Kafka – Message Broker
Kafka as “an open-source message broker project developed by the Apache Software Foundation written in Scala and is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system.
Kafka is designed for transferring Big data. Kafka has better throughput, built-in partitioning, replication and inherent fault-tolerance, which makes it a good fit for large-scale message processing applications.
Two types of messaging patterns are available − one is point to point and the other is publish-subscribe (pub-sub) messaging system. Most of the messaging patterns follow pub-sub.
| High Throughput | Support for millions of messages with modest hardware |
|---|---|
| Scalability | Highly scalable distributed systems with no downtime |
| Replication | Messages are replicated across the cluster to provide support for multiple subscribers and balances the consumers in case of failures |
| Durability | Provides support for persistence of message to disk |
| Stream Processing | Used with real-time streaming applications like Apache Spark & Storm |
| Data Loss | Kafka with proper configurations can ensure zero data loss |
-
Producer: responsible for producing messages for a specific topic.
-
Consumer: responsible for reading the messages that the producer puts on a topic.
-
Brokers – a set of servers where the publishes messages are stored
-
Topic: topic is a categorized group of messages.
-
Message: I think that all events in Kafka can be summarized in messages. A message can contain a simple text like “Hello World” or an object in json format for example.
Partition & Offset
In the above diagram, a topic is configured into three partitions.
-
Partition 1 has two offset factors 0 and 1.
-
Partition 2 has four offset factors 0, 1, 2, 3.
-
Partition 3 has one offset factor 0.
-
The id of the replica is same as the id of the server that hosts it.
Assume, if the replication factor of the topic is set to 3, then Kafka will create 3 identical replicas of each partition and place them in the cluster to make available for all its operations. To balance a load in cluster, each broker stores one or more of those partitions. Multiple producers and consumers can publish and retrieve messages at the same time.
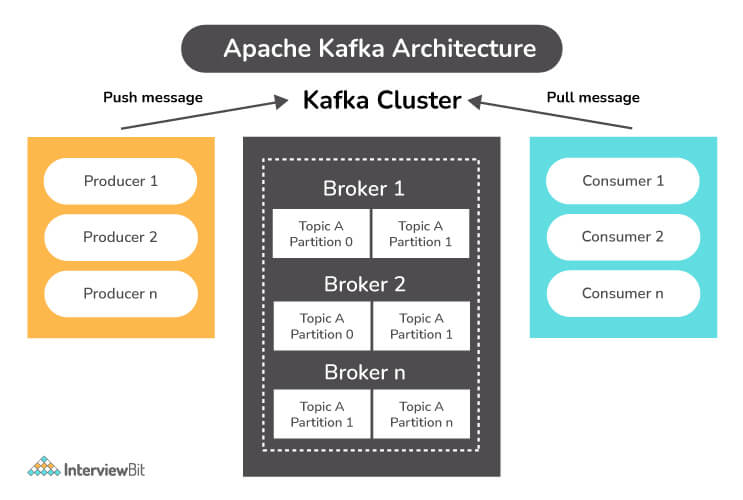
Cluster Architecture
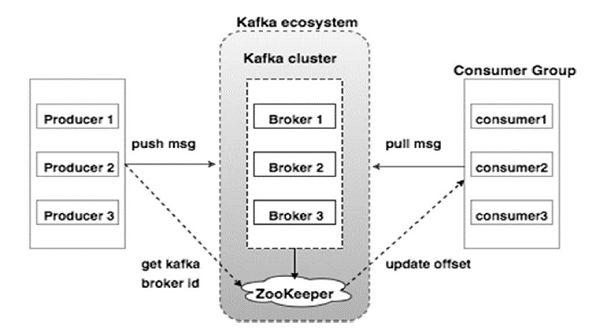
Broker: Kafka cluster typically consists of multiple brokers to maintain load balance. Kafka brokers are stateless, so they use ZooKeeper for maintaining their cluster state. One Kafka broker instance can handle hundreds of thousands of reads and writes per second and each bro-ker can handle TB of messages without performance impact. Kafka broker leader election can be done by ZooKeeper.
ZooKeeper: ZooKeeper is used for managing and coordinating Kafka broker. ZooKeeper service is mainly used to notify producer and consumer about the presence of any new broker in the Kafka system or failure of the broker in the Kafka system. As per the notification received by the Zookeeper regarding presence or failure of the broker then pro-ducer and consumer takes decision and starts coordinating their task with some other broker.
Producers: Producers push data to brokers. When the new broker is started, all the producers search it and automatically sends a message to that new broker. Kafka producer doesn’t wait for acknowledgements from the broker and sends messages as fast as the broker can handle
Windows Install & Configuration
-
Got to the Apache Kafka downloads page and download the https://kafka.apache.org/download the Scala 2.12 kafka_2.12-0.10.2.1.tgz. Next unzip & start Apache Kafka
-
This Kafka installation comes with an inbuilt zookeeper. Zookeeper is mainly used to track status of nodes present in Kafka cluster and also to keep track of Kafka topics, messages, etc.
-
Open a command prompt and start the Zookeeper-
cd C:\kafka
.\bin\windows\zookeeper-server-start.bat .\config\zookeeper.properties
- Open a new command prompt and start the Apache Kafka
cd C:\kafka
.\bin\windows\kafka-server-start.bat .\config\server.properties
//If any errors add below line in Environment propertis in User Serction
%SystemRoot%\System32\Wbem;%SystemRoot%\System32\;SystemRoot%
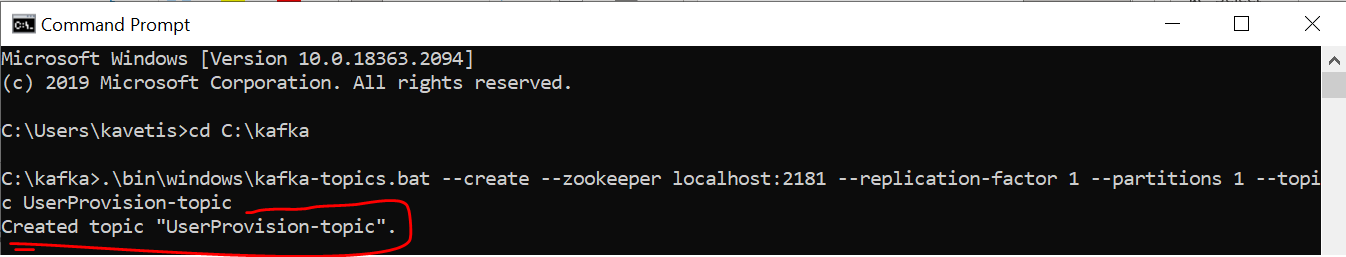
Create UserProvision Topic
- Open a new command prompt and create a topic with name UserProvision-topic, that has only one partition & one replica.
cd C:\kafka
.\bin\windows\kafka-topics.bat --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic UserProvision-topic
- Next Open a new command prompt and create a PRODUCER to send message to the above created UserProvision-topic and send a message - Hello World Javainuse to it-
cd C:\kafka
.\bin\windows\kafka-console-producer.bat --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic UserProvision-topic Hello Message:User is Created
- Finally Open a new command prompt and start the CONSUMER which listens to the topic javainuse-topic we just created above. We will get the message we had sent using the producer
cd C:\kafka
.\bin\windows\kafka-console-consumer.bat --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic UserProvision-topic --from-beginning
SpringBoot Kafka Application Example
When ever new User is Created, we need to send the User details to Kafka. Downstream applications will consume those User details. So we have need Create below Projects.
Producer: Send messages to Topic
- UserManagementMicroServiceWithKafka
Consumer: Consumes messages
-
EDC-MicroService
-
MI-MicroService
1.Producer Application : UserManagementMicroServiceWithKafka
Create SpringBoot Project & Add Dependencies
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
application.properties:
# Producer properties
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers=127.0.0.1:9092
spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.group-id=group_id
topic.name.producer=user.provision.topic
# Common Kafka Properties
auto.create.topics.enable=true
-
At first I put the StringSerializer class to serialize the messages, just to send some text.
-
The auto.create.topics.enable = true property automatically creates topics registered to those properties. In that case I put topic.name.producer = user.provision.topic
SpringBootMainClass : In the main class I put the annotation “@EnableKafka”, which makes it possible to connect to a topic.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableKafka
public class UserManagementKafkaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(UserManagementKafkaApplication.class, args);
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/userprovision/")
public class UserProvisionController {
@Autowired
KafkaSenderService kafkaSender;
@PostMapping(value = "/add", produces = "text/html")
public ResponseEntity<String> producer(@RequestBody UserDetails userDetails) {
kafkaSender.send(userDetails.toString());
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(userDetails.toString());
}
}
@Service
public class KafkaSenderService {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
//String kafkaTopic = "UserProvision-topic";
@Value("${topic.name.producer}")
private String kafkaTopic;
public void send(String data) {
System.out.println("KafkaSenderService : Message STRAT");
kafkaTemplate.send(kafkaTopic, data);
System.out.println("KafkaSenderService : Message SENT");
}
}
The KafkaTemplate class is the class that sends messages to topics, the first String is the topic and the second the type of information.
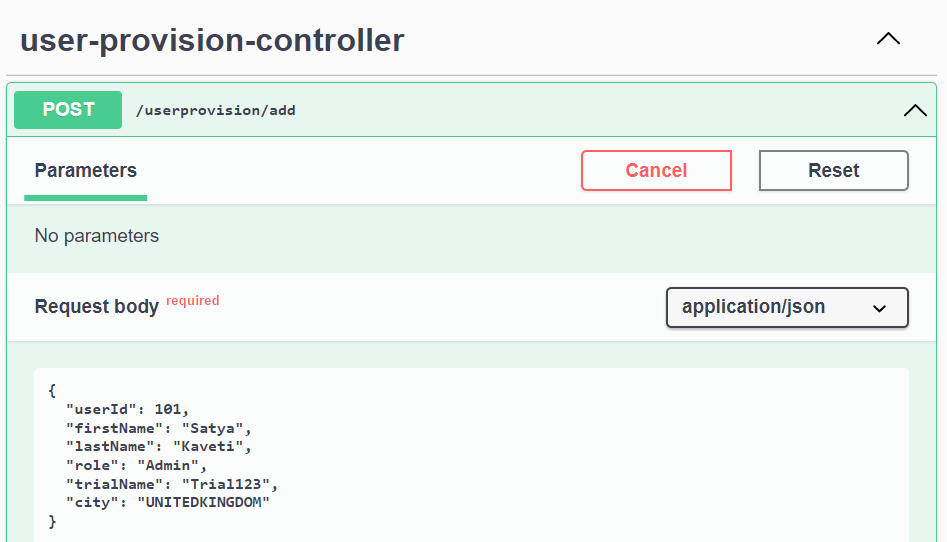
Test http://localhost:8051/userprovision/add
{
"userId": 101,
"firstName": "Satya",
"lastName": "Kaveti",
"role": "Admin",
"trialName": "Trial123",
"city": "UNITEDKINGDOM"
}
Consumer Application : EDC-MicroService, MI-MicroService
Add Dependecy to both pom.xmls
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-streams</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
Update Kafka application.properties:
# Consumer properties
spring.kafka.producer.bootstrap-servers=127.0.0.1:9092
spring.kafka.producer.key-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.value-serializer=org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
spring.kafka.producer.group-id=group_id
topic.name.consumer=user.provision.topic
# Common Kafka Properties
auto.create.topics.enable=true
main class annotated with “@EnableKafka”, which makes it possible to connect to a topic.
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableHystrix
@EnableHystrixDashboard
@EnableKafka
public class EDCMicroServiceMainApplication {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EDCMicroServiceMainApplication.class, args);
}
}
Create Service class which consumes Topic messages
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class KafkaConsumerService {
@Value("${topic.name.consumer")
private String topicName;
@KafkaListener(topics = "${topic.name.consumer}", groupId = "group_id")
public void consume(ConsumerRecord<String, String> payload) {
log.info("Tópico: {}", topicName);
log.info("key: {}", payload.key());
log.info("Headers: {}", payload.headers());
log.info("Partion: {}", payload.partition());
log.info("Order: {}", payload.value());
}
}
Start Both UserKafkaService & EDC, MI Services
Open SwaggerUI of user provison sent data
Producer Log
2022-03-16 12:42:36.322 INFO 15408 --- [ad | producer-1] org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata : [Producer clientId=producer-1] Cluster ID: kaWxu5VsTbulOsUgCos2zQ
KafkaSenderService : Message SENT
Consumer Log
Tópico: {}${topic.name.consumer
key: {}null
Headers: {}RecordHeaders(headers = [], isReadOnly = false)
Partion: {}0
Order: {}UserDetails [userId=101, firstName=Satya, lastName=Kaveti, role=Admin, trialName=Trial123, city=UNITEDKINGDOM]
Remember : We got errors while Sluth& Zipkin jars enabled in pom.xml. So while running Kafka please comment those