Hibernate- Inheritance Mapping
In hibernate inheritance, if we have base and derived classes, now if we save derived(sub) class object, base class object will also be stored into the database.
Hibernate supports 3 types of Inheritance Mappings:
-
Table per class hierarchy
-
Table per sub-class hierarchy
-
Table per concrete class hierarchy
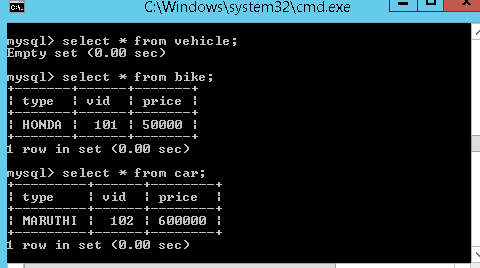
We will understand one by one with examples. Below tables are used in upcoming examples.
CREATE TABLE `vehicle` (
`vid` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`price` DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
PRIMARY KEY (`vid`));
CREATE TABLE `bike` (
`type` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE `car` (
`type` VARCHAR(50) NULL DEFAULT NULL
);
Following files are common to all examples, only we need to change mapping xml & Application class
Vehicle.java
package inheritance;
public class Vehicle {
private int vid;
private double price;
public int getVid() {
return vid;
}
public void setVid(int vid) {
this.vid = vid;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
Bike.java
package inheritance;
public class Bike extends Vehicle {
private String biketype;
public String getBiketype() {
return biketype;
}
public void setBiketype(String biketype) {
this.biketype = biketype;
}
}
Car.java
package inheritance;
public class Car extends Vehicle {
private String cartype;
public String getCartype() {
return cartype;
}
public void setCartype(String cartype) {
this.cartype = cartype;
}
}
hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration SYSTEM
"hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smlcodes</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- <mapping resource="EmployeeBo.hbm.xml" /> -->
<mapping resource="Vehicle.hbm.xml" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
InheritanceCommonApp.java
package inheritance;
import org.hibernate.*;
import org.hibernate.cfg.*;
public class TablePerClassExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration cfg = new Configuration();
cfg.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");
SessionFactory factory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
Session session = factory.openSession();
Bike bike = new Bike();
bike.setVid(101);
bike.setBiketype("HONDA");
bike.setPrice(50000);
Car car = new Car();
car.setVid(102);
car.setCartype("MARUTHI");
car.setPrice(600000);
Transaction tx = session.beginTransaction();
session.save(bike);
session.save(car);
tx.commit();
session.close();
factory.close();
}
}
1. Table per class hierarchy
If we save the derived class object in the database, then automatically base class data will also be saved into the database in base class Table
For example, if we save the derived class object like Car or Bike then automatically Vehicle class object will also be saved into the database, and in the database all the data will be stored into a single table only, which is base class table.
For this type of hierarchy, we must use one extra discriminator column in the database, to identify which derived class object we have been saved in the table along with the base class object, if we are not using this column hibernate will throws the exception.
Vehicle.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="inheritance.Vehicle" table="vehicle">
<id name="vid" column="vid"></id>
<discriminator column="DISC" type="string"/>
<property name="price" column="price"></property>
<subclass name="inheritance.Bike" discriminator-value="BIKE_DISC">
<property name="biketype" column="biketype"></property>
</subclass>
<subclass name="inheritance.Car" discriminator-value="CAR_DISC">
<property name="cartype" column="cartype"></property>
</subclass>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
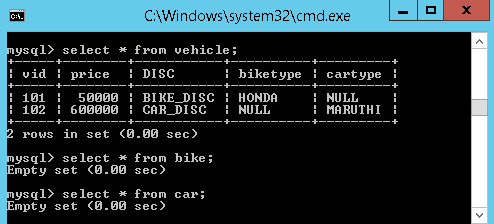
We added one new line discriminator, after the id element just to identify which derived class object we have been saved in the table. Here everything has been saved in a single table(vehicle)
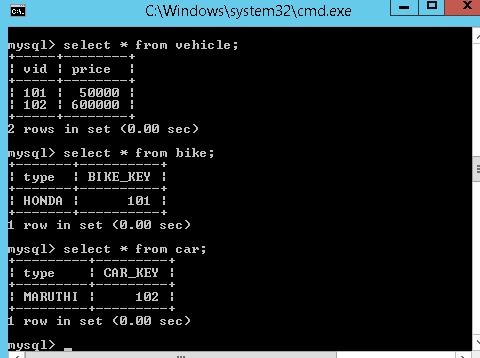
2. Table per sub-class hierarchy
In this type of hierarchy, if we save the Base class object, first hibernate will saves the Base class object into the base class table, then it will save the subclass object data into subclass table. Here first it will save data into Base class table.
In below Example, if we save the Car/Bike class object, first hibernate will saves the data related to Vehicle class object into the vehicle table and then Car/Bike object data in Car/Bike related tables.so we can say, No. of classes equals to No. of Tables
No. of classes = No. of Tables
Here <joined-subclass> element of <class> is used to map the child
class with parent class using the primary key and foreign key relation
Vehicle.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="inheritance.Vehicle" table="vehicle">
<id name="vid" column="vid"></id>
<property name="price" column="price"></property>
<joined-subclass name="inheritance.Bike" table="bike">
<key column="BIKE_KEY" />
<property name="biketype" column="type"></property>
</joined-subclass>
<joined-subclass name="inheritance.Car" table="car">
<key column="CAR_KEY" />
<property name="cartype" column="type"></property>
</joined-subclass>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
-
Once we save the derived class object, then hibernate will first save the base class object then derived class object.
-
At the time of saving the derived class object, hibernate will copy the primary key value of the base class into the corresponding derived class, by using
<key>tag. From the above output-
102 copied into CAR_KEY column of car table
-
101 copied into BIKE_KEY column of the bike table
-
3. Table per concrete class hierarchy
-
Once we save the derived class object, then derived class data and base class data will be saved in the derived class related table in the database
-
for this type we need the tables for derived classes, but not for the base class
-
we need to use one new element
<union-subclass>under<class>
Vehicle.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="inheritance.Vehicle" table="vehicle">
<id name="vid" column="vid"></id>
<property name="price" column="price"></property>
<union-subclass name="inheritance.Bike" table="bike">
<property name="biketype" column="type"></property>
</union-subclass>
<union-subclass name="inheritance.Car" table="car">
<property name="cartype" column="type"></property>
</union-subclass>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>