Hibernate Architecture
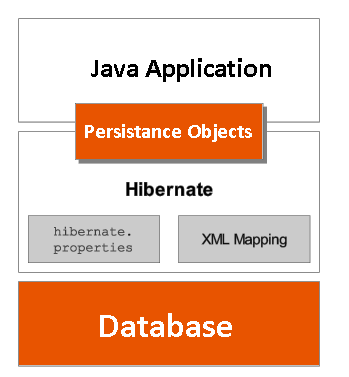
The diagram below provides a high-level view of the Hibernate architecture:
Following is a detailed view of the Hibernate Application Architecture
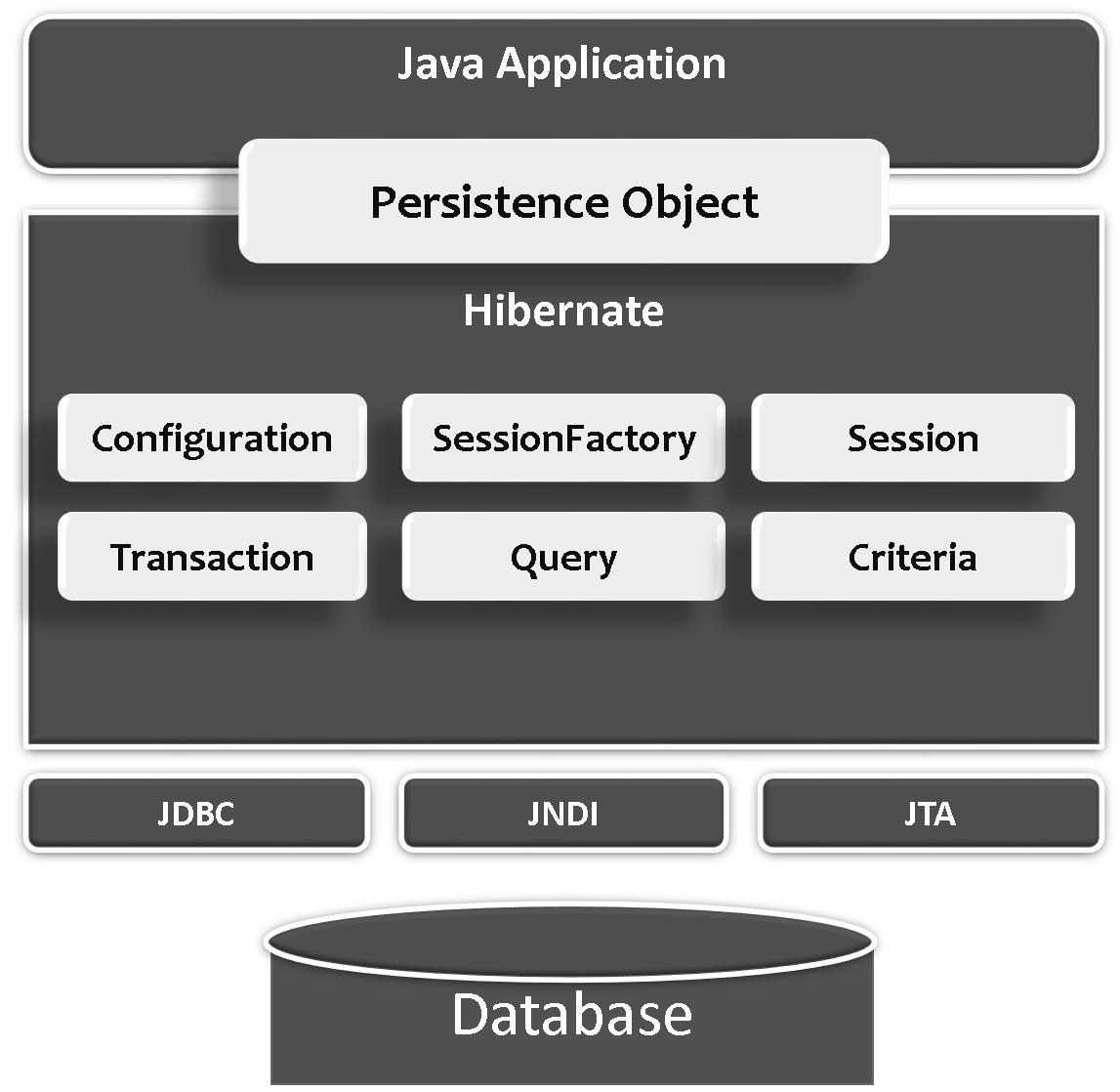
Hibernate uses various existing Java APIs, like JDBC, Java Transaction API(JTA), and Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) along with its own API objects like SessionFactory, Session, Transaction etc.,
1. Configuration
It represents a configuration or properties file required by the Hibernate. Configuration is the file loaded into hibernate application when working with hibernate.
Configuration file contains 3 types of information.
-
Connection Properties
-
Hibernate Properties
-
Mapping file name(s)
<? xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<! DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<! -- Connection properties -->
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<property name="connection.pool_size">1</property>
<! -- Hibernate Properties -->
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">validate</property>
<! -- Mapping file name(s)-->
<mapping resource="res/employee.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
How do you switch between relational databases without code changes?
Using Hibernate SQL Dialects, we can switch databases. Hibernate will generate
appropriate hql queries based on the dialect defined.
Hibernate dialect class vs Driver
Driver: A database driver is a program for which implements a protocol
(ODBC, JDBC) for connecting to a database. It is an Adaptor which connects a
generic interface to a specific vendor’s implementation, just like printer
drivers etc.
-Driver is like English”
Dialect : A database dialect is a configuration setting for platform
independent software (JPA, Hibernate, etc) which allows such software to
translate its generic SQL statements into vendor specific DDL, DML.
-Dialect is the different pronunciations of English”
We all know there are different versions of Oracle… Oracle 9i, Oracle8, Oracle 10g.The driver we would use would be a common for all of these. But the dialect we use is specific to each one of them, which helps Hibernate in generating optimized queries to those specific versions of database and also this is not mandatory to be given in cfg.xml.
This is the SQL dialect (database type) for the database being used.
For connecting any hibernate application with the database, you must specify the SQL dialects. There are many Dialects classes defined for RDBMS in the org.hibernate.dialect package. They are as follows:
| RDBMS | Dialect |
|---|---|
| Oracle (any version) | org.hibernate.dialect.OracleDialect |
| Oracle9i | org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle9iDialect |
| Oracle10g | org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect |
| MySQL | org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect |
| MySQL with InnoDB | org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLInnoDBDialect |
| MySQL with MyISAM | org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLMyISAMDialect |
| DB2 | org.hibernate.dialect.DB2Dialect |
| DB2 AS/400 | org.hibernate.dialect.DB2400Dialect |
| DB2 OS390 | org.hibernate.dialect.DB2390Dialect |
| Microsoft SQL Server | org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServerDialect |
| SAP DB | org.hibernate.dialect.SAPDBDialect |
| Informix | org.hibernate.dialect.InformixDialect |
2. SessionFactory Object
The org.hibernate.SessionFactory interface provides factory method to get the object of Session
It holds second level cache (optional) of data like Dialect, username and password. All these data are fixed for whole application, so it is immutable. And if many threads access at same time there is no change in data, so it is thread safe.
3. Session Object
It Opens a Session between Database and our Application. It holds a first-level cache (mandatory) of data. The org.hibernate.Session interface provides methods to insert, update and delete the object
Session is a light weight and a non-threadsafe object (No, you cannot share it
between threads) that represents a single unit-of-work with the database
4. Transaction Object
The org.hibernate.Transaction interface provides methods for transaction management.
5. Query Object
Query objects use SQL or Hibernate Query Language (HQL) string to retrieve data from the database and create objects.
6. Criteria Object
Criteria object are used to create and execute object oriented criteria queries to retrieve objects.