Fundamentals – Interview Questions
Difference between interpreter and JIT compiler?
The interpreter interprets the bytecode line by line and executes it sequentially. It results in poor performance. JIT compiler add optimization to this process by analyzing the code in blocks and then prepare more optimized machine code.
Difference between JRE and JVM?
JVM is the specification for runtime environment which executes the Java applications. Hotspot JVM is such one implementation of the specification. It loads the class files and uses interpreter and JIT compiler to convert bytecode into machine code and execute it.
Difference Between JVM & HotSpot VM
JVM: is a Specification, HotSpot : is a implementation of JVM.
HotSpot** **is an implementation of the JVM concept, originally developed by Sun and now owned by Oracle.
There are other implementations of the JVM specification, like
-
Open JDK
-
IBM JVM
-
SUN JVM
-
JRockit
-
Blackdown
-
Kaffe
JVM implementations can differ in the way they implement JIT compiling, optimizations, garbage collection, platforms supported, version of Java supported, etc
How does WeakHashMap work?
WeakHashMap operates like a normal HashMap but uses WeakReference for keys. Meaning if the key object does not hold any reference then both key/value mapping will become appropriate for garbage collection.
How do you locate memory usage from a Java program?
You can use memory related methods from java.lang.Runtime class to get the free memory, total memory and maximum heap memory in Java.
| public static Runtime getRuntime() | returns the instance of Runtime class. |
|---|---|
| public void exit(int status) | terminates the current virtual machine. |
| public void addShutdownHook(Thread hook) | registers new hook thread. |
| public Process exec(String command) | executes given command in a separate process. |
| public int availableProcessors() | returns no. of available processors. |
| public long freeMemory() | returns amount of free memory in JVM. |
| public long totalMemory() | returns amount of total memory in JVM. |
public class TestApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();
System.out.println(r.totalMemory()); //16252928
System.out.println(r.freeMemory()); //15709576
System.out.println(r.availableProcessors());//24
r.gc();
}
}
What is ClassLoader in Java?
When a Java program is converted into .class file by Java compiler which is collection of byte code. ClassLoader is responsible to load that class file from file system, network or any other location
-
Bootstrap ClassLoader - JRE/lib/rt.jar
-
Extension ClassLoader - JRE/lib/ext or any directory denoted by java.ext.dirs
-
Application ClassLoader - CLASSPATH environment variable, -classpath or -cp option, Class-Path attribute of Manifest inside **JAR file.**
Java heap memory
When a Java program started Java Virtual Machine gets some memory from Operating System.
whenever we create an object using new operator or by any another means the object is allocated memory from Heap and When object dies or garbage collected, memory goes back to Heap space.
How to increase heap size in Java
Default size of Heap space in Java is 128MB on most of 32 bit Sun’s JVM but its highly varies from JVM to JVM. change size of heap space by using JVM options -Xms and -Xmx. Xms denotes starting size of Heap while -Xmx denotes maximum size of Heap in Java.
Java Heap and Garbage Collection
As we know objects are created inside heap memory and Garbage Collection is a process which removes dead objects from Java Heap space and returns memory back to Heap in Java.
For the sake of Garbage collection Heap is divided into three main regions named as New Generation, Old Generation, and Perm space
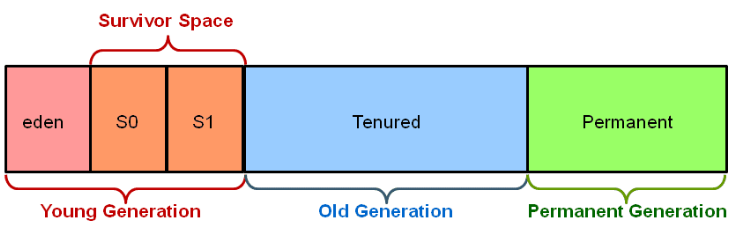
-
New Generation of Java Heap is part of Java Heap memory where a newly created object is stored,
-
Old Generation During the course of application many objects created and died but those remain live they got moved to Old Generation by Java Garbage collector thread
-
Perm space of Java Heap is where JVM stores Metadata about classes and methods, String pool and Class level details.
-
Perm Gen stands for permanent generation which holds the meta-data information about the classes.
-
Suppose if you create a class name A, it’s instance variable will be stored in heap memory and class A along with static classloaders will be stored in permanent generation.
-
Garbage collectors will find it difficult to clear or free the memory space stored in permanent generation memory. Hence it is always recommended to keep the permgen memory settings to the advisable limit.
-
JAVA8 has introduced the concept called meta-space generation, hence permgen is no longer needed when you use jdk 1.8 versions.
Garbage collection is performed by a daemon thread called Garbage Collector(GC). This thread calls the finalize() method before object is garbage collected.
The Garbage collector of JVM collects only those objects that are created by new keyword. So if you have created any object without new, you can use finalize method to perform cleanup processing (destroying remaining objects).
Neither finalization nor garbage collection is guaranteed.
Data Types
How do you convert bytes to String?
you can convert bytes to the string using string constructor which accepts byte[], just make sure that right character encoding otherwise platform’s default character encoding will be used which may or may not be same.
String str = new String(bytes, “UTF-8”);
How do you convert bytes to long in Java
The byte takes 1 byte of memory and long takes 8 bytes of memory. Assignment 1
byte value to 8 bytes is done implicitly by the JVM.
byte –> short –> int –> long –> float –> double
The left-side value can be assigned to any right-side value and is done implicitly. The reverse requires explicit casting.
byte b1 = 10; // 1 byte
long l1 = b1; // one byte to 8 bytes, assigned implicitly
Is ++ operator is thread-safe in Java?
No it’s not a thread safe operator because its involve multiple instructions like reading a value, incriminating it and storing it back into memory which can be overlapped between multiple threads.
What will this return 3*0.1 == 0.3? true or false?
Both are not equal, because floating point arithmetic has a certain precision. Check the difference (a-b) it should be really small.
In computer memory, floats and doubles are stored using IEEE 754 standard format.
-
f1 = (0.1+0.1+0.1….11 times) = 1.0999999999999999
-
f2 = 0.1*11 = 1.1
In BigDecimal class, you can specify the rounding mode and exact precision which you want to use. Using the exact precision limit, rounding errors are mostly solved. Best part is that BigDecimal numbers are immutable i.e. if you create a BigDecimal BD with value -1.23”, that object will remain -1.23” and can never be changed. You can use it’s .compareTo() method to compare to BigDecimal numbers
private static void testBdEquality()
{
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("2.00");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("2.0");
System.out.println(a.equals(b)); // false
System.out.println(a.compareTo(b) == 0); // true
}
Which one will take more memory, an int or Integer? (answer)
An Integer object will take more memory an Integer is the an object and it
store meta data overhead about the object and int is primitive type so its
takes less space.
How to convert Primitives to Wrapper & Wrapper to Primitive ??
// 1. using constructor
Integer i = new Integer(10);
// 2. using static factory method
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(10);
//3.wrapper to primitive
int val = i.intValue();
Autoboxing and Unboxing?
If a method(remember only method – not direct) requires Integer Object value, we can directly pass primitive value without issue. Autoboxing will take care about these.
We can also do direct initializations (1.8 V)
Integer i = 10;// it will create Integer value of 10 using Autoboxing
int j = i;// ;// it will convert Integer to int using Autoboxing
Previously it shows
Integer i = 10;// it will create Integer value of 10 using Autoboxing
int j = i;//But we cant assign int to Integer Type mismatch: cannot convert from Integer to int
what if I make main() private/protected ?
if you do not make main() method public, there is no compilation error. You will runtime error because matching main() method is not present. Remember that whole syntax should match to execute main() method.
Error: Main method not found in class Main, please define the main method as:
public static void main(String[] args)