Synchronization utilities
1.Semaphore(CountDownSemaphore)
Semaphore is one of the synchronization aid provided by Java concurrency util in Java 5 along with other synchronization aids like CountDownLatch, CyclicBarrier, Phaser and Exchanger.
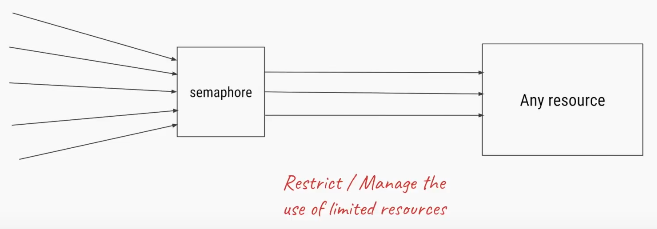
The Semaphore class present in java.util.concurrent package is a counting semaphore in which a semaphore, conceptually, maintains a set of permits.
Semaphore class in Java has two methods that make use of permits-
-
acquire()- Acquires a permit from this semaphore, blocking until one is available, or the thread is interrupted. It has another overloaded version acquire(int permits).
-
release()- Releases a permit, returning it to the semaphore. It has another overloaded method release(int permits).
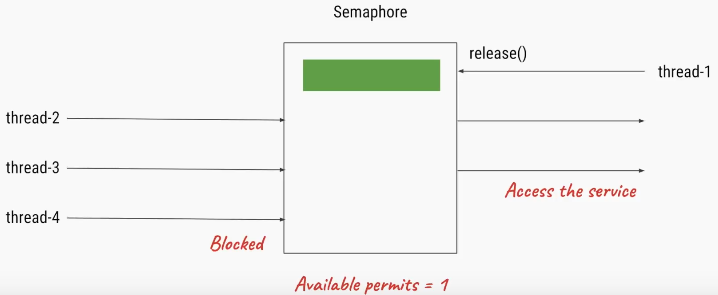
How Semaphore works in Java
-
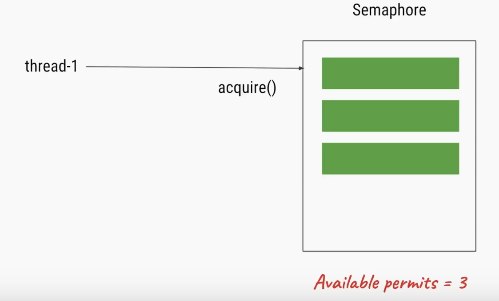
Thread that wants to access the shared resource tries to acquire a permit using acquire() method. At that time if the Semaphore’s count is greater than zero thread will acquire a permit and Semaphore’s count will be decremented by one.
-
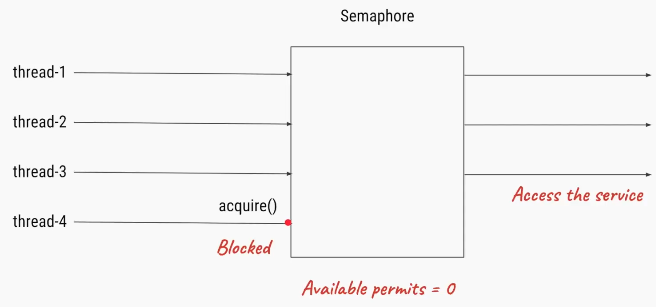
If Semaphore’s count is zero and thread calls acquire() method, then the thread will be blocked until a permit is available.
-
When thread is done with the shared resource access, it can call the release() method to release the permit. That results in the Semaphore’s count incremented by one.
Java Semaphore constructors
Semaphore(int permits)Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair)
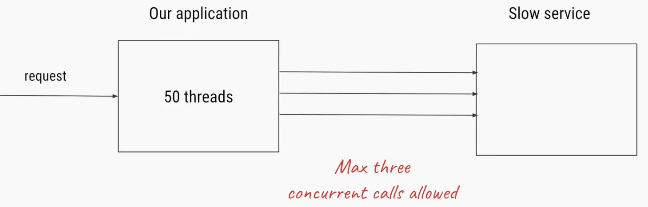
50 thraeds are trying to access a slow service , where only 3 threads are allowed.

Java semaphore example
Let’s see one example where Semaphore is used to control shared access. Here we
have a shared counter and three threads using the same shared counter and trying
to increment and then again decrement the count. So every thread should first
increment the count to 1 and then again decrement it to 0.
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
class SharedCounter implements Runnable{
private int c = 0;
private Semaphore s;
SharedCounter(Semaphore s){
this.s = s;
}
// incrementing the value
public void increment() {
try {
// used sleep for context switching
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
c++;
}
// decrementing the value
public void decrement() {
c--;
}
public int getValue() {
return c;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// acquire method to get one permit
s.acquire();
this.increment();
SOP("Value for Thread After increment-"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" " +this.getValue());
this.decrement();
SOP("Value for Thread at last"+Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + this.getValue());
// releasing permit
s.release();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class SemaphoreDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore s = new Semaphore(1);
SharedCounter counter = new SharedCounter(s);
// Creating three threads
Thread t1 = new Thread(counter, "Thread-A");
Thread t2 = new Thread(counter, "Thread-B");
Thread t3 = new Thread(counter, "Thread-C");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
------------- Output ---------------------
Value for Thread After increment - Thread-A 1
Value for Thread at last Thread-A 0
Value for Thread After increment - Thread-B 1
Value for Thread at last Thread-B 0
Value for Thread After increment - Thread-C 1
Value for Thread at last Thread-C 0