Spring Cloud – Microservices
The major use-case for Spring Cloud is the ready-to-use solution that it provides to common problems observed in distributed environments like load balancing, service discovery, circuit breaking, etc., which can easily be integrated in an existing Spring project.
Before we look at Spring Cloud, let’s have a brief overview on Microservice Architecture and the role of Spring Boot in creating microservices.
https://github.com/sivaprasadreddy/spring-boot-microservices-series
https://www.sivalabs.in/2018/03/microservices-using-springboot-spring-cloud-part-1-overview/
Microservices
Monoliths
Traditionally we are building large enterprise applications in modularised fashion, but finally deploy them together as a single deployment unit (EAR or WAR). These are called Monolithic applications.
There are some issues with the monolithic architecture such as:
-
Large codebases become mess over the time
-
Multiple teams working on single codebase become tedious
-
It is not possible to scale up only certain parts of the application
-
Technology updates/rewrites become complex and expensive tasks
Microservices
Microservice architecture is a style of application development where the application is broken down into small services and these services have loose coupling among them. Following are the major advantages of using microservice architecture –
Advantages of MicroServices
-
Comprehending smaller codebase is easy
-
Can independently scale up highly used services
-
Each team can focus on one (or few) MicroService(s)
-
Technology updates/rewrites become simpler
SpringBoot and SpringCloud are a good choice for MicroServices
Spring Cloud – Components
Spring Cloud provides a collection of components which are useful in building distributed applications in cloud. We can develop these components on our own, however that would waste time in developing and maintaining this boilerplate code.
That is where Spring Cloud comes into picture. It provides ready-to-use cloud design patterns for common problems which are observed in a distributed environment. Some of the patterns which it attempts to address are −
-
Service Registration
-
Centralized Configuration
-
Load Balancing
-
Circuit Breakers / Fault Tolerence
-
Distributed Messaging (Kafka)
-
Routing (API Gateway)
-
Distributed Logging
-
Distributed Lock
Spring Cloud Components
Look at the various components which Spring Cloud provides and the problems these components solve
| Problem | Components |
|---|---|
| Distributed Cloud Configuration | Spring Cloud Configuration, Spring Cloud Zookeeper, Spring Cloud Config |
| Distributed Messaging | Spring Stream with Kafka, Spring Stream with RabbitMQ |
| Service Discovery | Spring Cloud Eureka, Spring Cloud Consul, Spring Cloud Zookeeper |
| Logging | Spring Cloud Zipkin, Spring Cloud Sleuth |
| Spring Service Communication(Circuit Breakers / Fault Tolerence) | Spring Hystrix, Spring Ribbon, Spring Feign, Spring Zuul(API gateWay) |
Projects Of Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud Config Server: Configuring application properties, environment details etc. We can use Spring Cloud Config Server with git or Consul or ZooKeeper as config repository.
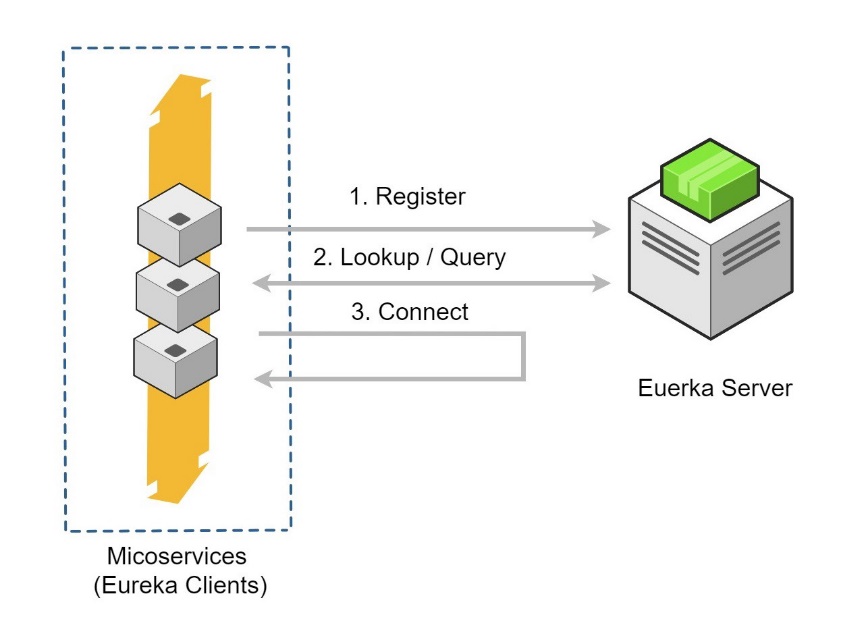
Service Registry and Discovery: As there could be many services and we need the ability to scale up or down dynamically. we need Service Registry and Discovery mechanism so that service-to-service communication should not depend on hard-coded hostnames and port numbers. Spring Cloud provides Netflix Eureka-based Service Registry and Discovery support with just minimal configuration. We can also use Consul or ZooKeeper for Service Registry and Discovery.
Circuit Breaker: In microservices based architecture, one service might depend on another service and if one service goes down then failures may cascade to other services as well. Spring Cloud provides Netflix Hystrix based Circuit Breaker to handle these kinds of issues.
Spring Cloud Data Streams: These days we may need to work with huge volumes of data streams using Kafka or Spark etc. Spring Cloud Data Streams provides higher-level abstractions to use those frameworks in an easier manner.
Spring Cloud Security: Some of the microservices needs to be accessible to authenticated users only and most likely we might want a Single Sign-On feature to propagate the authentication context across services. Spring Cloud Security provides authentication services using OAuth2.
Distributed Tracing: simple end-user action might trigger a chain of microservice calls, there should be a mechanism to trace the related call chains. We can use Spring Cloud Sleuth with Zipkin to trace the cross-service invocations.
Spring Cloud API gateway: There is a high chance that separate teams work on different microservices. There should be a mechanism for teams to agree upon API endpoint contracts so that each team can develop their APIs independently. Spring Cloud Contract helps to create such contracts and validate them by both service provider and consumer.