Spring 4 MVC REST Service Example
Spring 4 @RestControllerannotation is introduced. And also we have @RequestBody, @ResponseBody, @ResponseEntityannotations which are used to bind the HTTP request/response body with a domain object in method parameter or return type.
@RequestBody
If a method parameter is annotated with @RequestBody, Spring will bind the incoming HTTP request body to the method parameter. While doing that, Spring will use HTTP Message converters to convert the HTTP request body into class object based on Accept header present in request.
-
The Accept header is used by HTTP clients [browsers] to tell the server what content types they will accept.
-
The server sends back the response, which will include a Content-Type header telling the client what the content type of the returned content actually is. In case of POST or PUT request, browsers do send data in request, so they actually send content-type as well.
@RequestMapping(value="/user/create", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<Student> createUser(@RequestBody User user, UriComponentsBuilder ub){
System.out.println("Creating User "+user.getName());
if(userService.isUserExist(user)){
System.out.println("A User with name "+user.getName()+" already exist");
return new ResponseEntity<Void>(HttpStatus.CONFLICT);
}
userService.saveUser(user);
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setLocation(ub.path("/user/{id}").buildAndExpand(user.getId()).toUri());
See above, Method parameter user is marked with @RequestBody annotation
@ResponseEntity
It represents the entire HTTP response. Here we can specify status code, headers, and body.
@ResponseBody
If a method is annotated with @ResponseBody, Spring will bind the return value to outgoing HTTP response body.
While doing that, Spring will use HTTP Message converters to convert the return value to HTTP response body, based on Content-Type present in request HTTP header
Spring 4 MVC REST Controller Example
The demo REST application will have Student resource. This student resource can be accessed using standard GET, POST, PUT, DELETE http methods. We will create below REST endpoints for this project.
| REST Endpoint | HTTP Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| /students | GET | Returns the list of students |
| /students/{id} | GET | Returns student detail for given student {id} |
| /students | POST | Creates new student from the post data |
| /students/{id} | PUT | Replace the details for given student {id} |
| /students/{id} | DELETE | Delete the student for given student {id} |
1.Set Annotation based Configuration for Spring 4 MVC REST
For this Spring 4 MVC REST tutorial we are going to use Spring’s Java based configuration or annotation based configuration instead of old XML configuration. So now let us add the Java Configuration required to bootstrap Spring 4 MVC REST in our webapp.
Create AppConfig.java file under /src folder. Give appropriate package name to your file. We are using @EnableWebMvc, @ComponentScan and @Configuration annotations. These will bootstrap the spring mvc application and set package to scan controllers and resources.
package smlcodes.config;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "smlcodes")
public class AppConfig {
}
2.Set Servlet 3 Java Configuration
Create AppInitializer class under config package. This class will replace web.xml and it will map the spring’s dispatcher servlet and bootstrap it.
package smlcodes.config;
public class AppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { AppConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
3.Create the Student Model Next let us create Student model class that will have few properties such as firstName, lastName, email etc. This bean will hold student information
package smlcodes.model;
public class Student {
private int sno;
private String name;
private String address;
public Student(int sno, String name, String address) {
super();
this.sno = sno;
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
//Setters & getters
}
4.Create the Dummy Student Data Access Object (DAO)
we will create a dummy data access object that will store student details in a list. This DAO class can be easily replaced with Spring Data DAO or custom DAO.
The StudentDAO contains
methods list(), get(), create(), update() and delete() to perform CRUD operation
on students.
package smlcodes.dao;
@Component
public class StudentDAO {
private static List<Student> students;
//Instance block
{
students = new ArrayList();
students.add(new Student(101, "Satya", "Hyderabad"));
students.add(new Student(201, "Vijay", "Banglore"));
students.add(new Student(301, "Rajesh", "Vijayawada"));
}
public List list() {
return students;
}
public Student get(int sno) {
for (Student c : students) {
if (c.getSno()==sno) {
return c;
}
}
return null;
}
public Student create(Student student) {
student.setSno(new Random().nextInt(1000));
students.add(student);
return student;
}
public int delete(int sno) {
for (Student c : students) {
if (c.getSno()==sno) {
students.remove(c);
return sno;
}
}
return 0;
}
public Student update(int sno, Student student) {
for (Student c : students) {
if (c.getSno()==sno) {
student.setSno(c.getSno());
students.remove(c);
students.add(student);
return student;
}
}
return null;
}
}
5.Create the Student REST Controller
Now let us create StudentRestController class. This class is annotated with @RestControllerannotation.
Also note that we are using new annotations @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping and @DeleteMapping instead of standard @RequestMapping.
These annotations are available since Spring MVC 4.3 and are standard way of defining REST endpoints. They act as wrapper to @RequestMapping. For example @GetMapping is a composed annotation that acts as a shortcut for @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET).
package smlcodes.controller;
@RestController
public class StudentRestController {
@Autowired
private StudentDAO studentDAO;
@GetMapping("/students")
public List getStudents() {
return studentDAO.list();
}
@GetMapping("/students/{sno}")
public ResponseEntity getStudent(@PathVariable("sno") int sno) {
Student student = studentDAO.get(sno);
if (student == null) {
return new ResponseEntity("No Student found for ID " + sno, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return new ResponseEntity(student, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PostMapping(value = "/students")
public ResponseEntity createStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
studentDAO.create(student);
return new ResponseEntity(student, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@DeleteMapping("/students/{sno}")
public ResponseEntity deleteStudent(@PathVariable int sno) {
if (studentDAO.delete(sno) == 0) {
return new ResponseEntity("No Student found for ID " + sno, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return new ResponseEntity(sno, HttpStatus.OK);
}
@PutMapping("/students/{sno}")
public ResponseEntity updateStudent(@PathVariable int sno, @RequestBody Student student) {
student = studentDAO.update(sno, student);
if (null == student) {
return new ResponseEntity("No Student found for ID " + sno, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return new ResponseEntity(student, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
6.Test the Application
To test application, fisrt do mvn clean install
To run application use mvn tomcat7:run
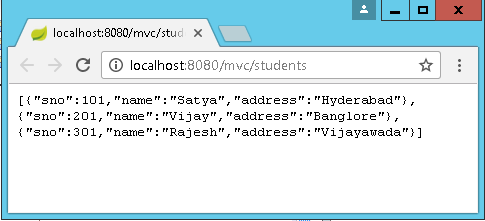
All List : http://localhost:8080/mvc/students
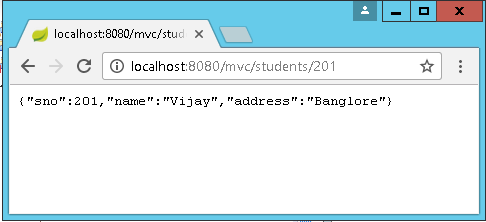
Get one : http://localhost:8080/mvc/students/{id}
POST the student details to http://localhost:8080/mvc/students using POSTMan extension