Amazon Web Services
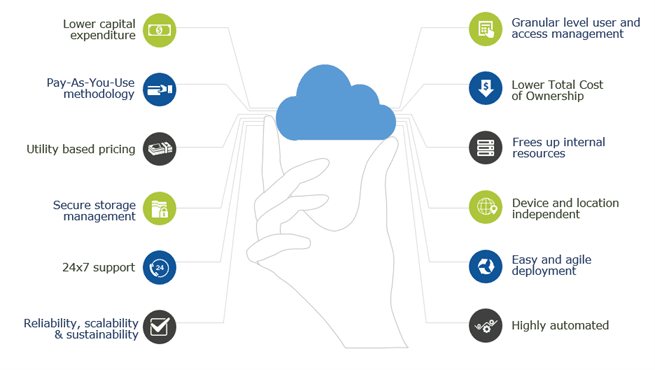
Cloud computing offers dynamic provisioning of resources based on demand, on a pay-as-you-use pricing. Instead of physical servers, cloud computing helps to spin out virtual servers. With dynamic scaling and load balancing features of cloud, long term planning is not necessary.
Why Cloud?
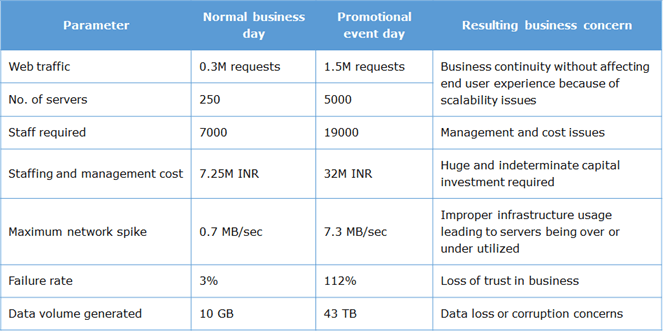
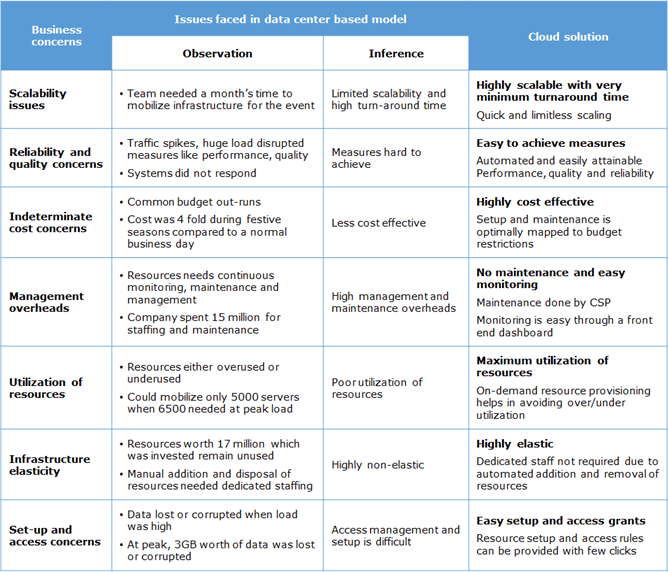
Amazon.com’s Great Indian Festival or Flipkart’s Big Billion Day, they also declare intermittent offer days.
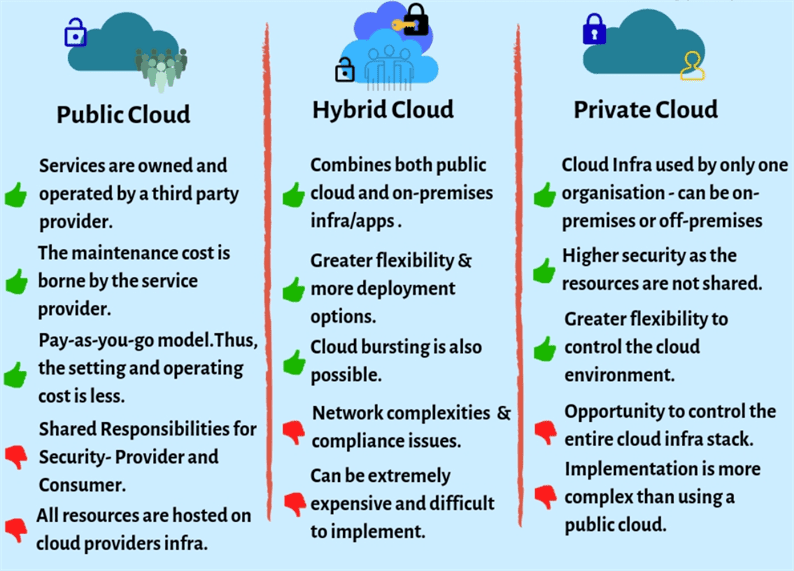
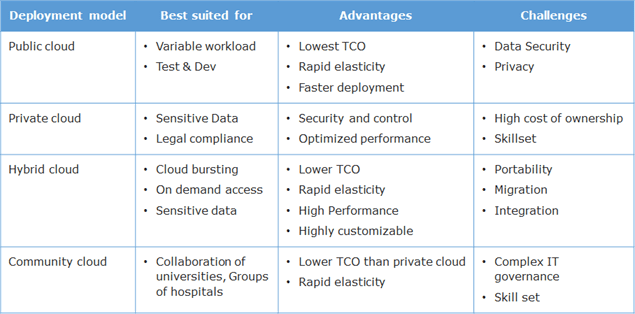
Types of Cloud Infrastructure
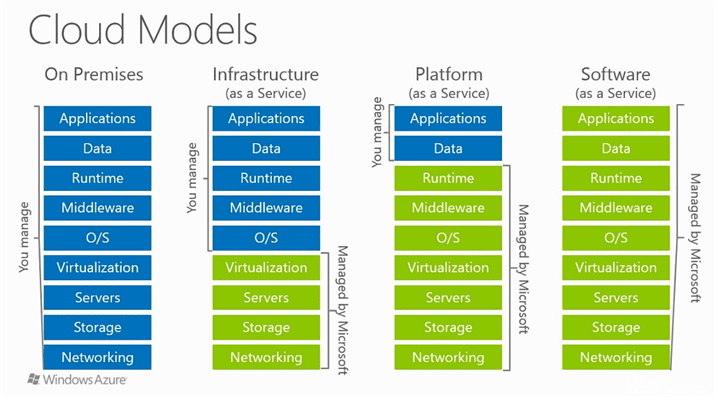
Types of Cloud Services
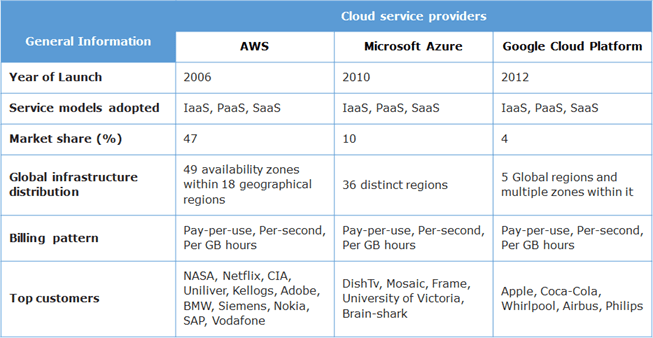
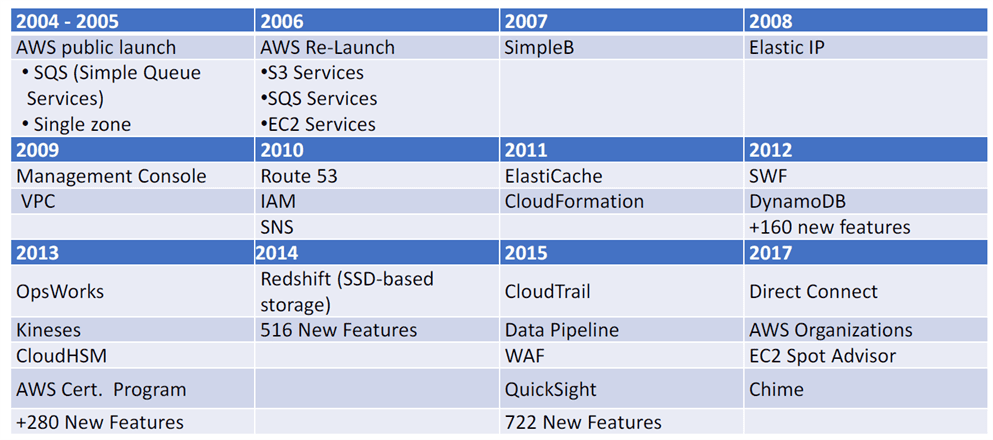
AWS History
Amazon Web Services(AWS) is a low-cost cloud service platform from Amazon, which provides services such as compute, storage, networking, CDN services etc to users. All AWS services are exposed as web services accessible from anywhere, any time, on a pay per use pricing model.
AWS services can be managed through a web-based management console, command line interface (CLI) or software development kits (SDK). With AWS, you can provision resources in seconds and build applications without upfront capital investment.
Global Infrastructure
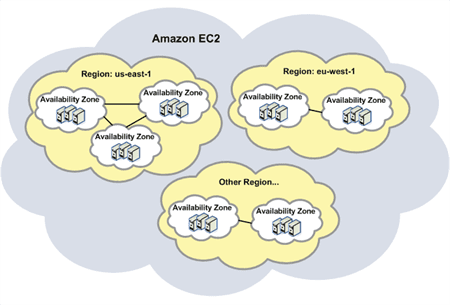
Region
-
is a physical location spread across globe to host your data
-
In each region, there will be at least two availability zones for fault tolerance
-
Regions are separate from one another
-
Enterprises can choose to have their data in a specific region
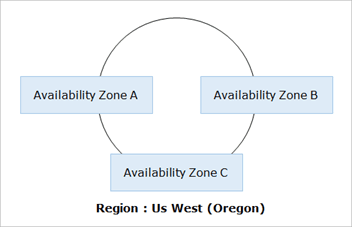
Availability zones
-
Availability zones are analogous to clusters of datacenters
-
Availability zones are connected through redundant low-latency links
-
These AZs offer scalable, fault tolerant and highly-available architecture
Most of the AWS services are region dependent and only a few are region independent. Few services may not be available in all the regions. So, while determining a region to push the workloads, the following parameters to be considered.
-
Availability of required services
-
Cost
-
Latency
-
Security & Compliance
-
Service Level Agreements(SLAs)