SpringBoot –MVC
4. Spring Boot –MVC
In old Spring MVC lets you create special @Controller or @RestController
beans to handle incoming HTTP requests. Methods in your controller are mapped to
HTTP using @RequestMapping annotations.
Spring MVC Summary
Spring MVC
@Controller
@RequestMapping("student")
@RequestMapping(value = "/add" method=RequestMethod.GET)
@RequestMapping(value = "/add" method=RequestMethod.POST)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
/student/fetch/100/satya
@RequestMapping(value="/fetch/{sno}/{name}")
public String getInfo(@PathVariable("sno") String sno, (@PathVariable("sno") String n ) {
}
/student/fetch? sno=100&name=satya
@RequestMapping(value="/fetch")
public String getBoth(@RequestParam("id") String id, @RequestParam("name") String n) {
}
//Form Data
@RequestMapping(value = "/addEmployee", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String submit( @ModelAttribute("employee") Employee employee ) {
}
WebServices
@Path("/student")
/student/add
@Path("/add")
@GET
@Path("/usa")
@Produces("text/html")
@POST
@Path("/usa")
@Produces("text/html")
@Path("{rollno}/{name}/{address}")
@Produces("text/html")
public Response get(@PathParam("rollno") String rollno,@PathParam("name") String name,
@PathParam("address") String address) { }
students?rollno=1218&name=SATYA KAVETI&address=VIJAYAWADA
@GET
@Produces("text/html")
public Response get (@QueryParam("rollno") String rollno,@QueryParam("name") String name,
@QueryParam("address") String address) { }
//DefaultValue
@GET
@Produces("text/html")
public Response getResultByPassingValue(@DefaultValue("1000") @QueryParam("rollno") String rollno, @DefaultValue("XXXX") @QueryParam("name") String name,
@DefaultValue("XXXX") @QueryParam("address") String address) {
customers;custNo=100;custName=Satya
@GET
@Produces("text/html")
public Response getResultByPassingValue(
@MatrixParam("rollno") String rollno,
@MatrixParam("name") String name,
@MatrixParam("address") String address) {}
//Form
@POST
@Path("/registerStudent")
@Produces("text/html")
public Response getResultByPassingValue(
@FormParam("rollno") String rollno,
@FormParam("name") String name,
@FormParam("address") String address) {}
// HeaderParam
@GET
@Path("/headerparam")
public Response getHeader(
@HeaderParam("user-agent") String userAgent,
@HeaderParam("Accept") String accept,
@HeaderParam("Accept-Encoding") String encoding,
@HeaderParam("Accept-Language") String lang) {
//Context
@Path("Context ")
public Response getHttpheaders(@Context HttpHeaders headers){
String output = "<h1>@@Context Example - HTTP headers</h1>";
output = output+"<br>ALL headers -- "+ headers.getRequestHeaders().toString();
output = output+"<br>All Cookies -- "+ headers.getCookies().values();
return Response.status(200).entity(output).build();
Spring 4
Spring4–Introduced GetMapping/PostMapping/XXXMapping in place of
RequestMethod.POST/RequestMethod.GET etc.
Sprin3 -@RequestMapping(value=”/user/create”, method=RequestMethod.POST)
Spring4 -
@GetMapping("/students/{sno}")
public ResponseEntity getStudent(@PathVariable("sno") int sno) {
}
@PostMapping(value = "/students")
public ResponseEntity createStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
}
@DeleteMapping("/students/{sno}")
public ResponseEntity deleteStudent(@PathVariable int sno) {
}
public ResponseEntity<Student> createUser(@RequestBody User user, UriComponentsBuilder ub){
}
SpringMVC example @RestController to serve JSON data
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value="/users")
public class SmlCodesRestController {
@RequestMapping(value="/{user}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long user) {
// ...
}
@RequestMapping(value="/{user}/customers", method=RequestMethod.GET)
List<Customer> getUserCustomers(@PathVariable Long user) {
// ...
}
@RequestMapping(value="/{user}", method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
public User deleteUser(@PathVariable Long user) {
// ...
}
}
Spring Boot MVC Example – Using TheamLeaf
Thymeleaf Quick Tutorial
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments.
We can use Thymeleaf directly in .html files. By just placing below line to activate Thymeleaf in our HTML.
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
If you want to use Thymleaf elements in our program, we have use th:<element> Tag in our HTML Tags
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th th:text="#{msgs.headers.name}">Name</th>
<th th:text="#{msgs.headers.price}">Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="prod: ${allProducts}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Oranges</td>
<td th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal(prod.price, 1, 2)}">0.99</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
We need add spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf dependency in our application’s pom.xml file to use Thymeleaf in our Application
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
Example – Employee CURD operations
Create Project: Ref :
Build with maven & Open Eclipse. If we see the Folder Structre
-
All static content like CSS, JS files will be placed unter →
resources\static\ -
all the result pages must be placed under→
resources\templates\
This type of floder structure we will use in TheamLeaf based UI.
Static Content
By default, Spring Boot serves static content from a directory called /static.
You can also customize the static resource locations by using the
spring.web.resources.static-locations property in applications.proerties
file.
Template Content (Template Engines)
Spring MVC supports a variety of templating technologies, including Thymeleaf,
FreeMarker, and JSPs. If you use one of these templating engines with the
default configuration, your templates are picked up automatically from
src/main/resources/templates
1. application.properties (DB Properties)
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/webapp?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
2. Employee.java entity class to map with Employee Table
package springboot;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column
private String name;
@Column
private String address;
@Column
private Double salary;
//Setters & Getters
}
3. EmployeeRepository.java – for performing CURD Operations on DB
package springboot.repository;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {
}
4. EmployeeService.java – Service Layer
public interface EmployeeService {
List<Employee> getAllEmployees();
void saveEmployee(Employee employee);
Employee getEmployeeById(long id);
void deleteEmployeeById(long id);
}
EmployeeServiceImpl.java – Service Layer Implenetation
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
@Autowired
EmployeeRepository repository;
@Override
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
return repository.findAll();
}
@Override
public void saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
Employee e = repository.save(employee);
System.out.println(" Employee Data Saved : " + e);
}
@Override
public Employee getEmployeeById(long id) {
Employee e = repository.getById(id);
System.out.println("Employee getEmployeeById : " + e);
return e;
}
@Override
public void deleteEmployeeById(long id) {
Employee e = repository.getById(id);
repository.delete(e);
System.out.println("Employee Deleted : ");
}
}
So far Good. Now come to actual Thymeleaf changes.
Model Interface
Java-5-specific interface that defines a holder for model attributes. Primarily designed for adding attributes to the model. Allows for accessing the overall model as a java.util.Map.
Display Homepage
1.Create index.html thymeleaf template under “resources/templates” folder and add below code.
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href=https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.1.3/css/bootstrap.min.css>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container my-2">
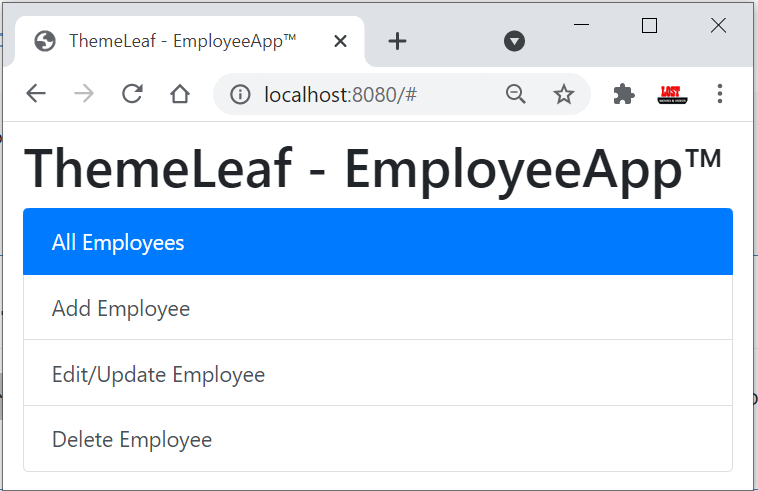
<h1>ThemeLeaf - EmployeeApp™</h1>
<div class="list-group">
<a href="#" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action">All Employees</a>
<a href="#" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action">Add Employee</a>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
2. Create a EmployeeController class, and add method to display homepage
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@GetMapping("/")
public String viewHomePage(Model model) {
System.out.println("Calling Home Page....");
return "index";
}
}
Now Run mian class & open Browser
To make our application more stylish, add CSS and JS files in src/main/resources/static folder.
You can see Complete code Example here (Code Ref.)
https://gitlab.com/satyacodes/books-sync-github_new/-/tree/main/Codes/SpringBoot-Thymeleaf
If you got this Error: Whitelabel Error page (type=Not Found, status=404)
Move your SpringBoot main class from sub package to Root package, example from spring.app package to spring package
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@GetMapping("/")
public String viewHomePage(Model model) {
System.out.println("Calling Home Page....");
return "index";
}
// display list of employees
@GetMapping("/all")
public String listEmployees(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("listEmployees", employeeService.getAllEmployees());
return "listEmployees";
}
// display list of employees
@GetMapping("/addEmployee")
public String addEmployee(Model model) {
// create model attribute to bind form data
Employee employee = new Employee();
model.addAttribute("employee", employee);
//An error happened during template parsing (template: "class path resource [templates/add.html]")
return "addEmployee";
}
@PostMapping("/saveEmployee")
public String saveEmployee(@ModelAttribute("employee") Employee employee) {
// save employee to database
employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
return "redirect:/all";
}
@GetMapping("/showEditForm/{id}")
public String showEditForm(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id, Model model) {
// get employee from the service
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(id);
employee.setId(id);
// set employee as a model attribute to pre-populate the form
model.addAttribute("employee", employee);
return "editEmployeeForm";
}
@GetMapping("/viewEmployee/{id}")
public String viewEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id, Model model) {
// get employee from the service
Employee employee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(id);
// set employee as a model attribute to pre-populate the form
model.addAttribute("employee", employee);
System.out.println("viewEmployee : " + employee);
return "viewEmployee";
}
@GetMapping("/deleteEmployee/{id}")
public String deleteEmployee(@PathVariable(value = "id") long id) {
// call delete employee method
this.employeeService.deleteEmployeeById(id);
return "redirect:/all";
}
}
<!-- index.html -->
<a href="all" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action active"> All Employees</a>
<a href="addEmployee" class="list-group-item list-group-item-action">Add Employee</a>
<!-- addEmployee -->
<form action="#" th:action="@{/saveEmployee}" th:object="${employee}" method="POST">
<input type="text" th:field="*{name}" placeholder="Employee Name" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{address}" placeholder="Employee Adress" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{salary}" placeholder="Employee Salary" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-info">Save</button>
</form>
<!-- editEmployee -->
<form action="#" th:action="@{/saveEmployee}" th:object="${employee}" method="POST">
<input type="text" th:field="*{id}" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{name}" placeholder="Employee Name" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{address}" placeholder="Employee Adress" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<input type="text" th:field="*{salary}" placeholder="Employee Salary" class="form-control mb-4 col-4">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-info">Save</button>
</form>
<!-- viewEmployee -->
ID : <span th:text="${employee.id}">
NAME : <span th:text="${employee.name}"></span>
ADDRESS : <span th:text="${employee.address}">
SALARY : <span th:text="${employee.salary}">
<a th:href="@{/all}"> Back to Employee List</a>
<!-- listEmployees -->
<table border="1" class="table table-striped table-responsive-md">
<thead>
<tr>
<th># Emp. ID</th>
<th>Name </th>
<th>Address </th>
<th>Salary </th>
<th>Actions </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="employee : ${listEmployees}">
<td th:text="${employee.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${employee.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${employee.address}"></td>
<td th:text="${employee.salary}"></td>
<td>
<a th:href="@{/viewEmployee/{id}(id=${employee.id})}" class="btn btn-primary">View <span> </span>
<a th:href="@{/showEditForm/{id}(id=${employee.id})}" class="btn btn-warning”> EDIT</a> <span> </span>
<a th:href="@{/deleteEmployee/{id}(id=${employee.id})}" class="btn btn-danger">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
SpringBoot – MVC using Standard JSP Pages
Add this extra dependency in pom.xml to work with jsp pages
<!-- JSTL -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Tomcat Embed -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Optional, test for static content, bootstrap CSS-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap</artifactId>
<version>3.3.7</version>
</dependency>
CSS, JS, assets related files
In old Spring, to use static files, we need configure those folders paths in SpringConfig.xml file
<!-- OLD Spring - These for Static images, css calls in jsp pages -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
<mvc:resources mapping="/assets/*" location="/assets/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/js/*" location="/js/" />
<mvc:resources mapping="/css/*" location="/css/" />
But in Spring Boot, no need to declare the resource mapping like above. The resource mapping will handle automatically. We need to place CSS or Javascript, in /src/main/resources/static/ folder.
JSP Files
JSP view files would be created inside src/main/resources/META-INF/resources/WEB-INF/jsp/. If you want use css, js files which are placed in static folder, just link into JSP view via
<link href=”/css/main.css” rel=”stylesheet”>
To resolve JSP file’s location, you can have two approaches.
-
Using application.properties
-
Using Java configuration
1.Using application.properties (Recommnded)
To Tell Spring, where JSP files located - we need to place those details in application.properties
spring.mvc.view.prefix: /WEB-INF/jsp/
spring.mvc.view.suffix: .jsp
2. Using Java configuration
Configure InternalResourceViewResolver to serve JSP pages using WebMvcConfigurerAdapter
package springboot.controller;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan
public class MVCConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/view/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
resolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
registry.viewResolver(resolver);
}
}
Spring Boot Application Initializer
So far we used .jar file to run our SpringBoot application. But for Web Applications recommended way is .war file Deployment. To Achive the .war file related stuff in SpringBoot we need to use SpringBootServletInitializer
Our SpringBoot main class need to extend SpringBootServletInitializer & override configure() method to produce .war file. This makes use of Spring Framework’s Servlet 3.0 support and allows you to configure your application when it’s launched by the servlet container.
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootAppApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringBootAppApplication.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootAppApplication.class, args);
System.out.println(" Hello, Again");
}
}
-
Controller classes created inside src/main/java
-
JSP pages created inside src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/view
-
CSS and JS files created inside src/main/resources/static
-
application.properties created inside src/main/resources
-
Application.java is a launch file for Spring Boot created inside src/main/java
pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jersey</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web-services</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-embed-jasper</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>bootstrap</artifactId>
<version>3.3.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
JSP’s - src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\views
//index.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags"%>
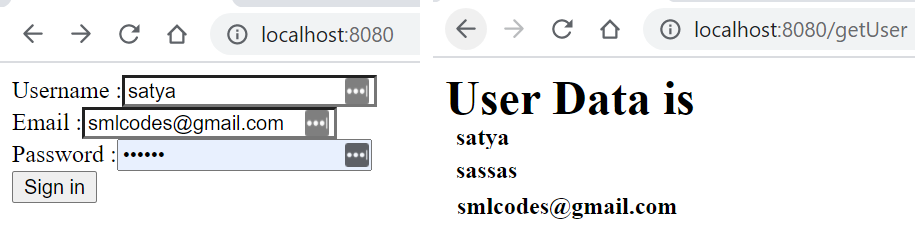
<form action="getUser" method="post">
Username :<input type="text" name="username" > <br>
Email :<input type="email" name="email" > <br>
Password :<input type="password" name="password"> <br>
<button type="submit">Sign in</button>
</form>
//user.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags"%>
<h1>User Data is</h1>
<h4>${user.username}</h4>
<h4>${user.password}</h4>
<h4>${user.email}</h4>
Add entries in application.properties
# for SpringMVC - JSP related Config
spring.mvc.view.prefix:/WEB-INF/views/
spring.mvc.view.suffix:.jsp
#For detailed logging during development
logging.level.org.springframework=TRACE
logging.level.com=TRACE
HomeController.java
package springboot.controller;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public ModelAndView homePage() {
ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView();
view.setViewName("index");
return view;
}
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
public ModelAndView getUser(@ModelAttribute UserBo user) {
ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView();
view.addObject("user", user);
view.setViewName("user");
return view;
}
}
UserBo.java to store input data
public class UserBo {
private int id;
private String username;
private String email;
private String password;
//Setters & Getters
}
SpringBootAppApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootAppApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringBootAppApplication.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootAppApplication.class, args);
}
}
Spring Boot –RESTful Web Service Example
To work with webservices, in SpringBoot we have to use two annotations
-
@RestController: tells Spring Boot to consider this class as REST controller
-
@RequestMapping: used to register paths inside it to respond to the HTTP requests.
@RestController is a stereotype annotation. It adds @Controller and @ResponseBody annotations to the class.
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
Note - The @RestController and @RequestMapping annotations are Spring MVC annotations. They are not specific to Spring Boot.
app.controller.SpringBootRestController.java
package app.controller;
@RestController
public class SpringBootRestController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String welcome() {
return "Spring Boot Home Page";
}
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String myData() {
return "Smalcodes : Hello Spring Boot";
}
}
app.SpringBootApp.java
package app;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApp.class, args);
}
}
Create pom.xml same as first example.
Test the Application
Right click on project > Run as >Java Application >select SpringBootApp
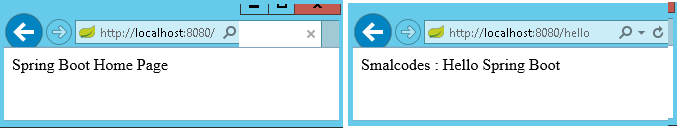
-
In above Spring Boot main application class in app package and controller class in app.controller.
-
While starting our application, SpringBootApp class will scan all the components under app package. we have created our controller class in app.controller which is inside app package.so our controller was registered by spring boot.
-
If you create the controller class outside of the main package, lets say com.smlcodes.controller, If you run the application it gives 404 error.To resolve this, we have to add @ComponentScan annotation in our Spring Boot main class, as below
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages="smlcodes.controller")
public class SpringBootApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootApp.class, args);
}
}
Spring Boot - Rest API exception handling (@ControllerAdvice)
In below Code, you can observe multiple Try/Catch blocks to handle exceptions.
@RestController
public class TutorialController {
@Autowired
TutorialRepository tutorialRepository;
@GetMapping("/tutorials")
public ResponseEntity<List<Tutorial>> getAllTutorials(@RequestParam(required = false) String title) {
try {
...
return new ResponseEntity<>(tutorials, HttpStatus.OK);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(null, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
@GetMapping("/tutorials/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Tutorial> getTutorialById(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
Optional<Tutorial> tutorialData = tutorialRepository.findById(id);
if (tutorialData.isPresent()) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(tutorialData.get(), HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
@PutMapping("/tutorials/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Tutorial> updateTutorial(@PathVariable("id") long id, @RequestBody Tutorial tutorial) {
Optional<Tutorial> tutorialData = tutorialRepository.findById(id);
if (tutorialData.isPresent()) {
...
return new ResponseEntity<>(tutorialRepository.save(_tutorial), HttpStatus.OK);
} else {
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
...
@DeleteMapping("/tutorials/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<HttpStatus> deleteTutorial(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
try {
tutorialRepository.deleteById(id);
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
@DeleteMapping("/tutorials")
public ResponseEntity<HttpStatus> deleteAllTutorials() {
// try and catch
}
@GetMapping("/tutorials/published")
public ResponseEntity<List<Tutorial>> findByPublished() {
// try and catch
}
}
You can see that we use try/catch many times for similar exception (INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR), and there are also many cases that return NOT_FOUND.
To avoid handling same excetions multiple times in a Single controller, we can use the concept called Global Exception handling using @ControllerAdvice and @ExceptionHandler
@GetMapping("/testReport/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<TestReport> getReportByID(@PathVariable int id){
TestReport data = repository.getById(id);
try {
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(data);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(null, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}
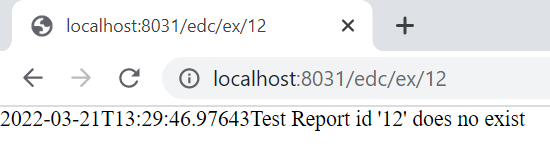
If we access above api call with invalid id like 12, you will get following response.
{ "timestamp": "2020-11-28T13:24:02.239+00:00",
"status": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"message": "",
"path": "/ testReport/12"}
We can see that besides a well-formed error response, the payload is not giving us any useful information. Even the message field is empty, which we might want to contain something like “Report with id 12 not found”.
We can handle this type of Global Exception Handling with below Annotations
-
@ControllerAdvice : is used with class level for global error/exception handling
-
@ExceptionHandler : is used with methods (not with class).
-
@ResponseStatus : is used annotate used defined exception classes.
We can configure multiple exceptions in this class so that in our application if that exception will occur, this class will get invoked and we will have a proper error message.
Steps to for Global Exception Handling
1.Create Custom Exception class for INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR & NOT_FOUND exceptions & annotate our Exception class with @ResponseStatus and pass value to HTTP.Exception property.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class RecordNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
String message;
public RecordNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
this.message = message;
}
}
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
public class InternalServerException extends RuntimeException {
String message;
public InternalServerException(String message) {
super(message);
this.message = message;
}
}
2.Now Create class which do Global Exception handling by
-
annotating class with @ControllerAdvice
-
annotating methods with @ExceptionHandler(RecordNotFoundException.class)
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandlerForAllExceptions extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(RecordNotFoundException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleRecordNotFoundException(RecordNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = new LinkedHashMap<>();
body.put("timestamp", LocalDateTime.now());
body.put("message", ex.getLocalizedMessage());
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
@ExceptionHandler(InternalServerException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Object> handleNodataFoundException(InternalServerException ex, WebRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> body = new LinkedHashMap<>();
body.put("timestamp", LocalDateTime.now());
body.put("message", "Server Has Issue while Processing this Request");
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR);
}
}
3.Update Controller class method Response to throw UserDefined exception.
@GetMapping(path = "/ex/{id}", produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public TestReport getReportByID(@PathVariable int id) {
return repository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(
() -> new RecordNotFoundException("Test Report id '" + id + "' does no exist"));
}
4.When ever Controller Class Throws exception, it will Automcatically forward exception handling to ControllerAdive class & Calls the method which is annotated with @ExceptionHandler with thrown exception class ex : InternalServerException.class)