Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) enables you to launch Amazon Web Services (AWS) resources into a virtual network that you’ve defined.
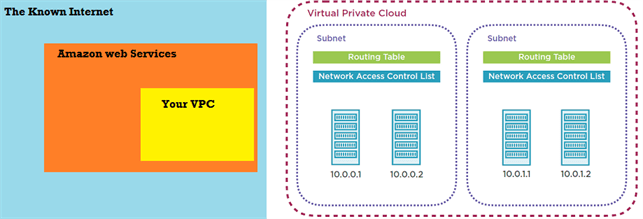
A “Virtual Private Cloud” is a sub-cloud inside the AWS public cloud. Sub-cloud means it is inside an isolated logical network. Other servers can’t see instances that are inside a VPC.
-
When an user register for AWS account, the VPC for that user is Created
-
All the Instances launch by that user is reside inside his VPC
-
So, for each User , his own VPC is there to play with aws Services
-
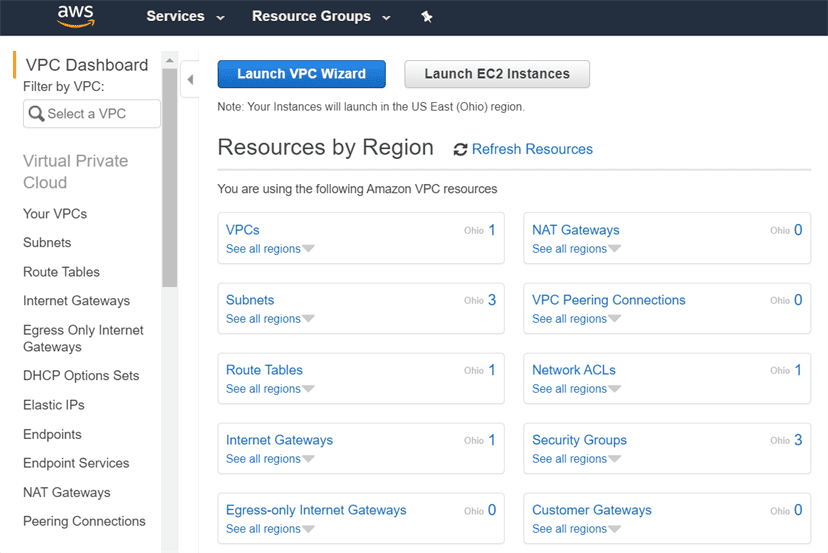
If we open VPC dashboard we already have a VPC, with tenancy : Default.
-
That means that on creating AWS account by default one VPC is created
-
all the S3 Buckets, instances we created will be created inside Default VPC
-
You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including a selection of your IP address range, the creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways.
-
Applications run in the VPC or on-premises
-
Subnets can be created in the VPC
-
Public subnets - Opens to outside internet
-
Private subnets - Inside Communication
-
-
Direct Connect provides VPN(Virtual Private Network) connections
-
Multiple VPCs can be connected by VPC pairing
-
VPC endpoints connect to Amazon resources which are outside the VPC
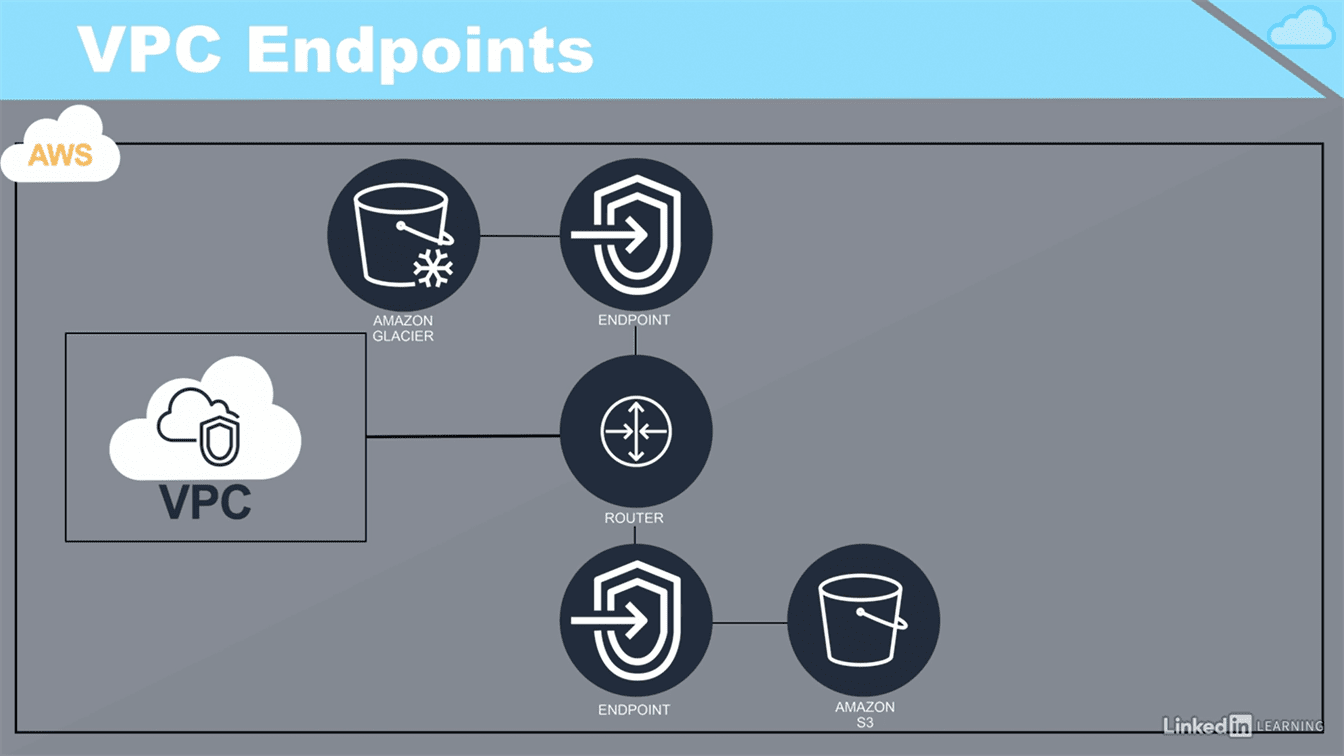
Endpoint - Kind of jump - direction of next connection
Features:
-
Dynamic private IP
-
Dynamic public IP
-
AWS-provisioned DNS names
-
Private DNS names
-
Public DNS names
VPC Architecture
-
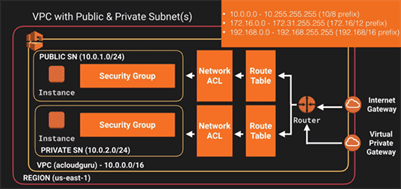
We have VPC inside Region – us-est-1
-
outside the VPC, we have internet gateway and virtual private gateway.
-
Both these connections go to the router in a VPC and then router directs the traffic to the Route Table.
-
Route table will then direct the traffic to Network ACL(kind of firewall or security groups)
-
We have two instances – each have their own security groups & their own public, private subnets.
In public subnet, the internet is accessible by an EC2 instance, but in private subnet, an EC2 instance cannot access the internet on their own