Stack– Internal implementation
The Stack class represents a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack of objects. It extends class Vector with five operations(below 5 methods) that allow a vector to be treated as a stack
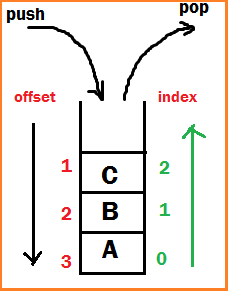
Object push(Object o) -Insert an object into top of the stack
Object pop() -Removes & returns from top of the stack
Object peak() -Just returns Object from top of the stack
boolean empty() -returns TRUE if stack is empty
int search(Object o) – returns offset if available otherwise -1
-
Adding item in Stack is called PUSH.
-
Removing item from stack is called POP.
-
Push and pop operations happen at Top of stack.
-
Stack follows LIFO (Last in first out) - means last added element is removed first from stack
-
Push - O(1) [as we push element at Top of Stack in java]
-
Pop - O(1) [as popping is also done at Top of Stack in java]
Uses Growable array, initial capacity as 10, same as ArrayList
public class StackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack s = new Stack();
s.push("A");
s.push("B");
s.push("C");
System.out.println(s);// [A, B, C]
System.out.println(s.search("A"));// 3
System.out.println(s.search("X"));// -1
s.pop();
System.out.println(s);//[A, B]
}
}
[A, B, C]
3
-1
Cursors - Enumeration VS Iterator VS ListIterator
ListIterator is subclass of List.so all the methods are available in ListIterator.
We have to follow 3 steps to use Cursors in our application
-
Get the all elements in a collection in Cursor Object
-
Check is next/previous element is exist or not
-
Get the element