4.Operators
System.out.print(9 / 3); // Outputs 3
System.out.print(9 % 3); // Outputs 0
System.out.print(10 / 3); // Outputs 3
System.out.print(10 % 3); // Outputs 1
System.out.print(11 / 3); // Outputs 3
System.out.print(11 % 3); // Outputs 2
System.out.print(12 / 3); // Outputs 4
System.out.print(12 % 3); // Outputs 0
Numeric Promotion Rules
-
If two values have different data types, Java will automatically promote one of the values to the larger of the two data types.
-
If one of the values is integral and the other is floating-point, Java will automatically promote the integral value to the floating-point value’s data type.
-
Smaller data types, namely byte, short, and char, are first promoted to int any time they’re used with a Java binary arithmetic operator, even if neither of the operands is int.
-
After all promotion has occurred and the operands have the same data type, the resulting value will have the same data type as its promoted operands.
What is the data type of x / y?
short x = 10;
short y = 3;
In this case, we must apply the third rule, namely that
- first x and y will both be promoted to int
- After promotion, operation will perform, resulting output of int type.
What is the data type of x * y / z?
All expressions will calculated from left to right (——»)
short x = 14;
float y = 13;
double z = 30;
we evaluate the multiple and division from left-to-right. In this case, we must apply all of the rules.
- First,
xwill automatically be promoted to int solely because it is a short and it is being used in an arithmetic binary operation. -
The promoted x value will then be automatically promoted to a float so that it can be multiplied with y.
-
The result of
(x * y)will then be automatically converted in to float, because y is float, which is higher datatype . -
The result of
(x * y) / zwill then be automatically converted in to double, because z is double, which is higher datatype . - Finally after all operations result stored in higher datatype, double
1.Increment/ Decrement
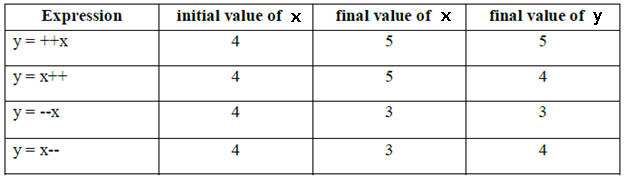
- For the final variables we can’t apply increment or decrement operators
final int i=10; i++; (or) i=20; Test.java:8: error: cannot assign a value to final variable i i++; ^ - We can apply increment or decrement operators even for floating point data
types also.
double d = 10.5; d++; System.out.println(d);// 11.5
How this following expression is evaluated?
int x = 3;
int y = ++x * 5 / x-- + --x;
(------------)
// All expressions will calculated from left to right (------)
System.out.println("x is " + x);
System.out.println("y is " + y);
int y = 4 * 5 / x-- + --x; // x assigned value of 4
int y = 4 * 5 / 4 + --x; // x assigned value of 3
int y = 4 * 5 / 4 + 2; // x assigned value of 2
we evaluate the multiple and division from left-to-right, and finish with the addition. The result is then printed: x is 2 & y is 7
Does it work?
long t = 192301398193810323; // DOES NOT COMPILE
It does not compile because Java interprets the literal as an int and notices that the value is larger than int allows. The literal would need a postfix L to be considered a long
short x = 10;
short y = 3;
short z = x * y; // DOES NOT COMPILE
short x = 10;
short y = 3;
short z = (short)(x * y);
long x = 10;
int y = 5;
y = y * x; // DOES NOT COMPILE
In last line could be fixed with an explicit cast to (int), but there’s a better way using the compound assignment operator:
long x = 10;
int y = 5;
y \*= x; //is equals to y =(int) y\*x;
The compound operator will first cast x to a long, apply the multiplication of two long values, and then cast the result to an int.
long x = 5;
long y = (x=3);
System.out.println(x); // Outputs 3
System.out.println(y); // Also, outputs 3
Infinity and -Infinity
-
In Integer Athematic (byte,int,short), if anything divide 0 will get
Runtime Exception:ArithematicException: Divide by 0. -
But In Floating point athematic, if anything divide by 0.0, we will get Infinity/ -Infinity
System.*out*.println(10 / 0.0); // Infinity System.*out*.println(-10 / 0.0);// -Infinity
NaN – Not a Number
-
In Integer Athematic (byte,int,short), 0 divide 0 will get R.E: A.E: Divide by 0.
-
But In Floating point athematic, 0 divide by 0.0, we will get Nan (no -Nan is there)
System.*out*.println(0.0 / 0.0); // NaN System.*out*.println(-0.0 / 0.0);// NaN
Equality Operators (==)
The comparisons for equality are limited to same Data Types, so you cannot mix and match types. For example, each of the following would result in a compiler error:
boolean x = true == 3; // DOES NOT COMPILE
boolean y = false != "Giraffe"; // DOES NOT COMPILE
boolean z = 3 == "Kangaroo"; // DOES NOT COMPILE
Conditional Statements
int x = 1;
if(x) { // DOES NOT COMPILE
...
}
int x = 1;
if(x = 5) { // DOES NOT COMPILE
...
}
System.out.println((y > 5) ? 21 : "Zebra");
int animal = (y < 91) ? 9 : "Horse"; // DOES NOT COMPILE
^ (X-OR) - Homogeneous are FALSE(T,T F,F), Heterogeneous are TRUE(T,F F,T)