Spring Bean Life Cycle
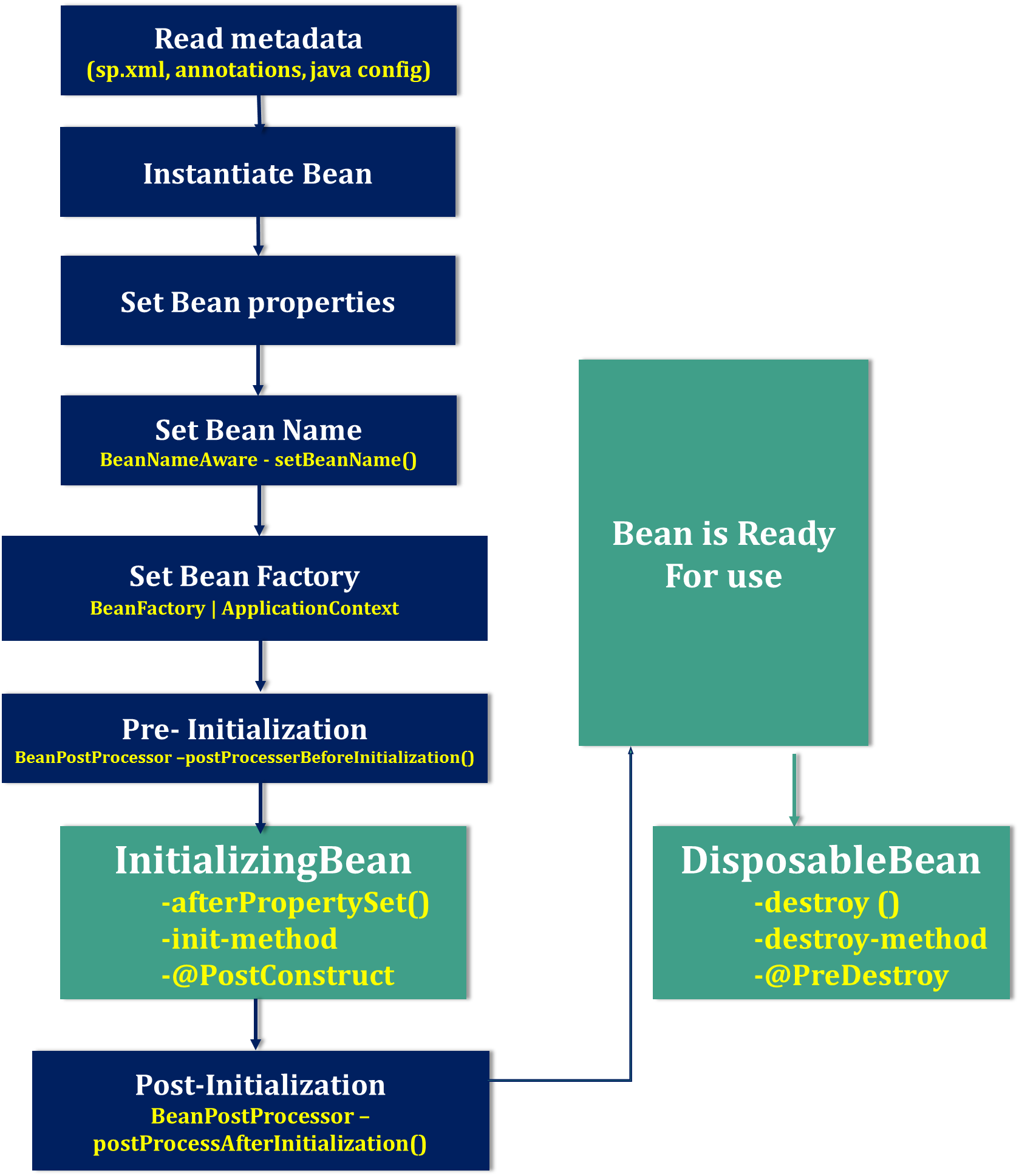
1.Read metadata
Spring container reads metadata from SpringConfiguration.xml (or annotations/javaConfig) file and looks for the
2.Instantiate
-
Spring instantiate the bean by calling
no argument default constructorof that class. -
If there is only parameterized constructor in the class, then bean must be defined in spring.xml file with constructor injection otherwise it will throw BeanCreationException.
3.Inject Bean properties
Once instantiate completed, Sprin injects the values and references into the bean’s properties.
4.Set Bean Name
If the bean implements BeanNameAware interface, Spring executes setBeanName() method by passing Bean Id(bean id=”ob”). By this method Spring container sets the bean name.
5.Set Bean Factory
-
If the bean implements BeanFactoryAware interface, Spring executes setBeanFactory() method by passing current BeanFactory reference which is used in our Appplciation.
-
If the bean implements ApplicationContextAware interface, Spring executes setApplicationContext() method by passing current ApplicationContext reference which is used in our Appplciation.
6.Pre- Initialization
Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance before any bean initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean’s afterPropertiesSet or a custom init-method) by using postProcesserBeforeInitialization() method. . The bean will already be populated with property values. Note it says that “The bean will already be populated with property values”
7. Initialize beans
-
By Class :If the bean implements IntializingBean,its afterPropertySet() method is called. -
By Xml :If the bean has custom init-method, then specified initialization method is called. -
By Annotations :If we are using annotations, use @PostConstruct on the Top of the method
8.Post-Initialization
Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance after any bean initialization callbacks (after InitializingBean’s, afterPropertiesSet, custom init-method) by postProcessAfterInitialization().
9.Ready to Use
Now the bean is ready to be used by the application.
10. DisposableBean
-
By Class :If the bean implements DisposableBean, the Spring IoC container will call the destroy() method . -
By Xml :If a custom destroy-method is defined, the container calls the specified method. -
By Annotations :If we are using annotations, use @PreDestroy on the Top of the method
Spring Bean Lifecycle Example
package lifycycle;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class Student implements BeanNameAware, BeanPostProcessor,
InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
public void setBeanName(String beanname) {
System.out.println("setBeanName : " + beanname);
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor : postProcessBeforeInitialization ");
return null;
}
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student Contrscutor...");
}
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1)
throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor : postProcessAfterInitialization ");
return null;
}
private int sno;
private String name;
private Address address;
public int getSno() {
return sno;
}
public void setSno(int sno) {
System.out.println("\t SNO Property Set");
this.sno = sno;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("\t NAME Property Set");
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
System.out.println("\t ADDRESS OBJECT Property Set");
this.address = address;
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("InitializingBean : afterPropertiesSet");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("DisposableBean : destroy");
}
}
package lifycycle;
public class Address {
private String city;
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
System.out.println("\t \t CITY Property Set");
this.city = city;
}
}
SpringConfig.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<bean id="st" class="lifycycle.Student">
<property name="sno" value="101" />
<property name="name" value="Satya" />
<property name="address">
<ref bean="addr" />
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="addr" class="lifycycle.Address">
<property name="city" value="HYDERABAD" />
</bean>
</beans>
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SpringConfig.xml");
Student s = (Student) context.getBean("st");
System.out.println(s.getSno());
System.out.println(s.getName());
System.out.println(s.getAddress().getCity());
}
}
Student Contrscutor...
CITY Property Set
Jan 03, 2019 12:43:46 PM org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext$BeanPostProcessorChecker postProcessAfterInitialization
INFO: Bean 'addr' of type [class lifycycle.Address] is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors (for example: not eligible for auto-proxying)
SNO Property Set
NAME Property Set
ADDRESS OBJECT Property Set
setBeanName : st
InitializingBean : afterPropertiesSet
Jan 03, 2019 12:43:46 PM org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory preInstantiateSingletons
INFO: Pre-instantiating singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@2a098129: defining beans [st,addr]; root of factory hierarchy
101
Satya
HYDERABAD