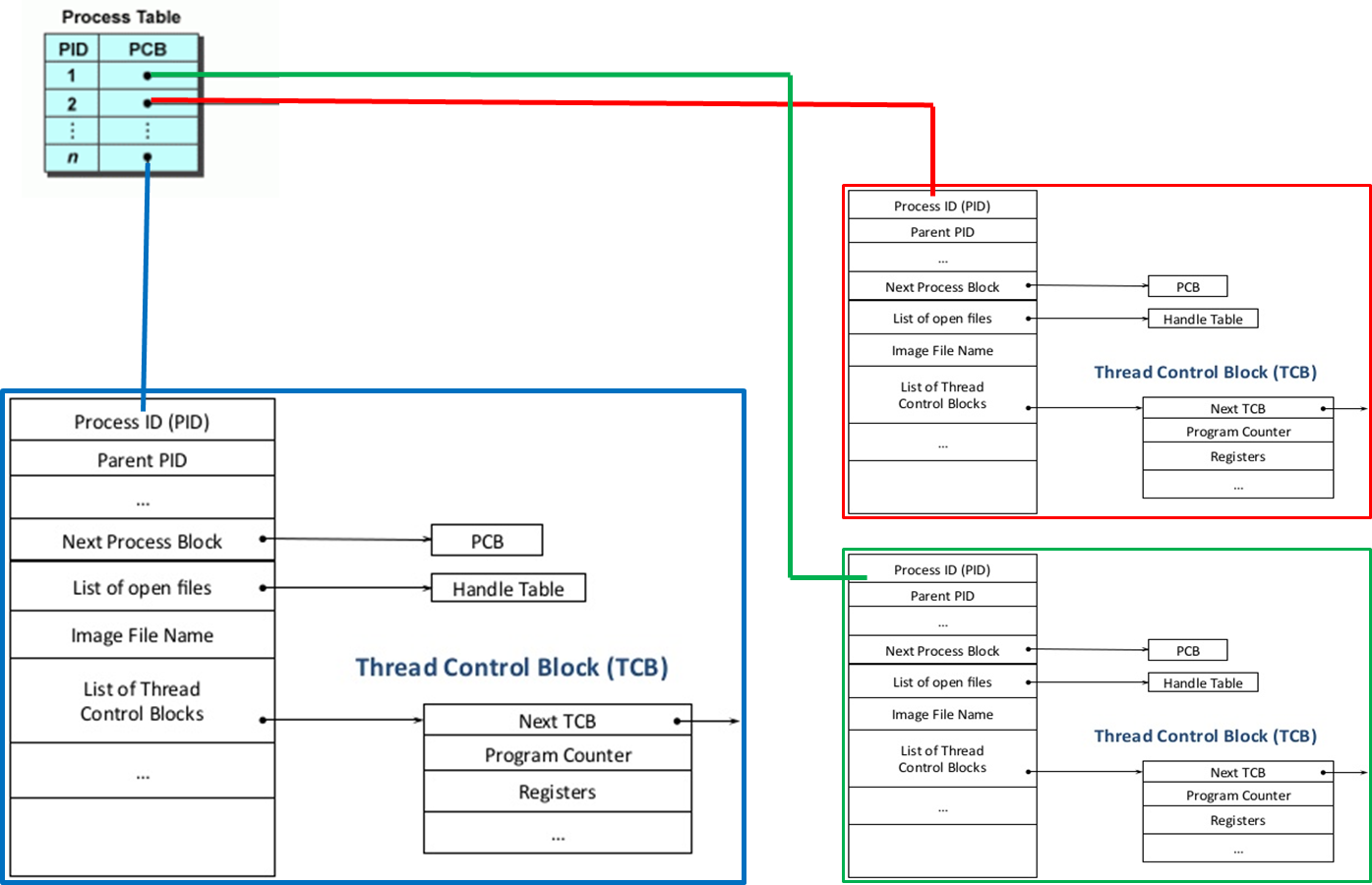
Here Context Switch time is very high because Process are running two Different address spaces.
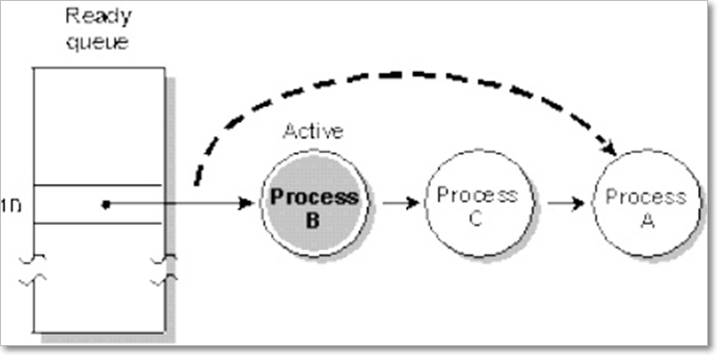
Control Switch in Threads
A thread is a sequential execution stream within a process. This means that a
single process may be broken up into multiple threads. Each thread has its own
Program Counter, registers, and stack, but they all share the same address
space within the process.
When we switch between two threads all threads share the same address space cost
of switching between threads is much smaller than the cost of switching between
processes.