SpringBoot - Introduction
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can “just run”.
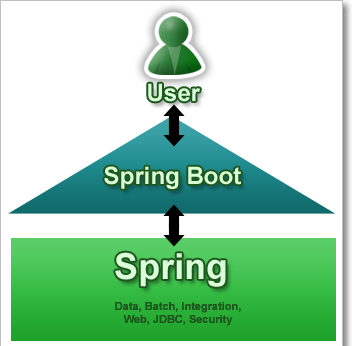
Spring vs SpringBoot
Spring: Spring started as a lightweight alternative to Java Enterprise Edition (J2EE). Spring offered a simpler approach to enterprise Java development, utilizing dependency injection and aspect-oriented programming to achieve the capabilities of EJB with plain old Java objects (POJOs).
But while spring was lightweight in terms of component code, it was heavyweight in terms of configuration. Initially, spring was configured with XML & Spring 2.5 introduced annotation-based component-scanning, even so, there was no escape from configuration.
Spring boot: project is just a regular spring project that happens to leverage Spring Boot starters and auto-configuration. Spring Boot is not a framework, it is a way to ease to create stand-alone application with minimal or zero configurations.
Finally, Spring Boot is just spring. Spring projects would not have any XML configurations as part of it, everything will be handled by the project Spring Boot.
Spring Boot Features
-
Create stand-alone Spring applications
-
Embed Tomcat, Jetty or Undertow directly (no need to deploy WAR files)
-
Provide opinionated ‘starter’ POMs to simplify your Maven configuration
-
Automatically configure Spring whenever possible
-
Provide production-ready features such as metrics, health checks and externalized configuration
-
Absolutely no code generation and no requirement for XML configuration
We can develop two flavors of Spring-Based Applications using Spring Boot
-
Java-Based Applications
-
Groovy Application
Groovy is also JVM language almost similar to Java Language. We can combine both Groovy and Java into one Project. Because like Java files, Groovy files are finally compiled into *.class files only. Both *.groovy and *.java files are converted to *.class file (Same byte code format).
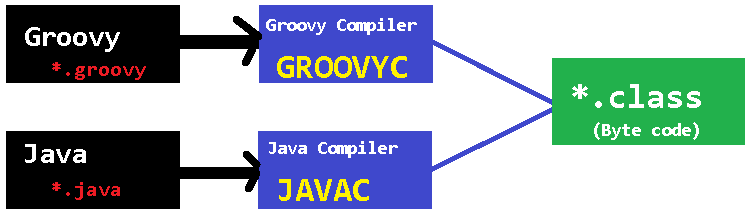
Spring Boot Framework Programming model is inspired by Groovy Programming model. Spring Boot internally uses some Groovy based techniques and tools to provide default imports and configuration.