Docket – Container
Docker Containers are the running instances of Docker Images. Whenever you run an image it will create the container.
In one line, Docker images are Static OS templates & Docker Containers are runtime instances of those images.
Docker Engine
Docker Engine is a client-server application with these major components:
-
A server which is a type of long-running program called a daemon process (the dockerd command).
-
A REST API which specifies interfaces that programs can use to talk to the daemon and instruct it what to do.
-
A command line interface (CLI) client (the docker command).
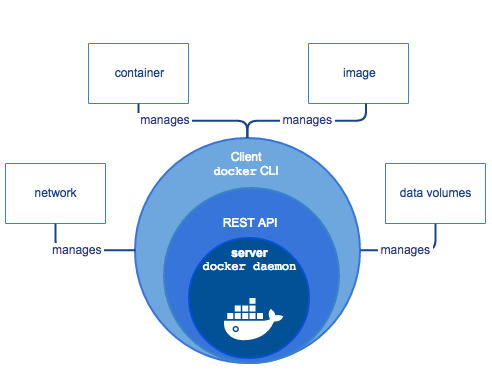
The CLI uses the Docker REST API to control or interact with the Docker daemon through scripting or direct CLI commands. Many other Docker applications use the underlying API and CLI.
The daemon creates and manages Docker objects, such as images, containers, networks, and volumes.
Docker Architecture
Docker uses a client-server architecture. The Docker client talks to the Docker daemon(Docker Host, where actually docker containers run), which does the heavy lifting of building, running, and distributing your Docker containers.
The Docker client and daemon can run on the same system(we are doing same), or you can connect a Docker client to a remote Docker daemon.
The Docker client and daemon communicate using a REST API, over UNIX sockets or a network interface.
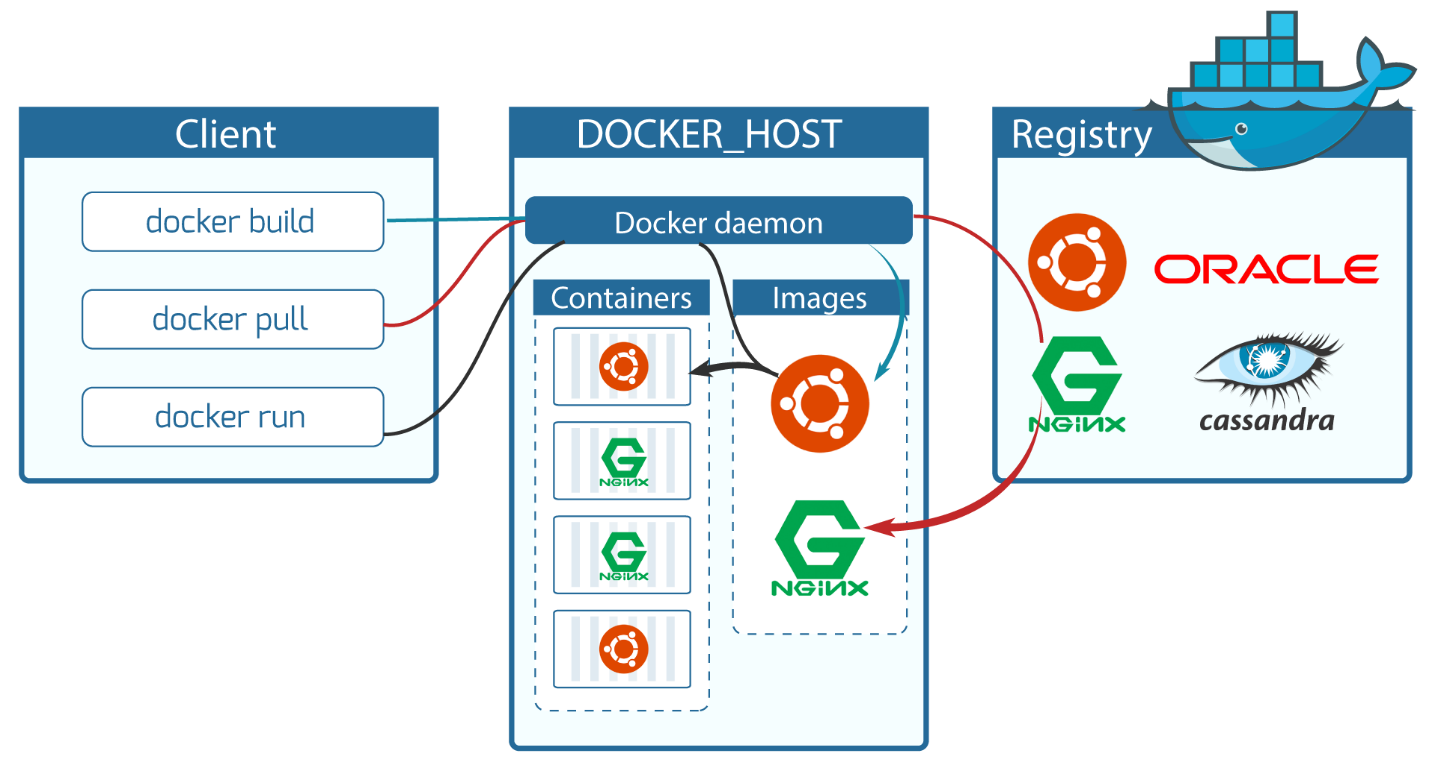
The Docker daemon
The Docker daemon (dockerd) listens for Docker API requests and manages Docker objects such as images, containers, networks, and volumes. A daemon can also communicate with other daemons to manage Docker services.
The Docker client
The Docker client (docker) is the primary way that many Docker users interact with Docker. When you use commands such as docker run, the client sends these commands to dockerd, which carries them out. The docker command uses the Docker API. The Docker client can communicate with more than one daemon.
Docker registries
A Docker registry stores Docker images. Docker Hub is a public registry that anyone can use, and Docker is configured to look for images on Docker Hub by default. You can even run your own private registry. If you use Docker Datacenter (DDC), it includes Docker Trusted Registry (DTR).
When you use the docker pull or docker run commands, the required images are pulled from your configured registry. When you use the docker push command, your image is pushed to your configured registry
Commands
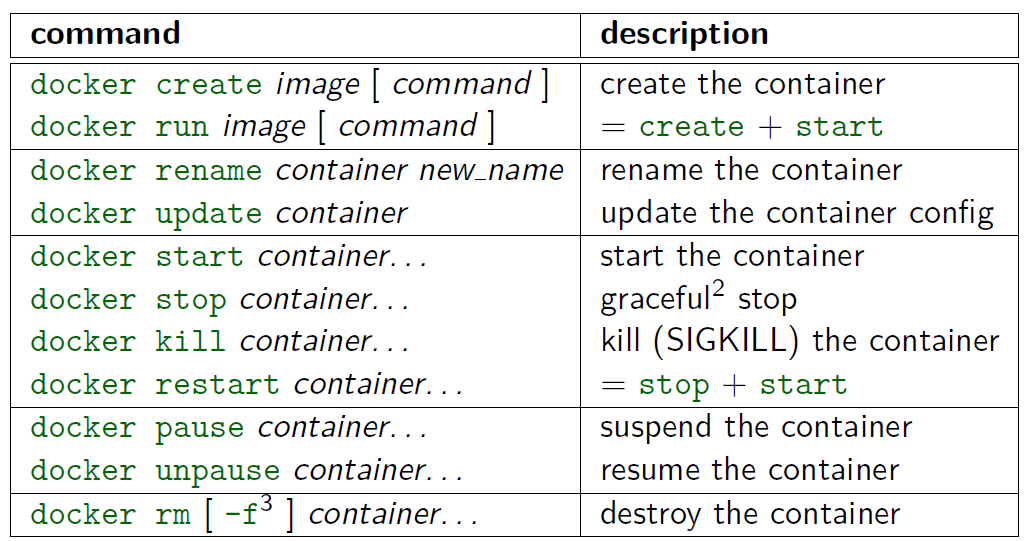
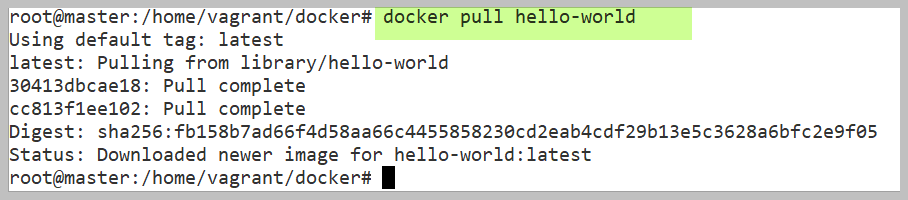
To run Docker Container first we need to get Docker Image, for that
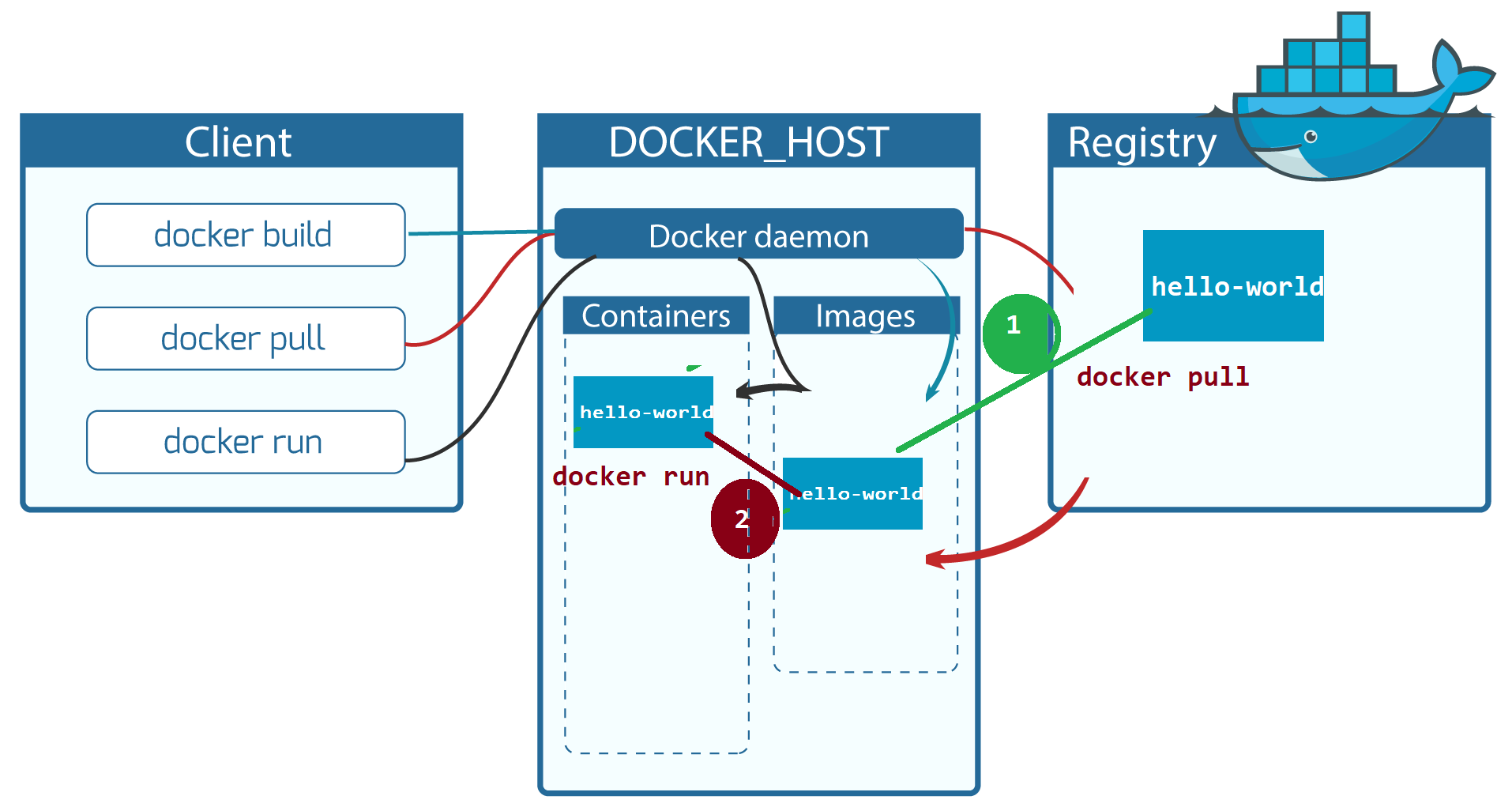
docker pull hello-world
we use above command it just pull the image from Docker hub to our local system(Docker Host) & saves it under Images section.
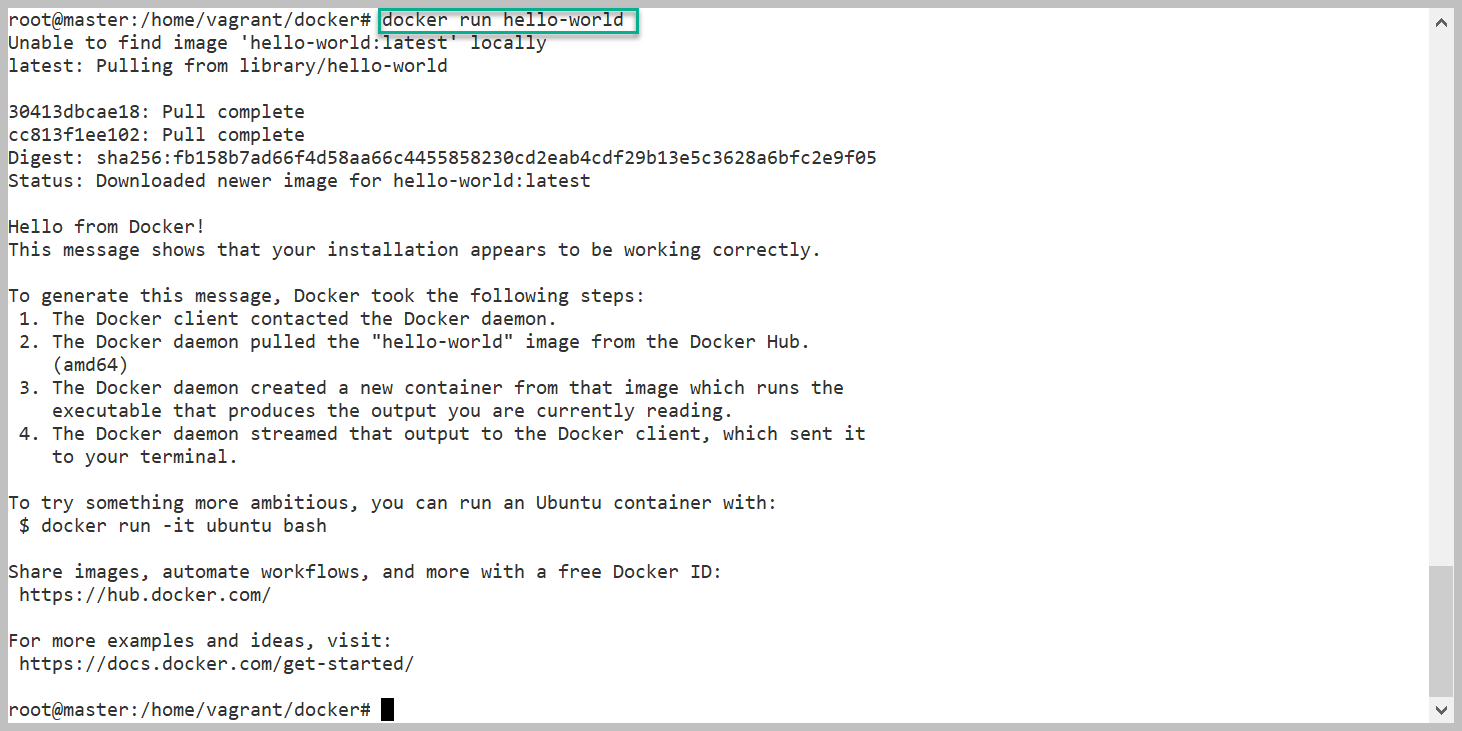
docker run hello-world
But if we run this command, first it will check Image is available in local system or not. if not it will download the image from Docker hub & its Run the image by creating Hello-world Container inside Containers block.
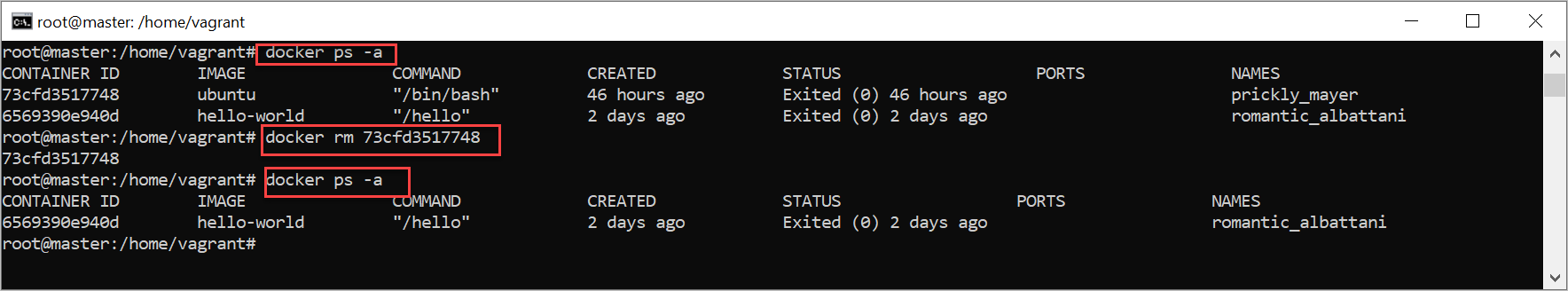
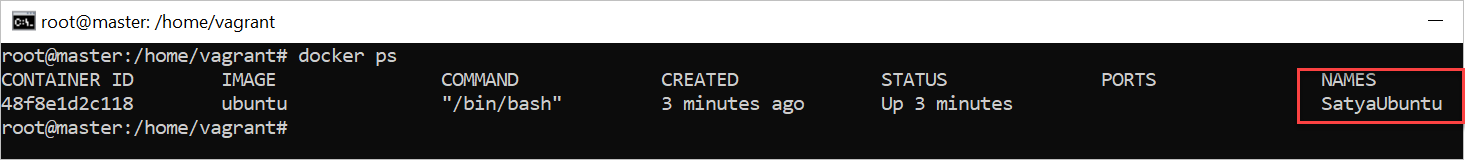
docker ps
Will display the all the available Containers
docker ps – will Displays only active/running containers
docker ps – will Displays only active/running containers
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE CREATED STATUS
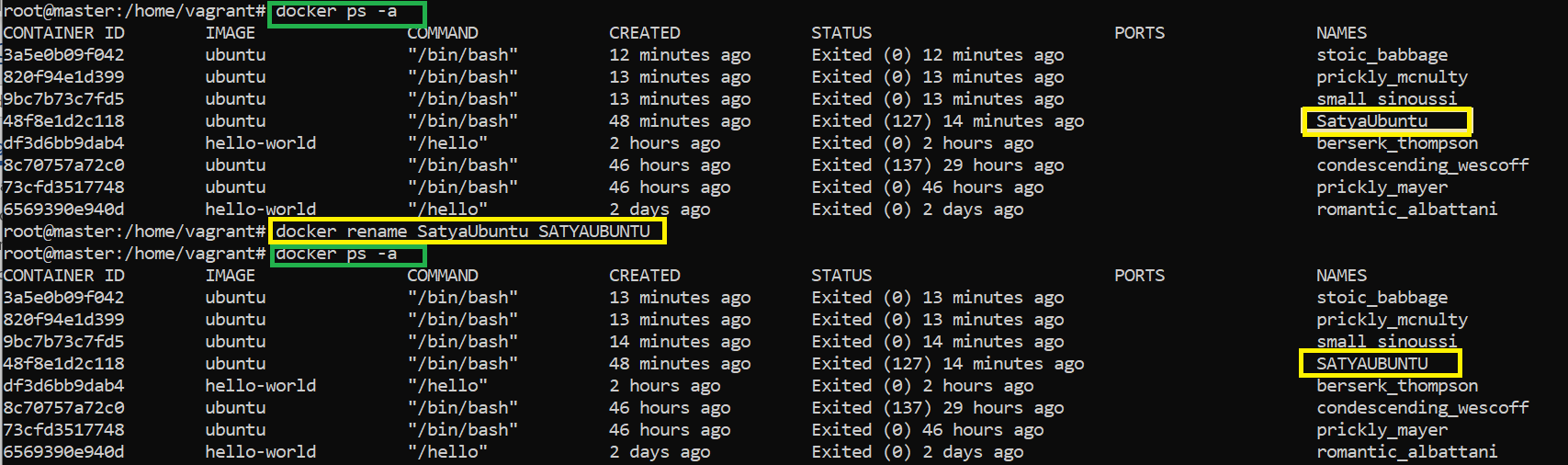
docker ps -a : will Displays both active/running containers
$ docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE CREATED STATUS
df3d6bb9dab4 hello-world 7 minutes ago Exited (0) 7 minutes ago
8c70757a72c0 68c4771c8a42 43 hours ago Exited (137) 27 hours ago
73cfd3517748 68c4771c8a42 43 hours ago Exited (0) 43 hours ago
6569390e940d hello-world 2 days ago Exited (0) 2 days ago
docker run
we already seen docker run basic command.
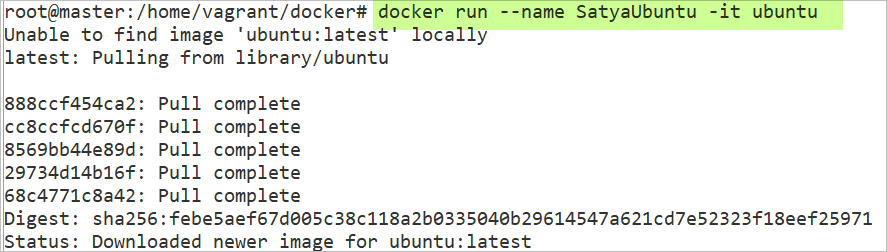
Now, i want to download Ubuntu Image & Run the container with Interactive mode(Login) and also want to give a name to the Container.
docker run --name SatyaUbuntu -it ubuntu
If container is already in running, we can do interactive by
docker exec -it <Container-ID> /bin/bash
or
docker attach <Con-id>
docker attach
This command to attach your terminal’s standard input, output, and error (or any combination of the three) to a running container using the container’s ID or name.
The docker exec and docker attach commands allow you to connect to a running container.
-
To get an interactive shell to a container, use the exec command to start a new shell session.
-
The attach command attaches your terminal to a running container.
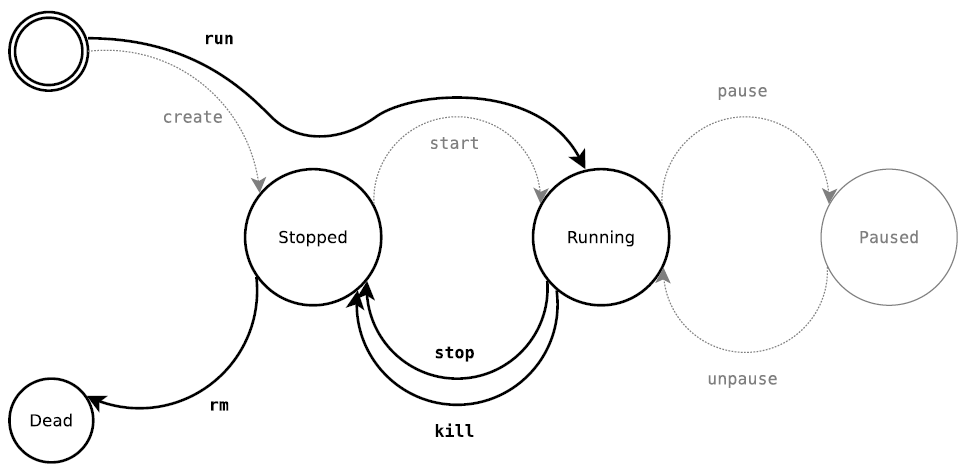
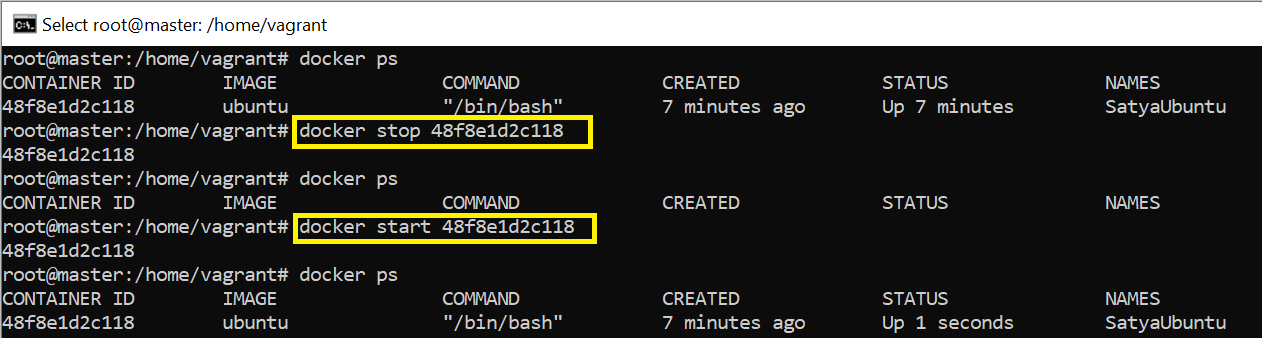
docker start/stop/restart
docker start <con _ID> : Start one or more stopped containers
docker stop <con _ID> : Stop a running container
docker restart <con _ID> : Restart a container
docker pause/unpause
docker pause <con-id> : Pause all processes within a container
docker unpause <con-id> : Unpause all processes within a container
docker top <con-id> : To Display the running processes of a container
docker stats
Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics like CPU, Memory & Disc usage details
#> docker stats 48f8e1d2c118
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/
48f8e1d2c118 0.00% 860.2 kB / 513.6 MB 0.17% 648 B / 648 / 0 B
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O
48f8e1d2c118 0.00% 860.2 kB / 513.6 MB 0.17% 648 B / 648 / 0 B
CONTAINER CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O
48f8e1d2c118 0.00% 860.2 kB / 513.6 MB 0.17% 648 B / 648 / 0 B
docker rename
Rename a container
docker rename <OLD_NAME> <NEW_NAME>
docker kill
Kill a running container
docker rm
Remove one or more containers from containers space.
docker rm <cont-id>