Elastic EC2 Container Service (ECS) – Docker Container
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a highly scalable, high-performance container orchestration service.
Docker
Docker is a client-server application that can be installed on Linux, Windows, and MacOS and that allows you to run Docker containers. Containers are lightweight environments containing everything needed to run a specific application or part of an application. Multiple different containers can be run on one machine, so long as it has the Docker software installed.
By using specified Docker containers to run your production code, you can be sure that your development environment is exactly the same as your production environment.
First we need to cover ECS terminology:
-
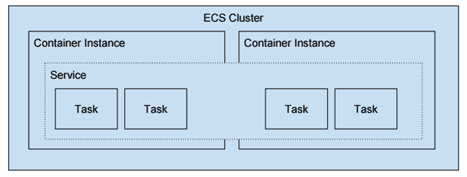
Task Definition — This a blueprint that describes how a docker container should launch. It contains settings like exposed port, docker image, cpu shares, memory requirement, command to run and environmental variables.
-
Task —It can be thought of as an -instance” of a Task Definition.
-
Service — Defines long running tasks of the same Task Definition. This can be 1 running container or multiple running containers all using the same Task Definition.
-
Cluster — A logic group of EC2 instances. When an instance launches the ecs-agent software on the server registers the instance to an ECS Cluster. This is easily configurable by setting the ECS_CLUSTER variable in /etc/ecs/ecs.config described here.
-
Container Instance — This is just an EC2 instance that is part of an ECS Cluster and has docker and the ecs-agent running on it.
Lab
Create ECS Cluster with 1 Container Instance
Create a Task Definition
Create an ELB and Target Group to later associate with the ECS Service
Create a Service that runs the Task Definition
Confirm Everything is Working
Scale Up the Service to 4 Tasks.
Clean It All Up