Spring Batch
Batch processing is a processing mode which involves execution of series of automated complex jobs without user interaction. A batch process handles bulk data and runs for a long time.
Spring Batch applications support −
-
Automatic retry after failure.
-
Tracking status and statistics during the batch execution and after completing the batch processing.
-
To run concurrent jobs.
-
Services such as logging, resource management, skip, and restarting the processing.
Example: Import Users via Excel
Components of Spring Batch
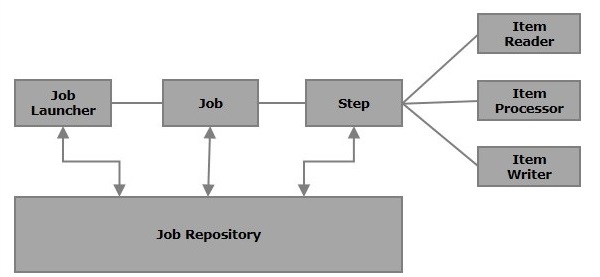
1.Job
In a Spring Batch application, a job is the batch process that is to be executed. It runs from start to finish without interruption. This job is further divided into steps (or a job contains steps).
We will configure a job in Spring Batch using an XML file or a Java class. Following is the XML configuration of a Job in Spring Batch.
<job id = "jobid">
<step id = "step1" next = "step2"/>
<step id = "step2" next = "step3"/>
<step id = "step3"/>
</job>
2.Step
A step is an independent part of a job which contains the necessary
information to define and execute the job (its part).
As specified in the diagram, each step is composed of an ItemReader,
ItemProcessor (optional) and an ItemWriter. A job may contain one or more
steps.
3.Readers, Writers, and Processors
-
Item reader reads data into a Spring Batch application from a particular source.
-
Item writer writes data from the Spring Batch application to a particular destination.
-
Item processor is a class which contains the processing code which processes the data read into the spring batch. If the application reads “n” records, then the code in the processor will be executed on each record.
For example, if we are writing a job with a simple step in it where we read data from MySQL database and process it and write it to a file (flat), then our step uses −
-
A reader which reads from MySQL database.
-
A writer which writes to a flat file.
-
A custom processor which processes the data as per our wish.
<job id = "helloWorldJob">
<step id = "step1">
<tasklet>
<chunk reader = "mysqlReader" writer = "fileWriter"
processor = "CustomitemProcessor" ></chunk>
</tasklet>
</step>
</ job>
4.Job repository
A Job repository in Spring Batch provides Create, Retrieve, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations for the JobLauncher, Job, and Step implementations. We will define a job repository in an XML file as shown below.
<job-repository id = "jobRepository"
data-source = "dataSource"
transaction-manager = "transactionManager"
isolation-level-for-create = "SERIALIZABLE"
table-prefix = "BATCH_"
max-varchar-length = "1000"/>
5.JobLauncher
JobLauncher is an interface which launces the Spring Batch job with the given set of parameters. SampleJoblauncher is the class which implements the JobLauncher interface. Following is the configuration of the JobLauncher.
<bean id = "jobLauncher"
class = "org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher">
<property name = "jobRepository" ref = "jobRepository" />
</bean>
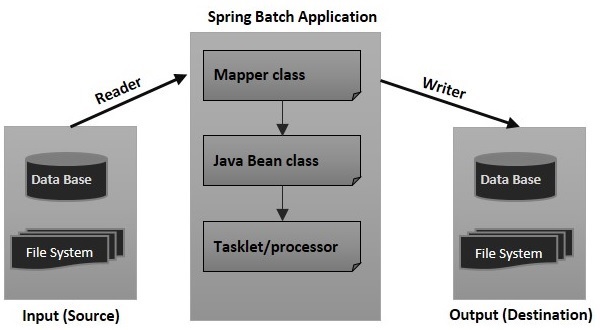
Spring Batch Example – Excel/CSV File To MySQL Database
CSV file data : src/main/resources/cvs/Users.csv
| uid | address | age | name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401 | Mumbai | 35 | Smith |
| 402 | Delhi | 36 | Kivell |
| 403 | Bangalore | 37 | Gill |
| 404 | Hyderabad | 38 | Jardine |
| 405 | Ahmedabad | 39 | Andrews |
| 406 | Chennai | 40 | Gill |
| 407 | Kolkata | 41 | Morgan |
| 408 | Surat | 42 | Andrews |
| 409 | Pune | 43 | Jardine |
Create Model class to Hold CSV Data
public class User {
private Integer uid;
private String address;
private Integer age;
private String name;
}
Job Cofiguration XML files
database.xml: /src/main/resources/spring/batch/config/database.xml
-
Contains
dataSourcebean contains DB connection details. -
transactionManager– Transaction managenet -
create job-meta tables configuration.
<beans>
<!-- connect to database -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/microservices" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.batch.support.transaction.ResourcelessTransactionManager" />
<!-- create job-meta tables automatically -->
<jdbc:initialize-database data-source="dataSource">
<jdbc:script location="org/springframework/batch/core/schema-drop-mysql.sql" />
<jdbc:script location="org/springframework/batch/core/schema-mysql.sql" />
</jdbc:initialize-database>
</beans>
Context.xml
It Spring Batch Core Settings. It Defines jobRepository and jobLauncher.
<beans>
<!-- stored job-meta in database -->
<bean id="jobRepository"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.JobRepositoryFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
<property name="databaseType" value="mysql" />
</bean>
<!-- stored job-meta in memory -->
<!--
<bean id="jobRepository"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.repository.support.MapJobRepositoryFactoryBean">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
</bean>
-->
<bean id="jobLauncher"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.launch.support.SimpleJobLauncher">
<property name="jobRepository" ref="jobRepository" />
</bean>
</beans>
jobConfig.xml
This is the main xml file to configure the Spring batch job. This jobConfig.xml file define a job to read a user.csv file, match it to User plain pojo and write the data into MySQL database.
<beans>
<bean id="userOb" class="com.spring.model.User" scope="prototype" />
<batch:job id="CsvToMySQL-job">
<batch:step id="step1">
<batch:tasklet>
<batch:chunk reader="cvsFileItemReader" writer="mysqlItemWriter"
commit-interval="2">
</batch:chunk>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
<bean id="cvsFileItemReader" class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.FlatFileItemReader">
<!-- Read a csv file -->
<property name="resource" value="classpath:cvs/Users.csv" />
<property name="lineMapper">
<bean class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.DefaultLineMapper">
<!-- split it -->
<property name="lineTokenizer">
<bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.transform.DelimitedLineTokenizer">
<property name="names" value="uid,address,age,name" />
</bean>
</property>
<property name="fieldSetMapper">
<!-- map to an object -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.file.mapping.BeanWrapperFieldSetMapper">
<property name="prototypeBeanName" value="userOb" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="mysqlItemWriter"
class="org.springframework.batch.item.database.JdbcBatchItemWriter">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="sql">
<value>
<![CDATA[
insert into batch_user(uid,address,age,name) values (:uid, :address, :age, :name)
]]>
</value>
</property>
<!-- It will take care matching between object property and sql name parameter -->
<property name="itemSqlParameterSourceProvider">
<bean
class="org.springframework.batch.item.database.BeanPropertyItemSqlParameterSourceProvider" />
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Create a main class , which calls CsvToMySQL-job via jobLauncher
public class CSVToMySQLExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] springConfig =
{ "spring/batch/config/database.xml",
"spring/batch/config/context.xml",
"spring/batch/jobs/jobConfig.xml"
};
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(springConfig);
JobLauncher jobLauncher = (JobLauncher) context.getBean("jobLauncher");
Job job = (Job) context.getBean("CsvToMySQL-job");
try {
JobExecution execution = jobLauncher.run(job, new JobParameters());
System.out.println("Exit Status : " + execution.getStatus());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Done");
}
}
Does Spring Batch require a database?
Spring Batch by default uses a database to store metadata on the configured batch jobs. In this example, we will run Spring Batch without a database. Instead, an in-memory Map based repository is used
How does Spring Batch handle transactions?
Spring Batch handles transactions at the step level. This means that Spring Batch will never use only one transaction for a whole job (unless the job has a single step). Remember that you’re likely to implement a Spring Batch job in one of two ways: using a tasklet or using a chunk-oriented step.
<batch:job id="CsvToMySQL-job">
<batch:step id="step1">
<batch:tasklet>
<batch:chunk reader="cvsFileItemReader" writer="mysqlItemWriter"
commit-interval="2">
</batch:chunk>
</batch:tasklet>
</batch:step>
</batch:job>
How One can keep track of failed records in Spring Batch?
Method1 : We can keep track of records which was failed during the reading step of a job. We need to use SkipListener for this.
public class SkipListener implements org.springframework.batch.core.SkipListener {
public void onSkipInProcess(Object arg0, Throwable arg1) {
}
public void onSkipInRead(Throwable arg0) {
System.out.println(arg0);
}
public void onSkipInWrite(Object arg0, Throwable arg1) {
}
}
I want to store the line skipped by reader in another csv file.
SpringBatch provides methods on the StepExecution objects :
-
Read : stepExecution.getReadCount()
-
Read Failed : stepExecution.getReadSkipCount()
-
Processed : stepExecution.getProcessCount()
-
Processed Failed : stepExecution.getProcessSkipCount()
-
Written : stepExecution.getWriteCount()
-
Written Failed : stepExecution.getWriteSkipCount()
Method 2 : Retry Sample
The purpose of this sample is to show how to use the automatic retry capabilities of Spring Batch.
The retry is configured in the step through the SkipLimitStepFactoryBean:
<bean id="step1" parent="simpleStep"
class="org.springframework.batch.core.step.item.FaultTolerantStepFactoryBean">
...
<property name="retryLimit" value="3" />
<property name="retryableExceptionClasses" value="java.lang.Exception" />
</bean>
Failed items will cause a rollback for all Exception types, up to a limit of 3 attempts. On the 4th attempt, the failed item would be skipped, and there would be a callback to a ItemSkipListener if one was provided (via the “listeners” property of the step factory bean).