SpringBoot –JPA Example
Spring Boot provides spring-boot-starter-data-jpa starter to connect Spring application with relational database efficiently. You can use it into project POM (Project Object Model) file.
JPA Annotations
By default, each field is mapped to a column with the name of the field. You can change the default name via @Column (name=”newColumnName”).
The following annotations can be used.
| @Entity | Marks java class to a Table name |
|---|---|
| @Table(name=”tabname”) | Provides table name, when table name & class names are different . |
| @Id | Identifies the unique ID of the database entry |
| @GeneratedValue | Together with an ID this annotation defines that value is generated automatically. |
| @Transient | Field will not be saved in database |
The central interface in Spring Data repository abstraction is Repository (probably not that much of a surprise). It takes the domain class to manage as well as the id type of the domain class as type arguments.
Spring 4 Data
Spring Data Commons provides all the common abstractions that enable you to connect with different data stores.
Spring Data Coomons provides classes & methods, which are common for all the SQL, NoSQL, BigData databases
The Spring Data Commons project provides general infrastructure and interfaces for the other, more specific data projects. Regardless of the type of datastore, Spring Data supports the following aspects with a single API:
-
Execute CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations
-
Sorting
-
Page-wise reading (pagination)
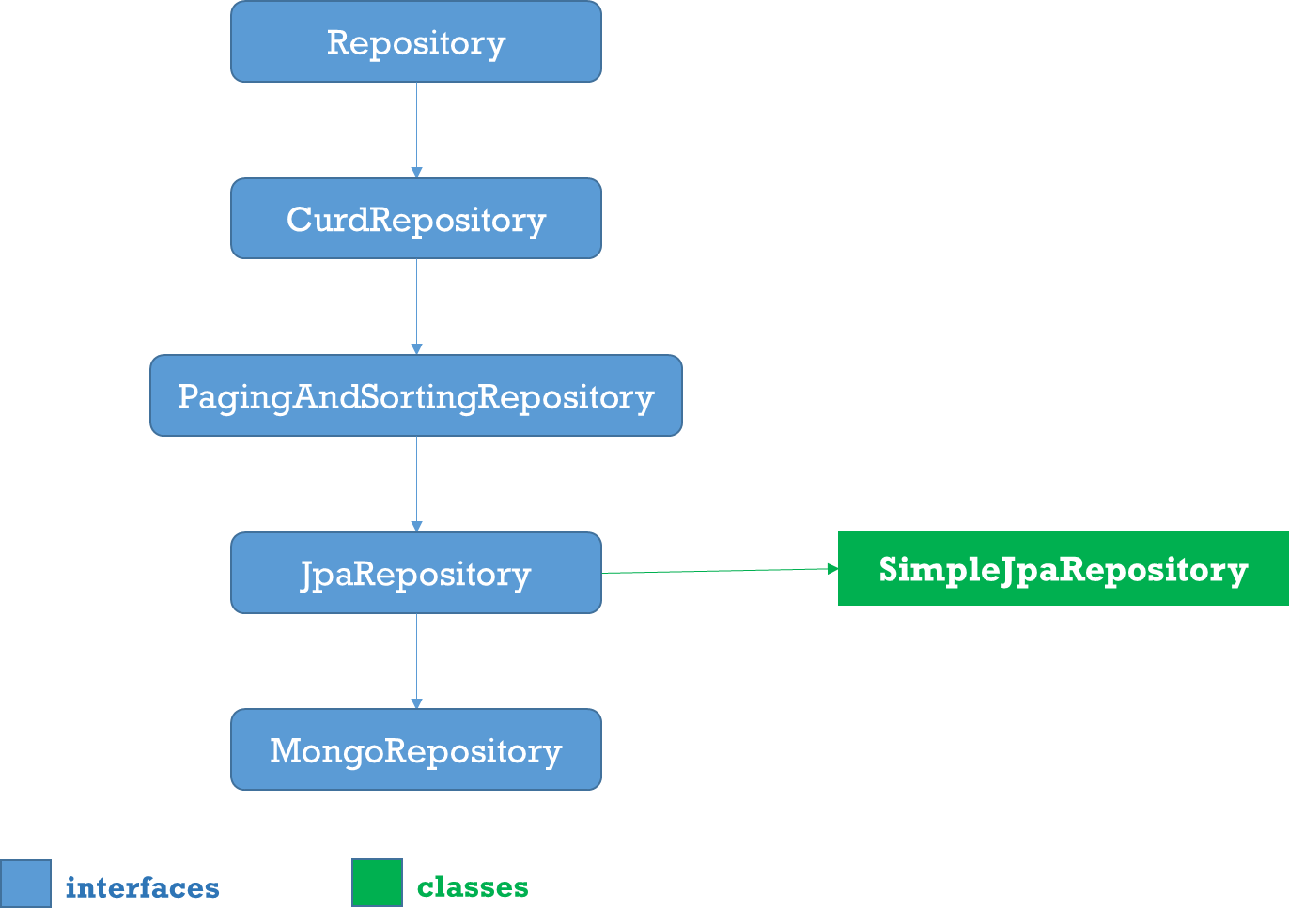
1.Repositoy
Root interface for all Repositoty classes. It is a marker interface(no methods)
2.CurdRepositoy
It provides generic CRUD operations irrespective of the underlying database. It extends Repository interface.
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID> extends Repository<T, ID> {
save(S entity);
saveAll(Iterable<S> entities);
Optional<T> findById(ID id);
Iterable<T> findAll();
Iterable<T> findAllById(Iterable<ID> ids);
void deleteById(ID id);
void delete(T entity);
void deleteAll(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
void deleteAll();
boolean existsById(ID id);
long count();
}
3.PagingAndSortingRepository
PagingAndSortingRepository provides options to
-
Sort your data using Sort interface
-
Paginate your data using Pageable interface, which provides methods for pagination - getPageNumber(), getPageSize(), next(), previousOrFirst() etc
public abstract interface PagingAndSortingRepository extends CrudRepository {
public Iterable findAll(Sort sort);
public Page findAll(Pageable pageable);
}
4.JpaRepository
JPA specific extension of Repository
public interface JpaRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends
PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> {
List<T> findAll();
List<T> findAll(Sort sort);
List<T> save(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
void flush();
T saveAndFlush(T entity);
void deleteInBatch(Iterable<T> entities);
}
5.MongoRepository
Mongo specific Repository interface.
public interface MongoRepository<T, ID> extends PagingAndSortingRepository {
List<T> findAll()
List<T> findAll(Sort sort)
List<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities)
List<S> insert(Iterable<S> entities)
S insert(S entity)
}
6.Custom Repository
-
You can create a custom repository extending any of the repository classes - Repository, PagingAndSortingRepository or CrudRepository. For example,
interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<User, Long> { } -
Spring Data also provides the feature of query creation from interface method names.
interface PersonRepository extends Repository<User, Long> {
List<Person> findByEmailAddressAndLastname(EmailAddress emailAddress, String lastname);
// Enables the distinct flag for the query
List<Person> findDistinctPeopleByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname);
List<Person> findPeopleDistinctByLastnameOrFirstname(String lastname, String firstname);
// Enabling ignoring case for an individual property
List<Person> findByLastnameIgnoreCase(String lastname);
// Enabling ignoring case for all suitable properties
List<Person> findByLastnameAndFirstnameAllIgnoreCase(String lastname, String firstname);
// Enabling static ORDER BY for a query
List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameAsc(String lastname);
List<Person> findByLastnameOrderByFirstnameDesc(String lastname);
}
7.Defining Query Methods
The repository proxy has two ways to derive a store-specific query from the method name:
-
By deriving the query from the method name directly.
List<Person> findByEmailAddressAndLastname(EmailAddress emailAddress, String lastname); -
By using a manually defined query.
@Query("select u from User u") List<User> findAllByCustomQueryAndStream(); -
Limiting the result size of a query with Top and First
User findFirstByOrderByLastnameAsc(); User findTopByOrderByAgeDesc(); Page<User> queryFirst10ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable); Slice<User> findTop3ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable); List<User> findFirst10ByLastname(String lastname, Sort sort); List<User> findTop10ByLastname(String lastname, Pageable pageable);
1.Entity class : Student.java ::create an entity class that contains the information of a single Student
entry
package app.entity;
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private int sno;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "address")
private String address;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(int sno, String name, String address) {
super();
this.sno = sno;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
//Setters & getters
}
2.StudentRepository.java
We can create the repository that provides CRUD operations for Student objects
by using one of the following methods:
-
Create an interface that extends the CrudRepository interface.
-
Create an interface that extends the Repository interface and add the required methods to the created interface.
package app.repository;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import app.entity.Student;
public interface StudentRepository extends CrudRepository<Student, String>{
}
3.StudentService.java
package app.service;
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository repository;
public List<Student> getAllStudents() {
List<Student> studentRecords = new ArrayList<>();
repository.findAll().forEach(studentRecords::add);
return studentRecords;
}
public Student getStudent(String id) {
return repository.findOne(id);
}
public void addStudent(Student studentRecord) {
repository.save(studentRecord);
}
public void delete(String id) {
repository.delete(id);
}
}
//StudentController.java
package app.controller;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@RequestMapping("/")
public List<Student> getAllStudent() {
return studentService.getAllStudents();
}
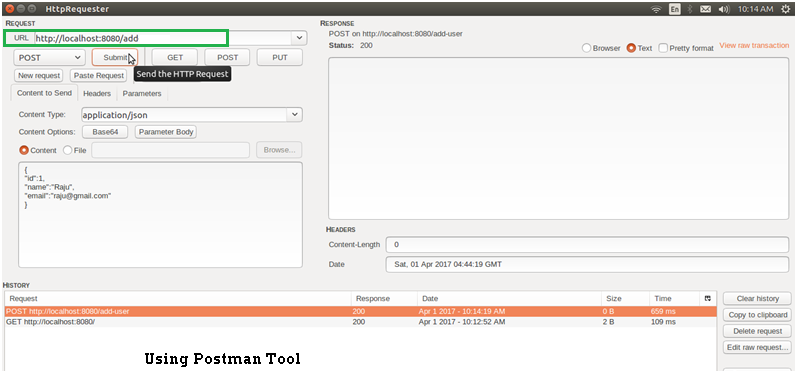
@RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void addStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
studentService.addStudent(student);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/get/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable String id) {
return studentService.getStudent(id);
}
}
//SpringBootApp.java
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApp.class, args);
}
}
http://localhost:8080/ -get All Srudents
[
{
"sno": 189,
"name": "Satya",
"address": "Vijayawada"
},
{
"sno": 508,
"name": "Satya",
"address": "Hyd"
}
]