CloudFront
CDN – content delivery network
Amazon CloudFront is a web service that speeds up distribution of your static and dynamic web content, such as .html, .css, .js, and image files, to your users. CloudFront delivers your content through a worldwide network of data centers called edge locations. When a user requests content that you’re serving with CloudFront, the user is routed to the edge location that provides the lowest latency (time delay), so that content is delivered with the best possible performance.
-
If the content is already in the edge location with the lowest latency, CloudFront delivers it immediately.
-
If the content is not in that edge location, CloudFront retrieves it from an origin that you’ve defined—such as an Amazon S3 bucket, a MediaPackage channel, or an HTTP server (for example, a web server) that you have identified as the source for the definitive version of your content
CloudFront components
Origin: It defines the origin of all the files that CDN will distribute. Origin can be either an S3 bucket, an EC2 instance or an Elastic Load Balancer.
Edge Location: Edge location is the location where the content will be cached. It is a separate to an AWS Region or AWS availability zone. Edge locations spread all around the world and currently, there are 50 edge locations.
Distribution: consists of a collection of edge locations. The distribution can be of two types:
-
Web Distribution: It is typically used for websites, html, .css, .php, via HTTP or HTTPS
-
RTMP: It is used for media files like videos, streaming etc
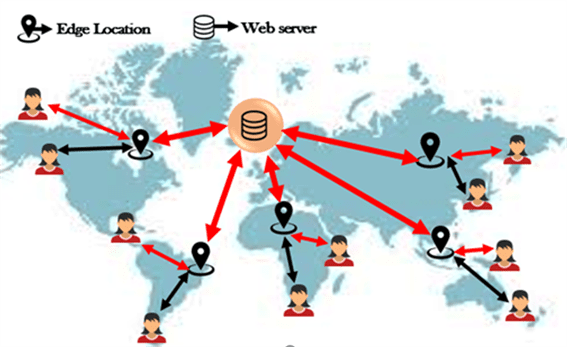
-
When the first user requests to get the content, and the request goes to the nearest edge location.
-
The nearest edge will be read first to determine whether it contains the cached data or not.
-
If an edge does not contain the cached data, the edge location pulls the data from the S3 bucket. Suppose the S3 bucket is in Ireland. But this process is not quicker for the first user.
-
However, when the second user accesses the same file, this file is already cached to the edge location, so it pulls the data from its edge location. It speeds up the delivery of the data.
Lab – CloudFront Cache example for HTML website
Create a bucket and upload content in a bucket. Now we can able to access the website using
https://satyacodes.s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/index.html
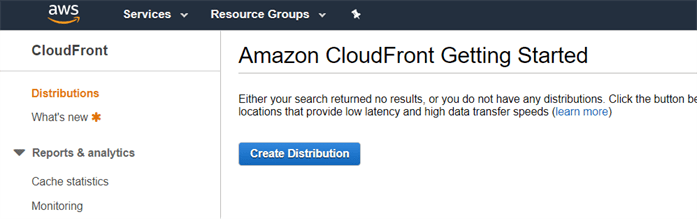
Create a CloudFront Distribution > Open the CloudFront Console > Create Distribution
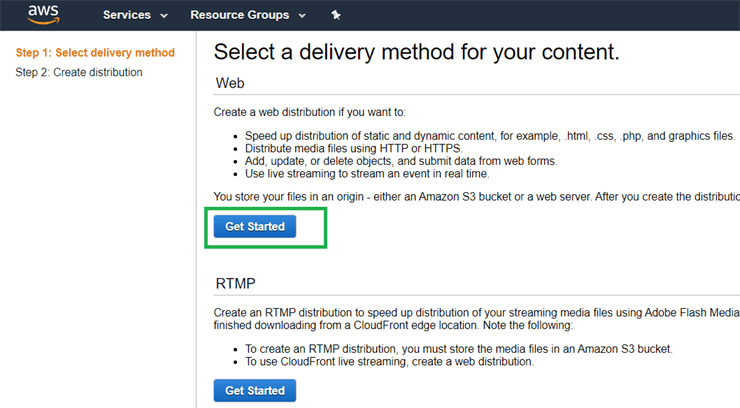
Select the delivery method for your content, for websites it is Web Distribution,
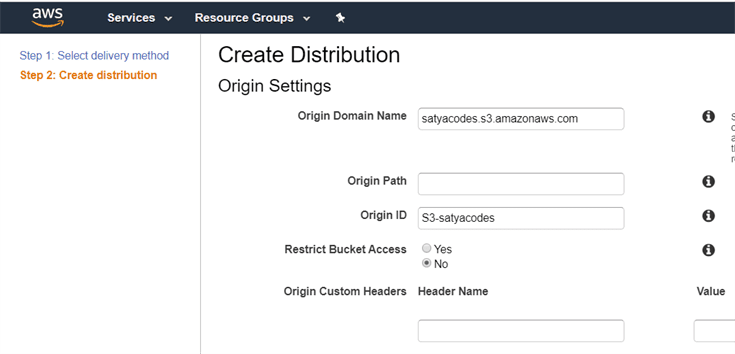
Origin Settings
-
Origin Domain Name: It defines from where the origin is coming from.
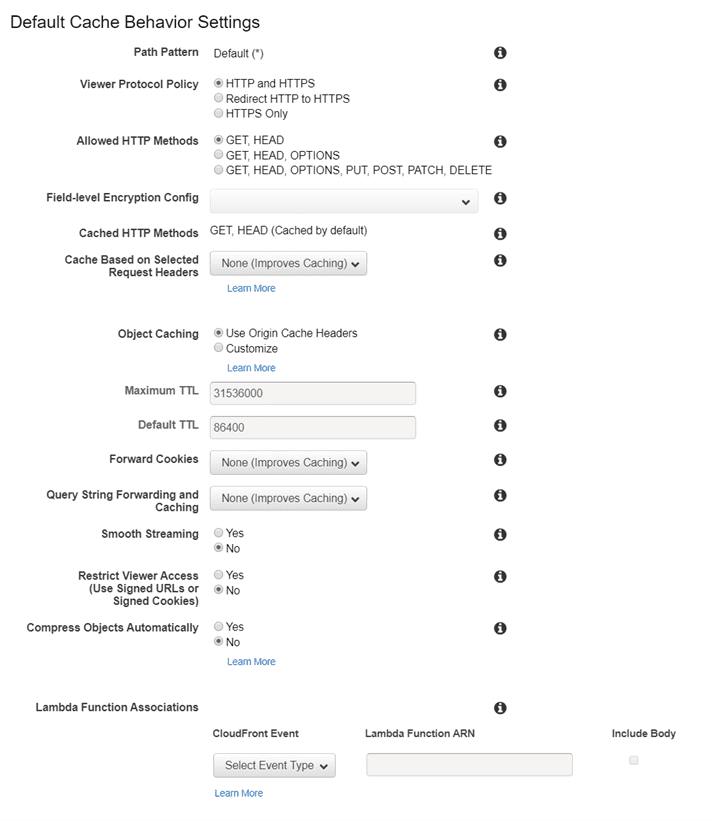
After the Distribution has been created, we get the domain name of the CloudFront Distribution and we also know the object name that we have placed in the S3 bucket.
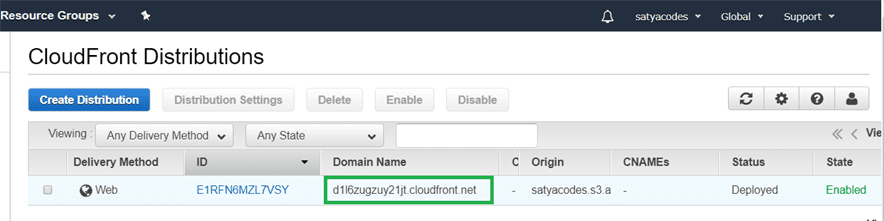
Now we can access our website, though CloudFront CDN – **http://domain
name