Spring Cloud Config Server – to Store our Properties
SpringBoot provides lot of flexibility in externalizing configuration properties via properties or YAML files. We can also configure properties for each environment (dev, qa, prod etc) separately using profile specific configuration files such as application.properties, application-dev.properties, application-prod.properties etc. But once the application is started we can not update the properties at runtime. If we change the properties we need to restart the application to use the updated configuration properties.
To Solve this, We can use Spring Cloud Config Server to centralize all the applications configuration and use Spring Cloud Config Client module from the applications to consume configuration properties from Config Server. We can also update the configuration properties at runtime without requiring to restart the application.
Spring Cloud Config Server is nothing but a SpringBoot application with a
configured configuration properties source. The configuration source can be a
git , svn or any
repository.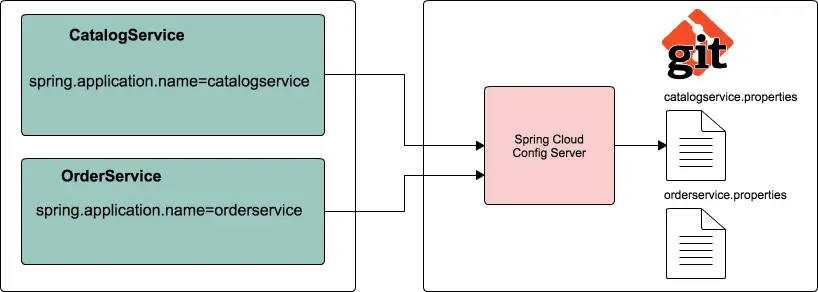
Steps to configure Spring Cloud Config Server
1.Create a git repo to store our properties with different envromnets.
https://github.com/smlcodes/SpringConfigServer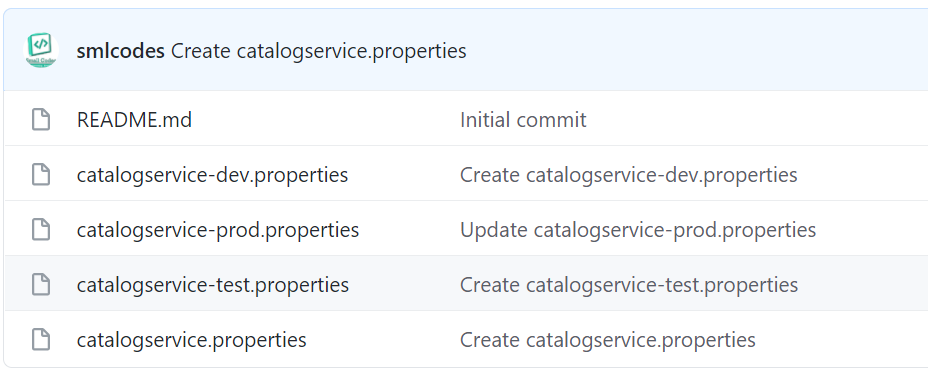
2.Let us create a SpringBoot application spring-cloud-config-server from http://start.spring.io by selecting the starters Config Server and Actuator.
3.To make our SpringBoot application as a SpringCloud Config Server, we just need to add @EnableConfigServer annotation to the main entry point class
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class SpringCloudConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
4.configure git url property pointing to the git repository in application.propertis
spring.config.name=configserver
server.port=8182
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/smlcodes/SpringConfigServer.git
spring.cloud.config.server.git.default-label=main
management.security.enabled=false
5.Start the application. Spring Cloud Config Server exposes the following REST endpoints to get application specific configuration properties:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]
/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml
/{application}-{profile}.properties
/{label}/{application}-{profile}.properties
Here {application} refers to value of spring.config.name property, {profile} is an active profile and {label} is an optional git label (defaults to “master”).
Now if you access the URL http://localhost:8182/catalogservice/default then
you will get the following response with catalogservice default
configuration details: 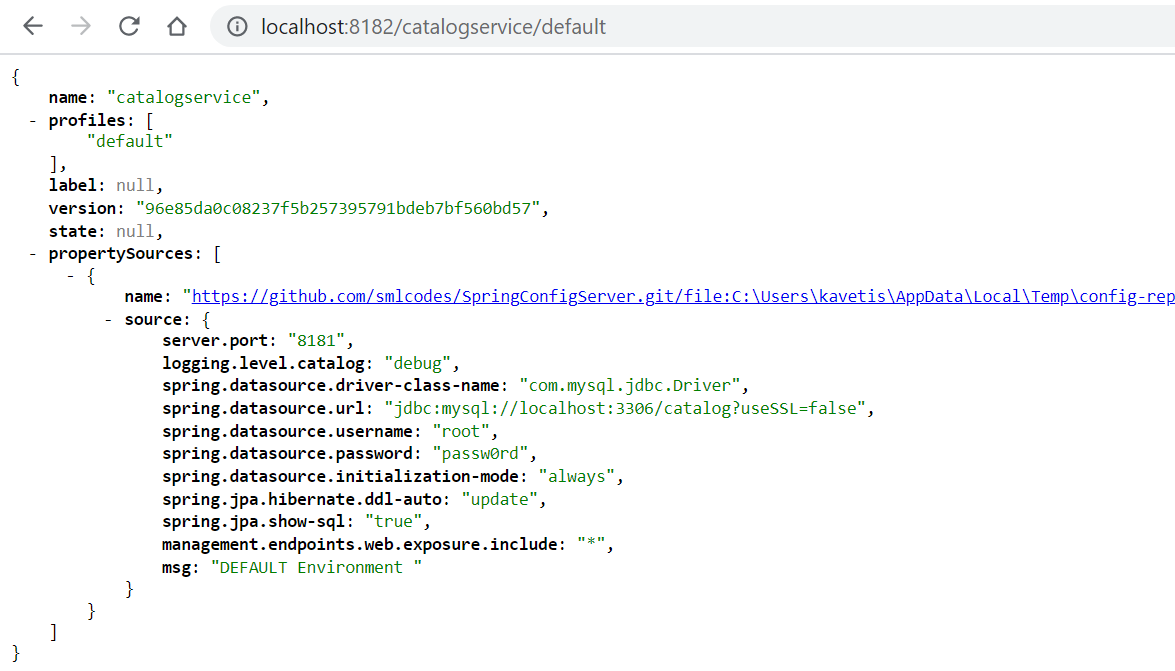
Similary we can enviroment propertils like
Spring Cloud Config Client Example
Let us see how we can create a SpringBoot application and use configuration properties from Config Server instead of putting them inside the application.
1.Update catalog-service with Config Client, Web and Actuator starters.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.Create REST Resource
Add one RestController to view the Server side property values in the response. And add a method to request/response the perticalur value from Repository values.
@RefreshScope
@RestController
class SpringCloudConfigClinet{
@Value("${msg:Config Server is not working. Please check...}")
private String msg;
@GetMapping("/msg")
public String getMsg() {
return this.msg;
}
}
Usually in SpringBoot application, we configure properties in application.properties. But while using Spring Cloud Config Server we use bootstrap.properties or bootstrap.yml file to configure the URL of Config Server.
Configure the following properties in src/main/resources/bootstrap.properties:
server.port=8181
spring.application.name=catalogservice
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8182
management.security.enabled=false
Note that the value of spring.application.name property should match with base filename (catalogservice) in config-repo
Now run the following catalog-service main entry point class. We can access the actuator endpoint http://localhost:8181/env to see all the configuration properties.
You open http://localhost:8181/msg you get property value of msg
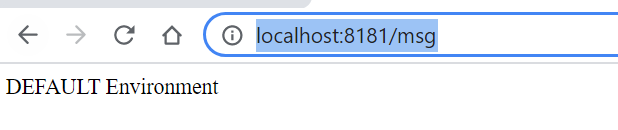
Now if we delete the application.properties file, the application will works normally. Ref. https://www.sivalabs.in/2017/08/spring-cloud-tutorials-introduction-to-spring-cloud-config-server/
Azure Key Vault
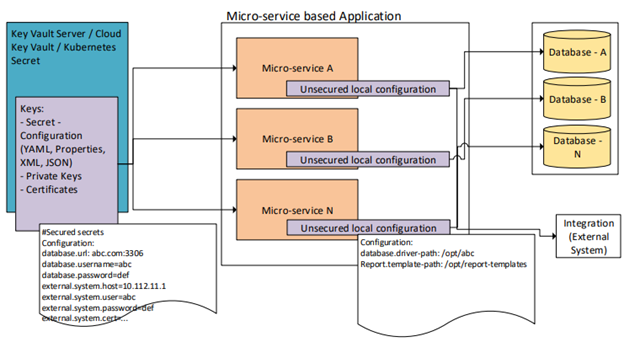
1.Create Azure Key Valut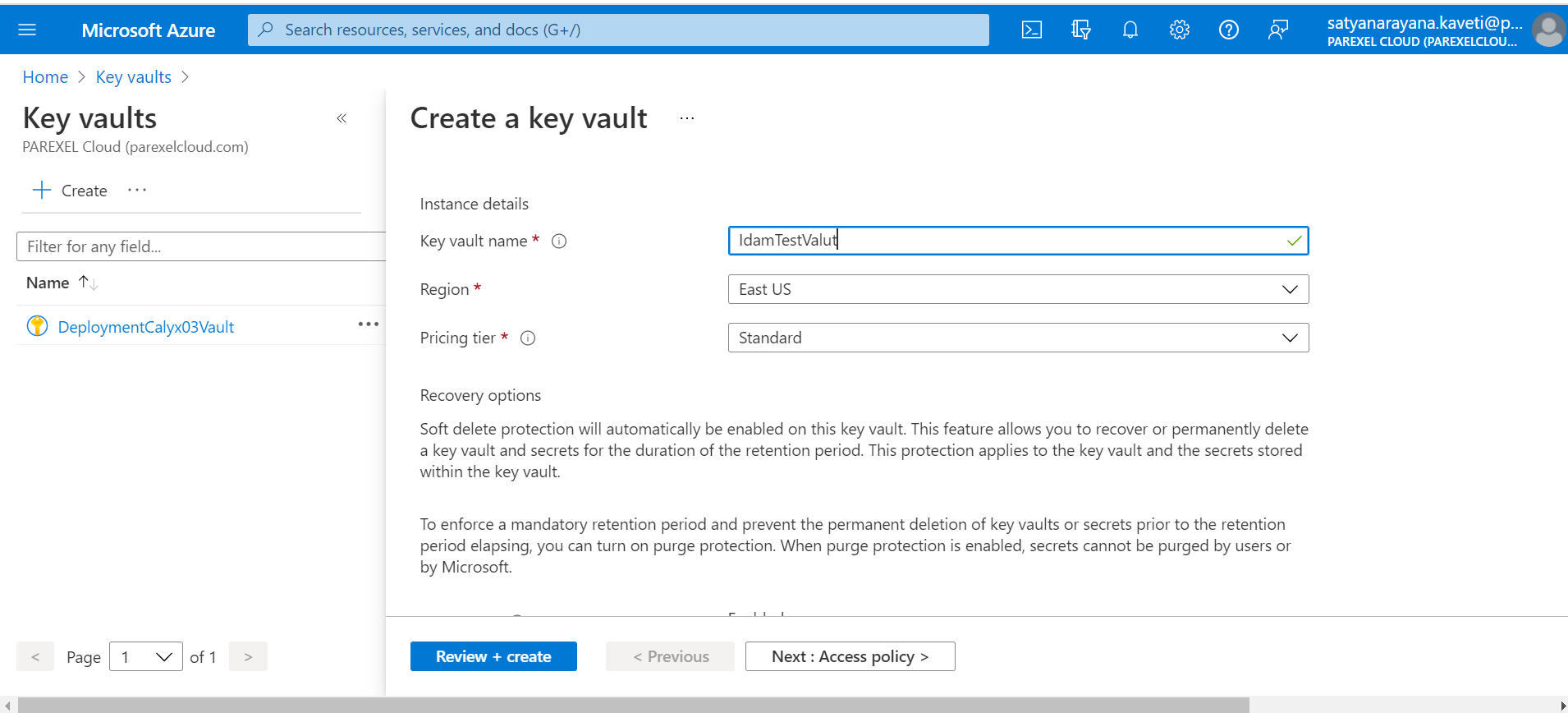
Configure these properties:
azure.keyvault.enabled=true
azure.keyvault.uri=put-your-azure-keyvault-uri-here
azure.keyvault.client-id=put-your-azure-client-id-here
azure.keyvault.client-key=put-your-azure-client-key-here
Add dependency. <version> can be skipped because we already add azure-spring-boot-bom.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.azure.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-spring-boot-starter-keyvault-secrets</artifactId>
</dependency>
Now we can read Azure KeyVault secrets directly as any other Spring boot configuration properties,( as Key Vault will be bound as custom Properties Datasource) Example in TestController.java, where @Value(“${my-very-secret}”) is read from Azure KeyVault.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v1")
public class TestController {
@Value("${my-very-secret}")
private String secretValue;
@Value("${my-not-secret}")
private String nosecretValue;
@GetMapping("/values")
public String[] Values() {
return new String[] { secretValue, nosecretValue};
}
}
Azure KeyValut properties are automatically available, due to Azure Valut Dependency.So we can directly Access