AWS - Databases
-
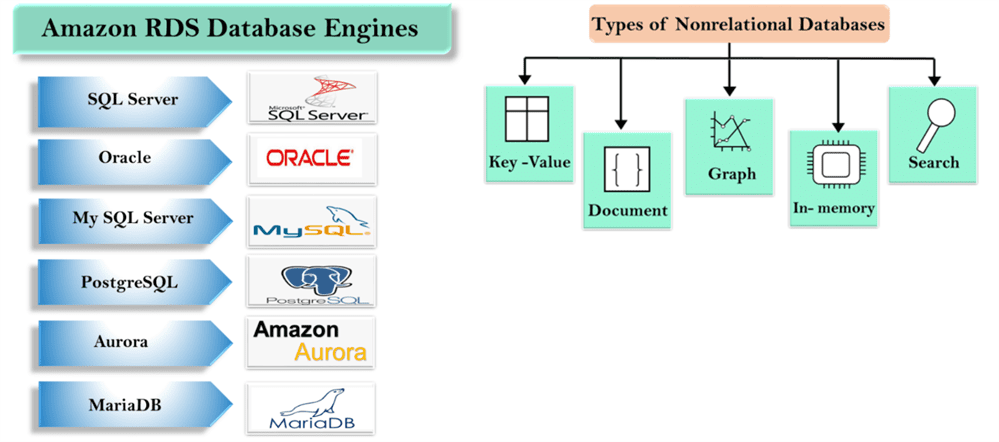
Amazon Relational Database Service: It supports six commonly used database engines.
-
Amazon Aurora: It is a MySQL-Compatible relational database with five times performance.
-
Amazon DynamoDB: It is a fast and flexible NoSQL database service.
-
Amazon Redshift: It is a petabyte-scale data warehouse service.
-
Amazon Elasticache: It is an in-memory cache service with support for Memcached and Redis.
-
AWS Database Migration Service: It is a service that provides easy and inexpensive to migrate your databases to AWS cloud.
AWS Database types
Types of DBs
Flat file databases
-
Have one line per record
-
Doesn’t contain multiple tables
-
Ex: xls
Relational databases
-
Store portions of the data in designated tables
-
Tables are related based on unique identifier
NoSQL
-
Not based on SQL or relational design theory
-
Design supports fast transactions
-
DynamoDB is a NoSQL service
-
Create
-
Query
-
Read/write/modify
Data Warehouses
-
Large, central repository for data
-
Data aggregated from one or more sources
-
Used for Online Analytical Processing (OLAP), bigdata
-
Ex. AWS Redshift
Redshift is a data warehouse database solution. It is optimized for OLAP and is managed by AWS through the RDS service.
Types DB hosting in AWS
EC2 Instance-Based Database Hosting
1.Launch an instance
2.Install the database service
3.Open appropriate ports in security groups
4.Connect to the database
AWS Service-Based
With AWS Service-Based databases in the RDS service, you do not need to be concerned with operating system installation and configuration, but you will still need to create the databases, manage security, and perform backup procedures
1.Create the database
2.Connect to the database
High Availability Solutions
Clustering
-
Multiple servers (instances)
-
One database with replication
-
Increases availability
-
Automatic failover
-
Increased cost
Standby Instances
-
Multiple servers (instances)
-
One database with replication
-
Increases recoverability
-
No automatic failover
-
Reduced costs
Multiple AZ Deployment
-
Multiple instances
-
Multiple AZs
-
One region
-
Replicated storage
-
Increased availability
-
Increased performance
-
Cost
Database Security
RDS databases support Storage encryption
If someone steals a hard drive for example, they cannot get the data off of that hard drive, because it’s encrypted on the hard drive.
Administration access based on IAM.
RDS databases do support encryption; however, it must be enabled during database creation. The only other option is to backup the database and then recover it with encryption. However, database recovery is really the creation of a new database and that is why encryption can be enabled during recovery.