Traditional Data Structures
Data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.
Depending on the organization of the elements, data structures are classified into two types:
1) Linear data structures : Elements are accessed in a sequential order but it is not compulsory to store all elements sequentially (say, Linked Lists). Examples: Linked Lists, Stacks and Queues.
2) Non – linear data structures : Elements of this data structure are stored/accessed in a non-linear order. Examples: Trees and graphs.
Analysis of Algorithms?
To go from city -A” to city -B”, there can be many ways of accomplishing this: by flight, by bus, by train and also by bicycle. Depending on the availability and convenience, we choose the one that suits us. Similarly, in computer science, multiple algorithms are available for solving the same problem (for example, a sorting problem has many algorithms, like insertion sort, selection sort, quick sort and many more). Algorithm analysis helps us to determine which algorithm is most efficient in terms of time and space consumed.
Worst case
-
Defines the input for which the algorithm takes a long time (slowest time to complete).
-
Input is the one for which the algorithm runs the slowest.
Best case
-
Defines the input for which the algorithm takes the least time (fastest time to complete).
-
Input is the one for which the algorithm runs the fastest.
Average case
-
Provides a prediction about the running time of the algorithm.
-
Run the algorithm many times, using many different inputs take the average of them.
For analysis (best case, worst case and average), we try to give the upper bound (O) and lower bound (Ω) and average running time (Θ).
Types Of Data Structures
-
Primitive data structures
-
Non-primitive data structures
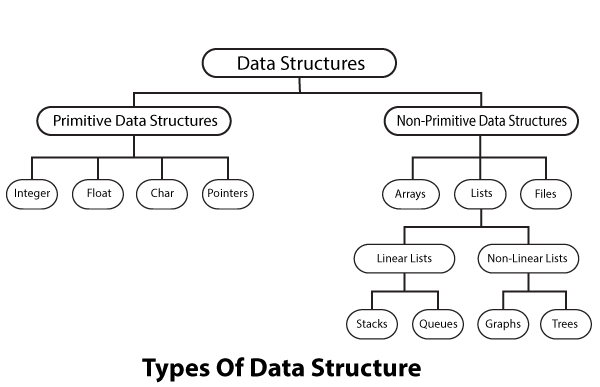
Primitive Data Structures
-
Primitive Data Structures are the basic data structures that directly operate upon the machine instructions.
-
Integers, Floating point numbers, Character constants, String constants and Pointers come under this category.
Non-primitive Data Structures
-
Non-primitive data structures are more complicated data structures and are derived from primitive data structures.
-
They emphasize on grouping same or different data items with relationship between each data item.Arrays, Lists and Files come under this category.
Data Structures
DSA - Data Structure Basics
DSA - Array Data Structure
Linked Lists
DSA - Linked List
DSA - Doubly Linked List
DSA - Circular Linked List
Stack & Queue
DSA - Stack
DSA - Queue
Graph Data Structure
DSA - Graph Data Structure
DSA - Depth First Traversal
DSA - Breadth First Traversal
Tree Data Structure
DSA - Tree Data Structure
DSA - Tree Traversal
DSA - Binary Search Tree
DSA - AVL Tree
DSA - Spanning Tree
DSA - Heap
Arrays
An array is a sequential collection of elements of same data type and stores data elements in a continuous memory location. The elements of an array are accessed by using an index. The index of an array of size N can range from 0 to N−1.
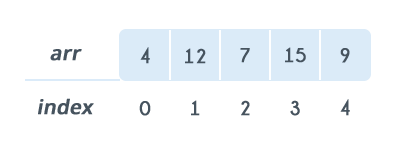
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by an array.
-
Traverse − print all the array elements one by one.
-
Insertion − Adds an element at the given index.
-
Deletion − Deletes an element at the given index.
-
Search − Searches an element using the given index or by the value.
-
Update − Updates an element at the given index.