18.Hibernate Interview Questions
Updated Hibernate Interview Questions
1.What are advantages of Hibernate?
-
Lazy Loading
-
Caching
-
You do not need to maintain JDBC code , Hibernate takes care of it.
-
You need to write less code
-
It provides high level object oriented API
2 What is caching?
Anything you can do to minimize traffic between a database and an application server is probably a good thing. In theory, an application ought to be able to maintain a cache containing data already loaded from the database, and only hit the database when information has to be updated. When the database is hit, the changes may invalidate the cache
3 What are some core interfaces of hibernate?
-
Configuration
-
SessionFactory
-
Session
-
Transaction
-
Query and Criteria interface
4 Difference between get() vs load() method in Hibernate? (detailed answer)
The key difference between get() and load() method is that
-
load() will throw an exception if an object with id passed to them is not found
-
get() will return **null.**
Another important difference is that load can return proxy without hitting the database unless required (when you access any attribute other than id) but get() always go to the database, so sometimes using load() can be faster than the get() method. It makes sense to use the load() method if you know the object exists but get() method if you are not sure about object’s existence.
| Parameter | get | load |
|---|---|---|
| Database retrieval | It always hits the database | It does not hit database |
| If null | If it does not get the object with id, it returns null | If it does get the object with id, it throws ObjectNotFoundException |
| Proxy | It returns real object | It returns proxy object |
| Use | If you are not sure if object with id exists or not, you can use get | If you are sure about existence of object, you can use load |
5 What is the difference between save() and persist() method in Hibernate?
-
Serializable Object save() returns a Serializable object
-
void persist() method is void, so it doesn’t return anything.
6 What is the difference between and merge and update?
Use update() if you are sure that the session does not contain an already persistent instance with the same identifier, and merge() if you want to merge your modifications at any time without consideration of the state of the session.
7 Different between cascade and inverse
Many Hibernate developers are confuse about the cascade option and inverse keyword. In some ways..they really look quite similar at the beginning, both are related with relationship.
However, there is no relationship between cascade and inverse, both are totally different notions.
1.inverse
This is used to decide which side is the relationship owner to manage the relationship (insert or update of the foreign key column).
Example
In this example, the relationship owner is belong to stockDailyRecords (inverse=true).
<!-- Stock.hbm.xml -->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.mkyong.common.Stock" table="stock" ...>
...
<set name="stockDailyRecords" table="stock_daily_record" inverse="true">
<key>
<column name="STOCK_ID" not-null="true" />
</key>
<one-to-many class="com.mkyong.common.StockDailyRecord" />
</set>
...
When you save or update the stock object
session.save(stock);
session.update(stock);
Hibernate will only insert or update the STOCK table, no update on the foreign key column. More detail example here…
2.cascade
In cascade, after one operation (save, update and delete) is done, it decide whether it need to call other operations (save, update and delete) on another entities which has relationship with each other.
Example
In this example, the cascade=”save-update” is declare on stockDailyRecords.
<!-- Stock.hbm.xml -->
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.mkyong.common.Stock" table="stock" ...>
...
<set name="stockDailyRecords" table="stock_daily_record"
cascade="save-update" inverse="true">
<key>
<column name="STOCK_ID" not-null="true" />
</key>
<one-to-many class="com.mkyong.common.StockDailyRecord" />
</set>
...
When you save or update the stock object
session.save(stock);
session.update(stock);
It will inserted or updated the record into STOCK table and call another insert or update statement (cascade=”save-update”) on StockDailyRecord. More detail example here…
Conclusion
In short, the -inverse” is decide which side will update the foreign key, while -cascade” is decide what’s the follow by operation should execute. Both are look quite similar in relationship, but it’s totally two different things. Hibernate developers are worth to spend time to research on it, because misunderstand the concept or misuse it will bring serious performance or data integrity issue in your application.
8 Does SessionFactory is thread-safe in Hibernate? (detailed answer)
SessionFactory is both Immutable and thread-safe and it has just one single
instance in Hibernate application. It is used to create Session object and it
also provide caching by storing SQL queries stored by multiple session. The
second level cache is maintained at SessionFactory level.
9 Does Hibernate Session interface is thread-safe in Java? (detailed answer)
No, Session object is not thread-safe in Hibernate and intended to be used
with-in single thread in the application.
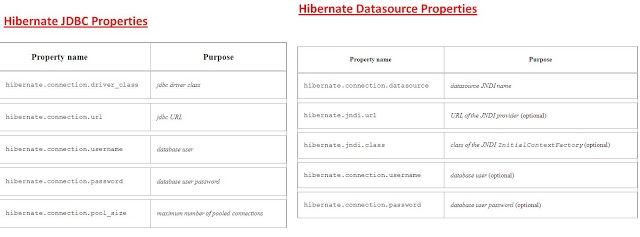
What is difference between getCurrentSession() and openSession() in Hibernate?
openSession() When you call SessionFactory.openSession, it always create new Session object afresh and give it to you. As session objects are not thread safe, you need to create one session object per request in multithreaded environment and one session per request in web applications too.
getCurrentSession() When you call SessionFactory. getCurrentSession , it creates a new Session if not exists , else use same session which is in current hibernate context. It automatically flush and close session when transaction ends, so you do not need to do externally.If you are using hibernate in single threaded environment , you can use getCurrentSession, as it is faster in performance as compare to creating new session each time.
You need to add following property to hibernate.cfg.xml to use getCurrentSession method
<session-factory>
<!-- Put other elements here -->
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class"></property>
</session-factory>
If you do not configure above property, you will get error as below.
Exception in thread "main" org.hibernate.HibernateException: No
CurrentSessionContext configured!
Can you declare Entity(Bean) class as final in hibernate?
Yes, you can declare entity class as final but it is not considered as a good practice because hibernate uses proxy pattern for lazy initialization, If you declare it as final then hibernate won’t be able to create sub class and won’t be able to use proxy pattern, so it will limit performance and improvement options.
Does entity class (Bean) in hibernate require no arg constructor?
Yes, Entity class in hibernate requires no arg constructor because Hibernate use reflection to create instance of entity class and it mandates no arg constructor in Entity class
How do you log SQL queries issued by the Hibernate framework in Java application?
You can procedure the show_sql property to log SQL queries delivered by the Hibernate framework
What is named SQL query in Hibernate?
Named queries are SQL queries which are defined in mapping document
using **
you can define named query in hibernate either by using annotations or XML mapping file, as I said above. @NameQuery is used to define single named query and @NameQueries is used to define multiple named query in hibernate.
@NamedQueries({
@NamedQuery(
name = “findStockByStockCode”,
query = “from Stock s where s.stockCode = :stockCode”
)
})
Query query = session.getNamedQuery(“findStockByStockCode”)
.setString(“stockCode”, “7277”);
Explain Criteria API
Criteria is a simplified API for retrieving entities by composing Criterion objects. This is a very convenient approach for functionality like -search” screens where there is a variable number of conditions to be placed upon the result set.
Example:
List employees = session.createCriteria(Employee.class)
.add(Restrictions.like(-name”, -a%”) )
.add(Restrictions.like(-address”, -Boston”))
.addOrder(Order.asc(-name”) )
.list();
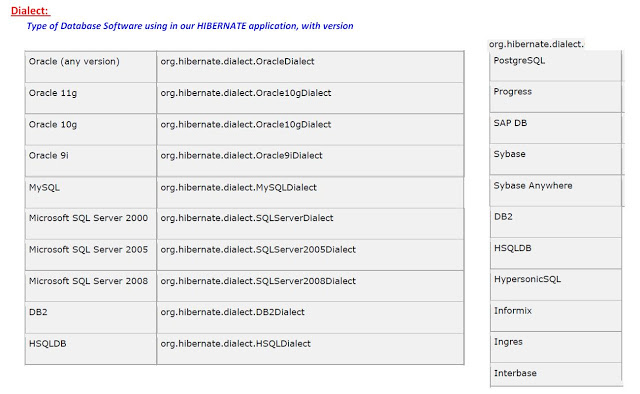
How do you switch between relational databases without code changes?
Using Hibernate SQL Dialects, we can switch databases. Hibernate will generate appropriate hql queries based on the dialect defined.
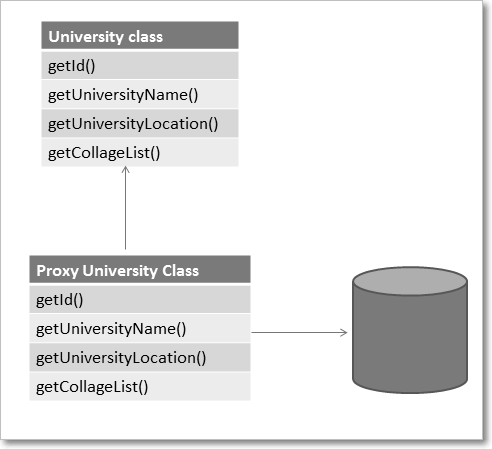
What is Hibernate proxy?
The proxy attribute enables lazy initialization of persistent instances of the class. Hibernate will initially return CGLIB proxies which implement the named interface. The actual persistent object will be loaded when a method of the proxy is invoked.
What is automatic dirty checking?
Automatic dirty checking is a feature that saves us the effort of explicitly asking Hibernate to update the database when we modify the state of an object inside a transaction.
If Dirty-checking is enabled, if we forget to call save() before the commit, dirty-checking automatically saves the data into the database.
Consider the below code which loads a simple Entity from the database and updates it.
public static void testUpdate() {
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = session.beginTransaction();
Entity entity = (Entity) session.load(Entity.class, 1);
entity.setData(“Updating the data”);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
Although we haven’t made any session.update(entity) call, the logs indicate that the database record was updated successful
What is query cache in Hibernate?
.Query cache can be used along with second level cache for improved performance. QueryCache actually stores the result of SQL query for future calls. Hibernate support various open source caching solution to implement Query cache e.g. EhCache
What are two types of Collections in hibernate?
-
Sorted Collection
-
Ordered Collection
| Parameter | Sorted Collection | Ordered Collection |
|---|---|---|
| Sorting | Sorted collection uses java’s sorting API to sort the collection. | Ordered Collections uses order by clause while retrieval of objects |
| Default | It is enabled by default | It is not enabled by default, you need to enable it explicitly |
What is lazy loading in hibernate?
Sometimes you have two entities and there’s a relationship between them. For example, you might have an entity called University and another entity called Student
public class University {
private String id;
private String name;
private String address;
private List
// setters and getters
}
Now when you load a University from the database, JPA loads its id, name, and address fields for you. But you have two options for students: to load it together with the rest of the fields (i.e. eagerly) or to load it on-demand (i.e. lazily) when you call the university’s getStudents() method.
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL, fetch=FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinColumn(name=”countryId”)
private List
FetchType.LAZY: It fetches the child entities lazily, that is, at the time of fetching parent entity it just fetches proxy (created by cglib or any other utility) of the child entities and when you access any property of child entity then it is actually fetched by hibernate.
FetchType.EAGER: it fetches the child entities along with parent.
Lazy initialization improves performance by avoiding unnecessary computation and reduce memory requirements.
Eager initialization takes more memory consumption and processing speed is slow.
lazy=”true/false in xml