Spring Data Redis
Spring Data Redis - Spring Boot Cache with Redis is used to reduce the no.of round trips between Application & Database
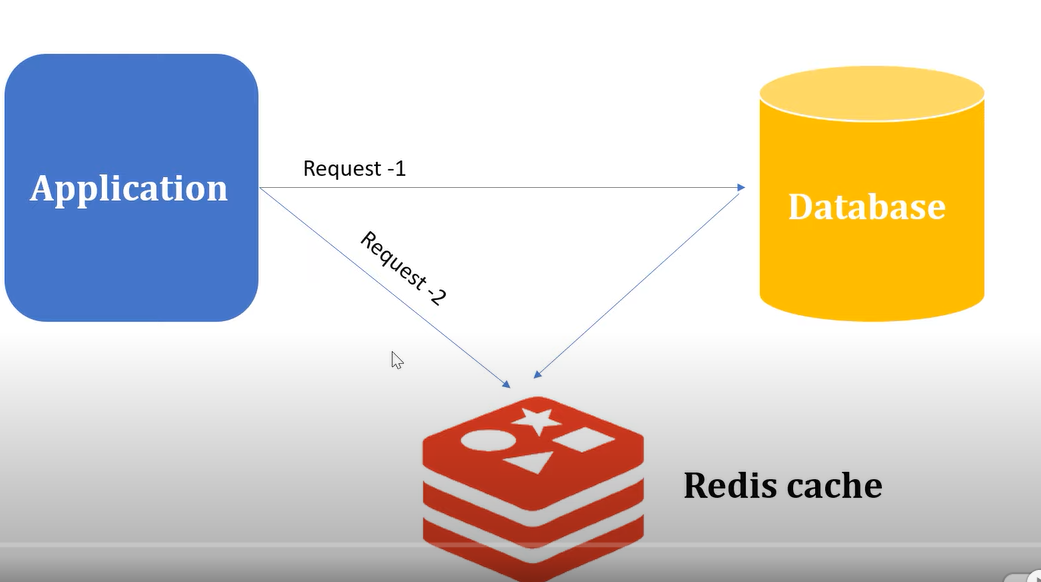
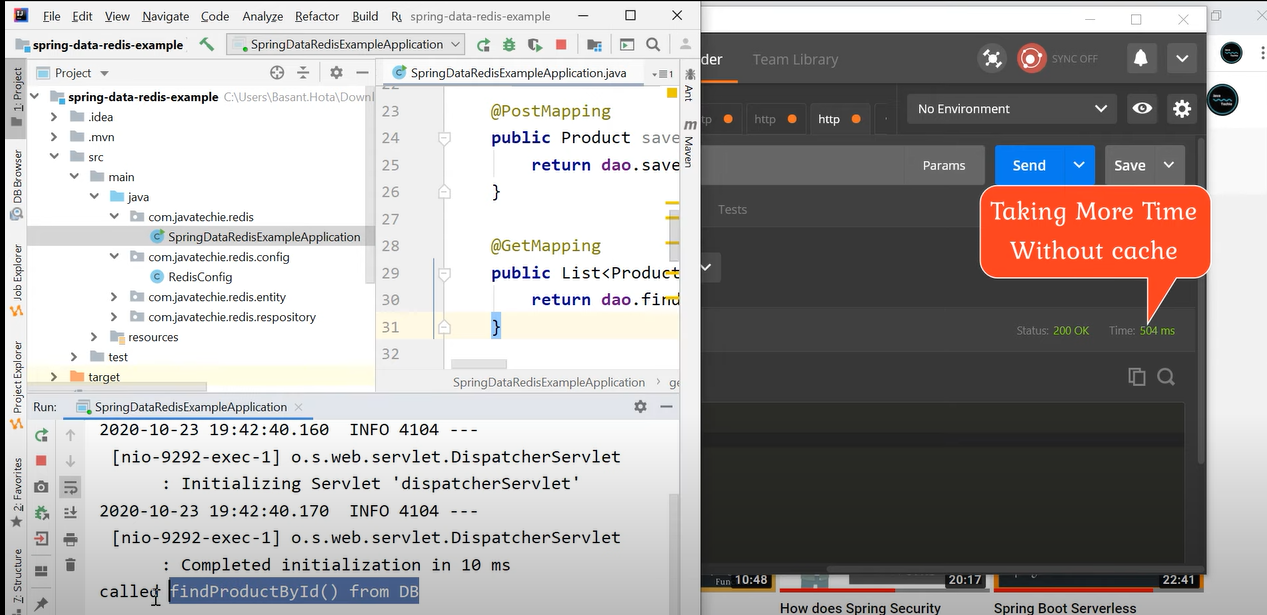
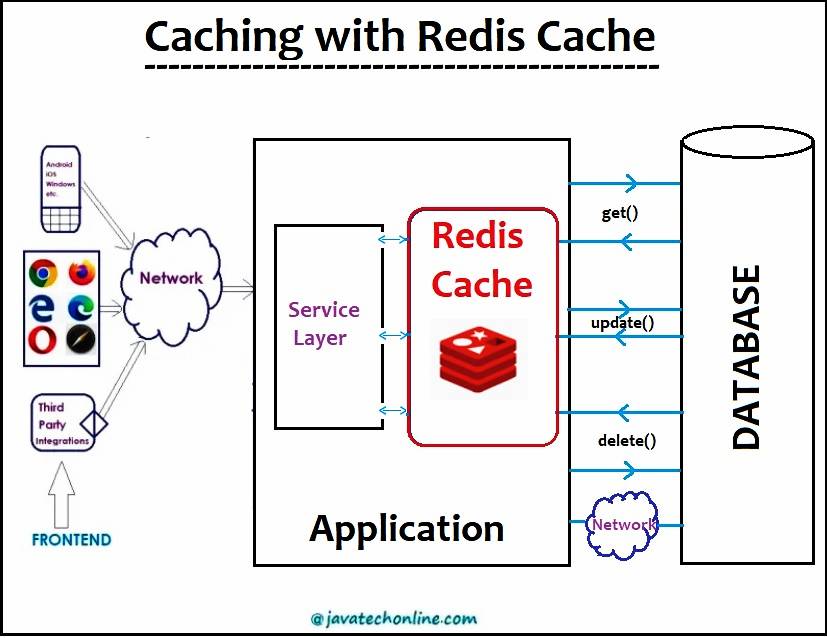
When we perform a DB retrieve operation via an Application, the Redis Cache stores the result in it’s cache. Further, when we perform the same retrieve operation, it returns the result from the cache itself and ignore the second call to database.
What is Redis Database?
-
Redis Database is an in-memory database that persists on disk. It means when we use Redis Database, we occupy a memory on the disk to use as a Database.
-
The data model is key-value, but many several kind of values are supported such as Strings, Lists, Sets, Sorted Sets, Hashes, Streams, HyperLogLogs, Bitmaps etc.
What is Redis Server?
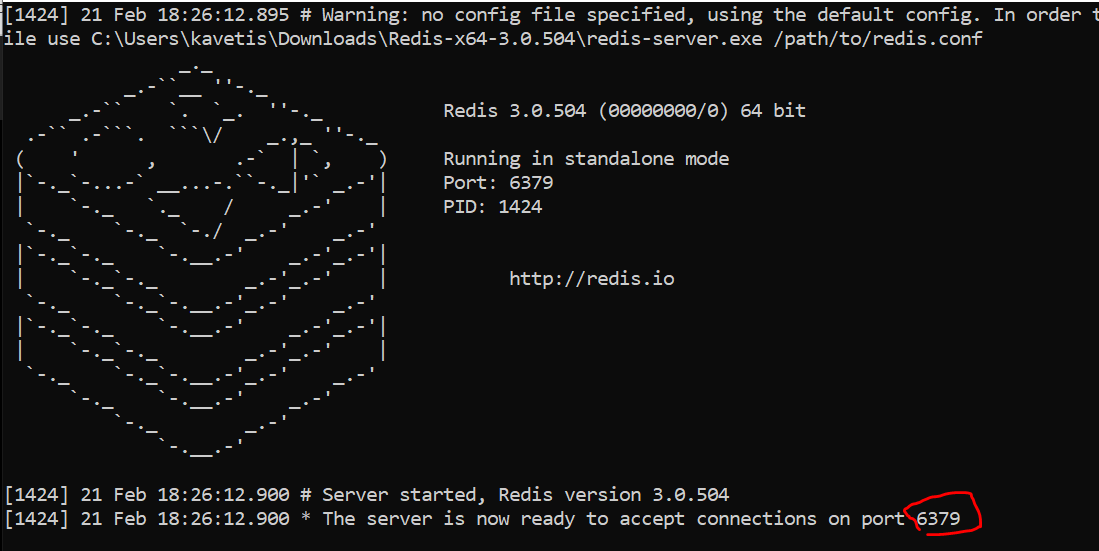
The full form of Redis is REmote DIctionary Server. When we use Redis in any form such as database, cache or Message Broker, we need to download a Redis Server in our system. People in the industry just call it Redis Server.
-
- Visit any of the link below to download Redis
- [Download Redis
- Server](https://github.com/microsoftarchive/redis/releases/tag/win-3.2.100)
- version 3.2.100
Download Redis Server : version 5.0.10
-
unzip ‘Redis-x64-5.0.10’, you will find redis-server.exe
- In order to start Redis Server, double click on ‘redis-server.exe’ to start Redis Server
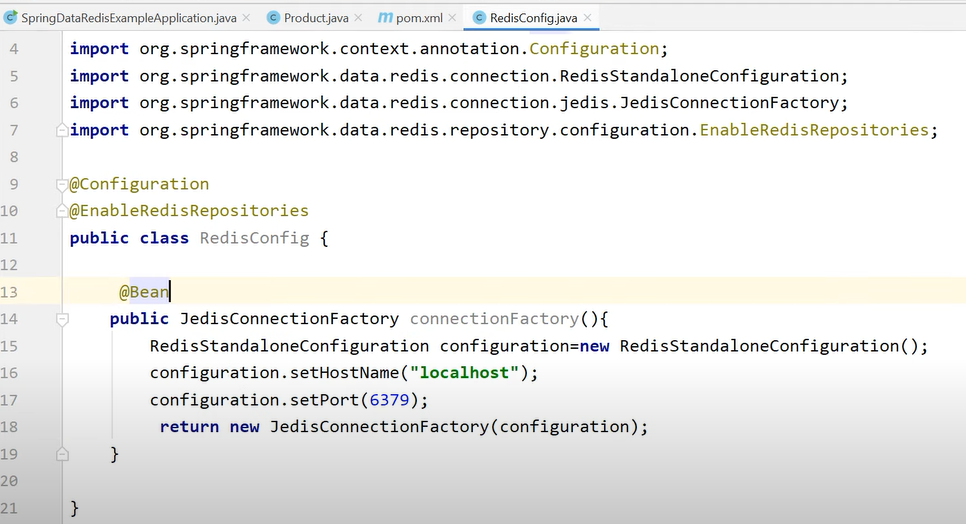
@EnableCaching : We apply this annotation at the main class (starter class) of our application in order to tell Spring Container that we need Caching feature in our application.
@Cacheable :@Cacheable is used to fetch(retrieve) data from the DB to application and store in Redis Cache. We apply it on the methods that get (retrieve) data from DB. (SELECT oprations).
@CachePut :We use @CachePut in order to update data in the Redis Cache while there is any update of data in DB. We apply it on the methods that make modifications in DB (DML oprations).
@CacheEvict :We use @CachePut in order to remove data in the Redis Cache while there is any removal of data in DB. We apply it on the methods that delete data from DB.
@Service
public class InvoiceServiceImpl implements InvoiceService {
@Autowired
private InvoiceRepository invoiceRepo;
@Override
public Invoice saveInvoice(Invoice inv) {
return invoiceRepo.save(inv);
}
@Override
@CachePut(value="Invoice", key="#invId")
public Invoice updateInvoice(Invoice inv, Integer invId) {
Invoice invoice = invoiceRepo.findById(invId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new InvoiceNotFoundException("Invoice Not Found"));
invoice.setInvAmount(inv.getInvAmount());
invoice.setInvName(inv.getInvName());
return invoiceRepo.save(invoice);
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(value="Invoice", key="#invId")
// @CacheEvict(value="Invoice", allEntries=true) //in case there are multiple entires to delete
public void deleteInvoice(Integer invId) {
Invoice invoice = invoiceRepo.findById(invId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new InvoiceNotFoundException("Invoice Not Found"));
invoiceRepo.delete(invoice);
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value="Invoice", key="#invId")
public Invoice getOneInvoice(Integer invId) {
Invoice invoice = invoiceRepo.findById(invId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new InvoiceNotFoundException("Invoice Not Found"));
return invoice;
}
@Override
@Cacheable(value="Invoice")
public List<Invoice> getAllInvoices() {
return invoiceRepo.findAll();
}
}