Jenkins – Master & Slave
Jenkins uses a Master-Slave architecture to manage distributed builds. In this architecture, Master and Slave communicate through TCP/IP protocol.
Jenkins Master
Your main Jenkins server is the Master. The Master’s job is to handle:
-
Scheduling build jobs.
-
Dispatching builds to the slaves for the actual execution.
-
Monitor the slaves (possibly taking them online and offline as required).
-
Recording and presenting the build results.
-
A Master instance of Jenkins can also execute build jobs directly.
Jenkins Slave
A Slave is a Java executable that runs on a remote machine. Following are the characteristics of Jenkins Slaves:
-
It hears requests from the Jenkins Master instance.
-
Slaves can run on a variety of operating systems.
-
The job of a Slave is to do as they are told to, which involves executing build jobs dispatched by the Master.
-
You can configure a project to always run on a particular Slave machine, or a particular type of Slave machine, or simply let Jenkins pick the next available Slave.
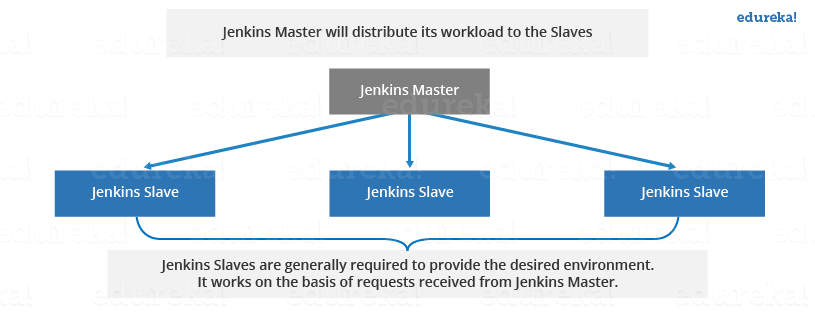
Jenkins master/slave architecture is used for distributed build environments, where the workload of building projects is distributed to multiple agent nodes, and we can use different environments for each build.
Jenkins master node will be used for scheduling jobs, monitoring slave nodes, dispatching builds to slave nodes, recording and representing the build result, and also executing build jobs directly.
Jenkins slave nodes can run on a variety operating system like Windows and Linux, and there is no need to install full Jenkins packages on it.
Master -Windows 192.168.33.1
Slave1 -Ubuntu 192.168.33.10
Slave2 -CentOS 192.168.33.11
There are two ways of authentication for setting up the Jenkins slaves. Ref.
-
Using username and password
-
Using ssh keys.
Using Username & password
We will go for this scenario where
-
Master – Windows
-
Slavers – Linux Systems
In Slave Nodes
1.Install Java on Node machines
2.Create user
We need to create a user on Slave Machine, Master node will use the credentials
to make connection with slave/agent nodes. Here The new user will be
calledjenkinswith new directory /var/lib/jenkins as home directory
# Create new Directory for Jenkins user
mkdir /var/lib/jenkins
# Change Permiisnons
sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/jenkins
# Create Jenkins user
sudo useradd -d /var/lib/jenkins jenkins
passwd jenkins
If user already exist , delete all instances with that user
sudo userdel -r jenkins
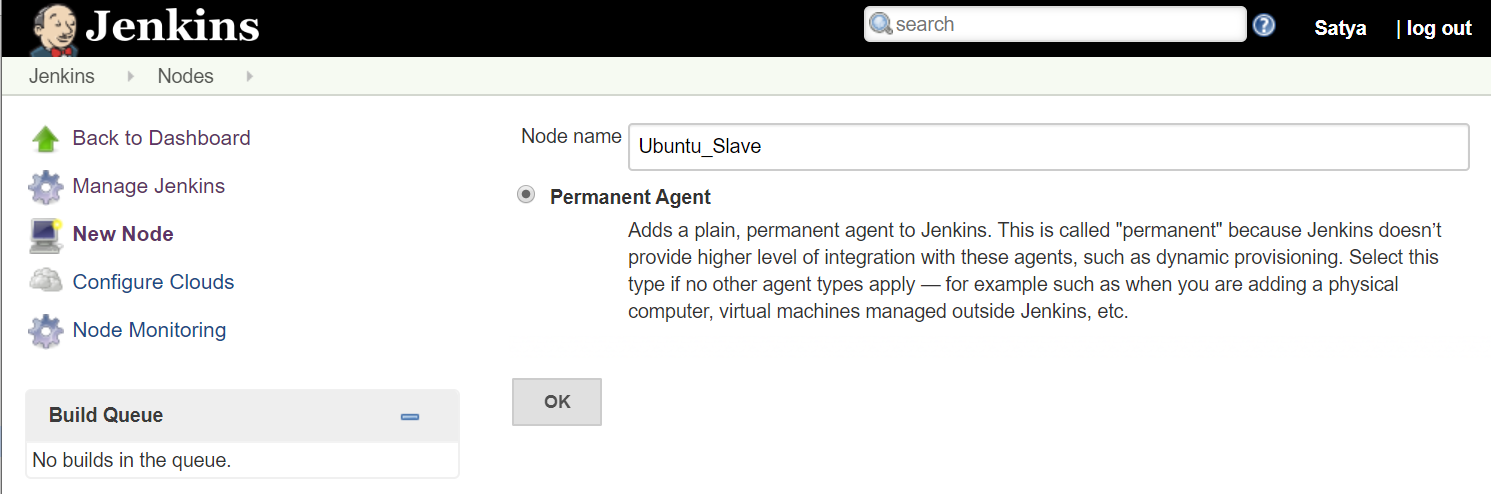
In Jenkins Master Node
Go to Dashboard > Manage Jenkins > Manage Nodes > New Node - tick: Permanent Agent
On next screen, fill below details
-
# of executors - No. of jobs run at a time.
-
Remote root directory - folder to store build artifacts/ output files on slave node
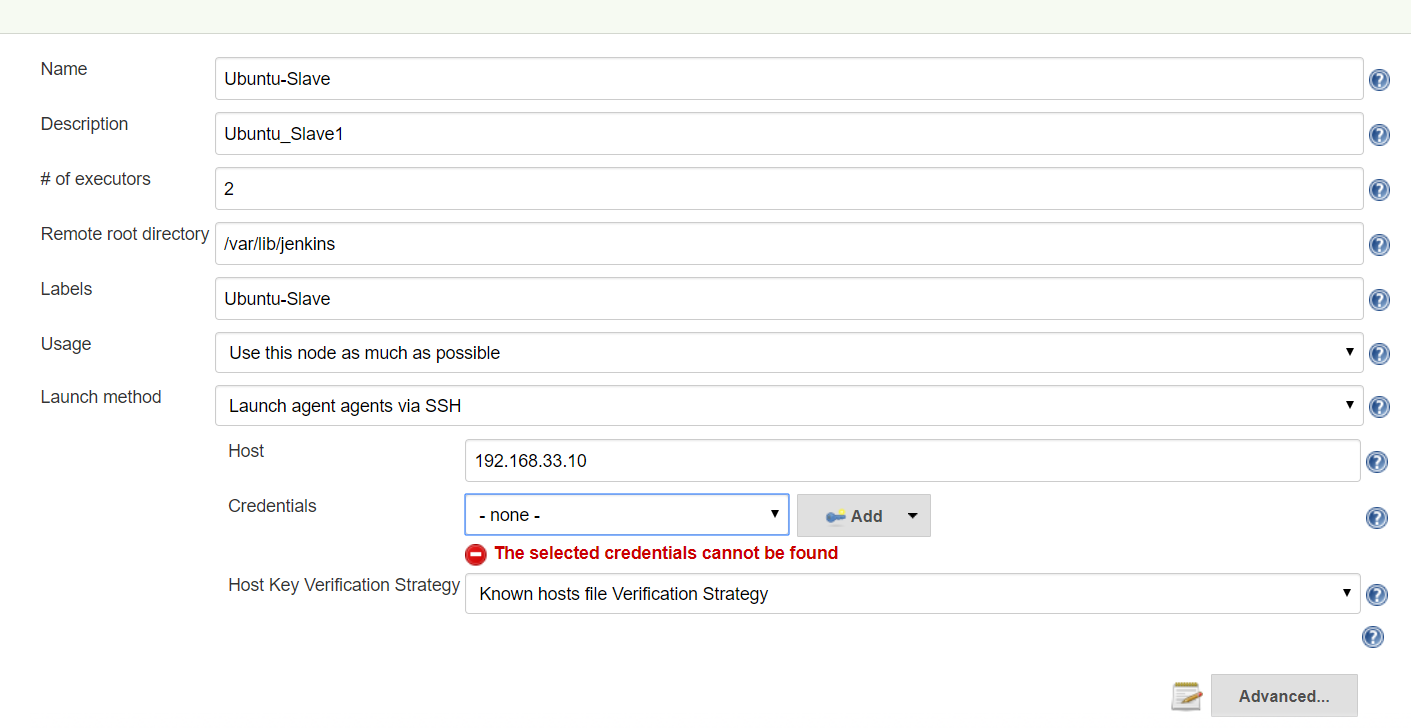
Click on credentials > Add button : Jenkins – it will open a pop-up window. Fill with below details
-
Domain : Global
-
Kind : Username/password
-
Username : Created agent user
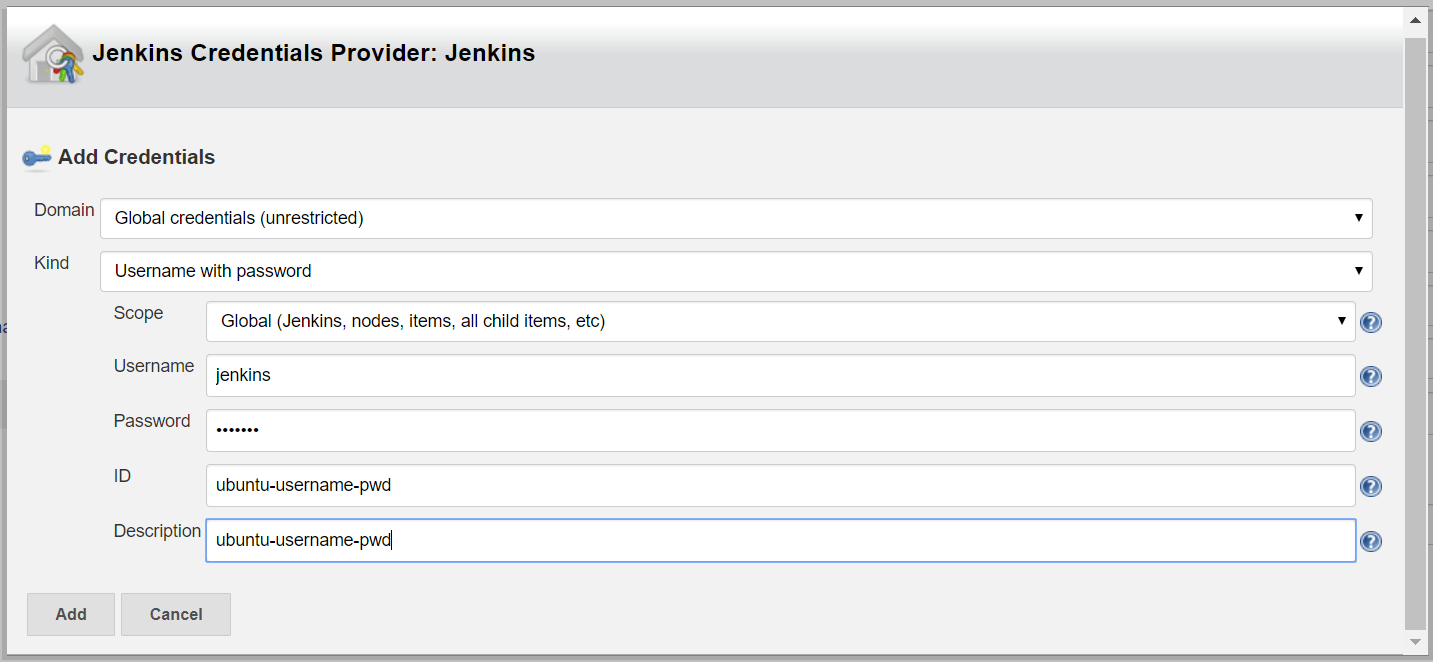
Selected created Credentials & select Host Key Verification Strategy : Manually trusted key Verification Strategy > SAVE
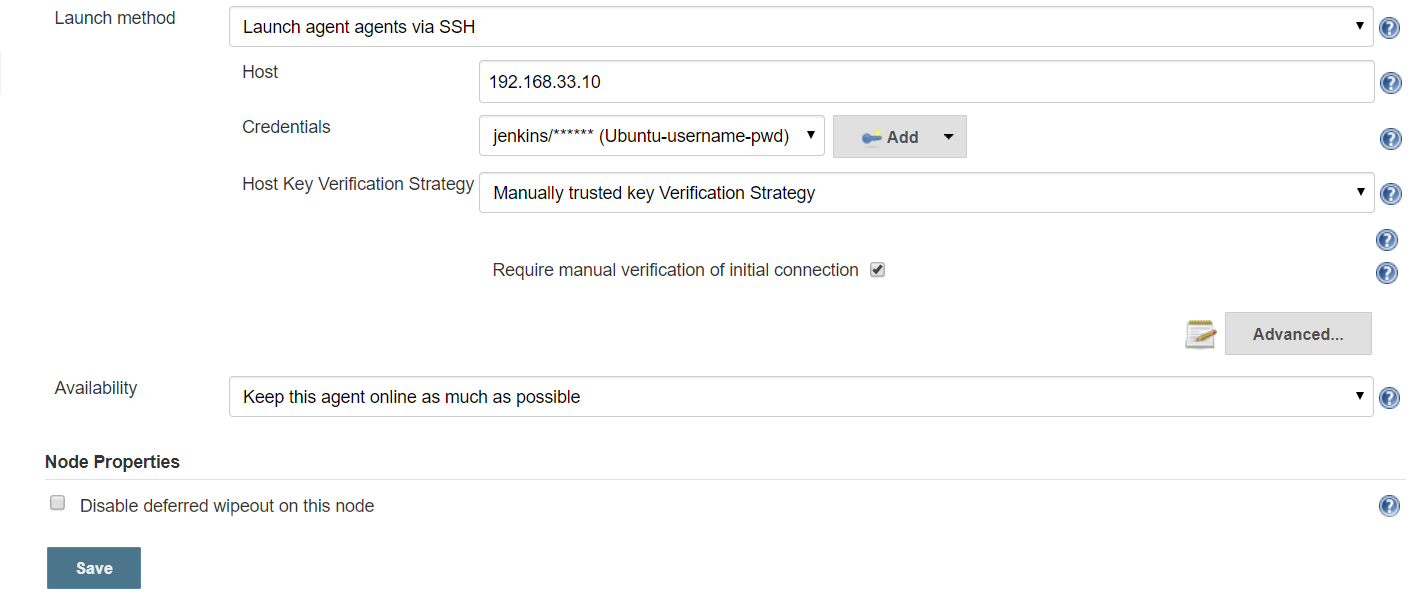
Open created Slave & do Luanch Agent
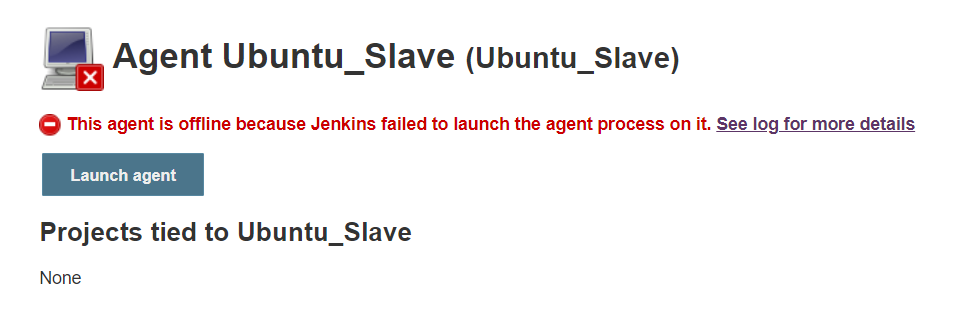
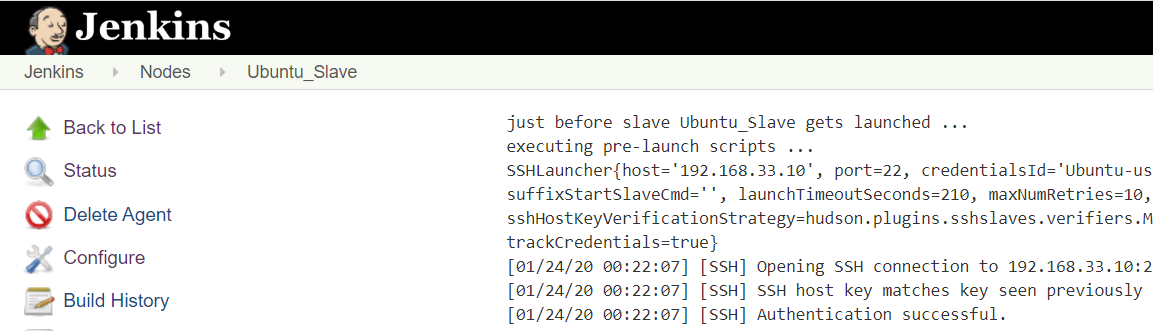
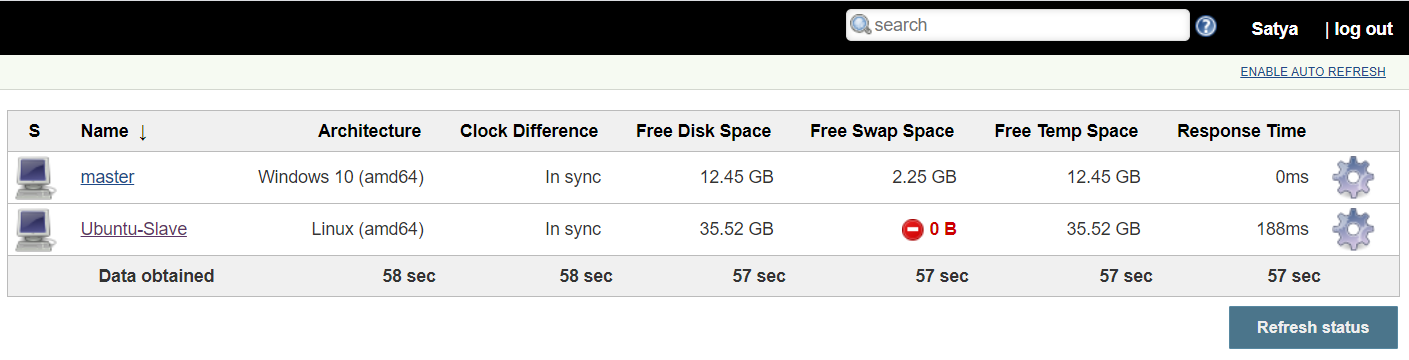
Using SSH
We will go for this scenario where
-
Master – Linux
-
Slavers – Linux/Windows Systems
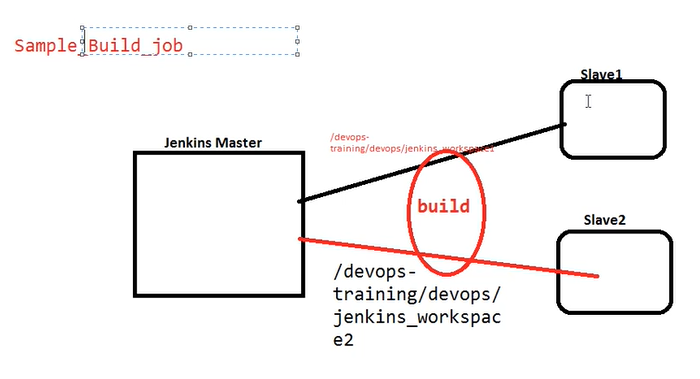
we have Jenkins workspace in Master Node, where all Job-related details & created artifacts will store here. we can find this location by opening Jenkins Master URL
Dashboard > Configure System > Home directory : /var/lib/jenkins
In the same way, if we trigger build in Slave node - it has to store all jobs related data in somewhere. For that we need to create a Directory in Slave machine
mkdir /var/lib/sshjenkins
sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/sshjenkins
Provide this location as ‘Remote Directory laction’ in master-slave configuration.
Create user
sudo useradd -d /var/lib/sshjenkins sshjenkins
passwd sshjenkins
Go to above created folder. Create private and public SSH key for that user
private key : id_rsa
public key : id_rsa.pub
Switch to #sshuser
su - sshjenkins
cd /var/lib/sshjenkins
ssh-keygen -t rsa -m PEM -C "Jenkins agent key" -f "id_rsa"
Add the public SSH key to the list of authorized keys on the agent machine
cat id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Copy the private SSH key (/var/lib/sshjenkins/id_rsa) from the agent machine to
your OS clipboard
cat id_rsa
\-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
\-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
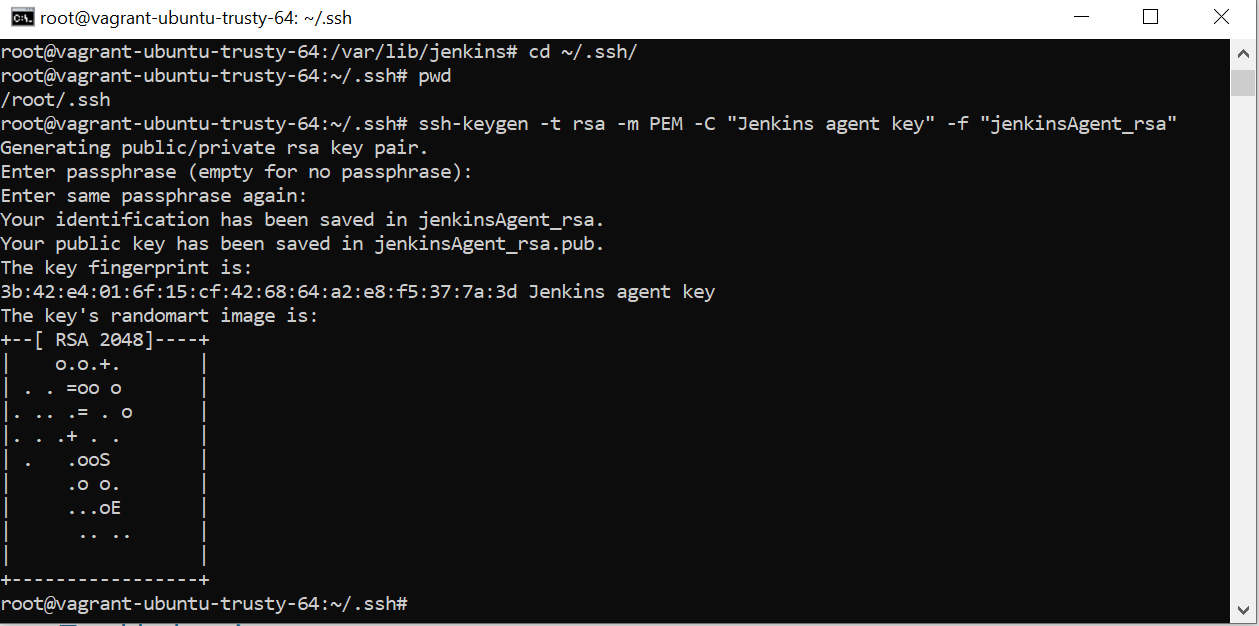
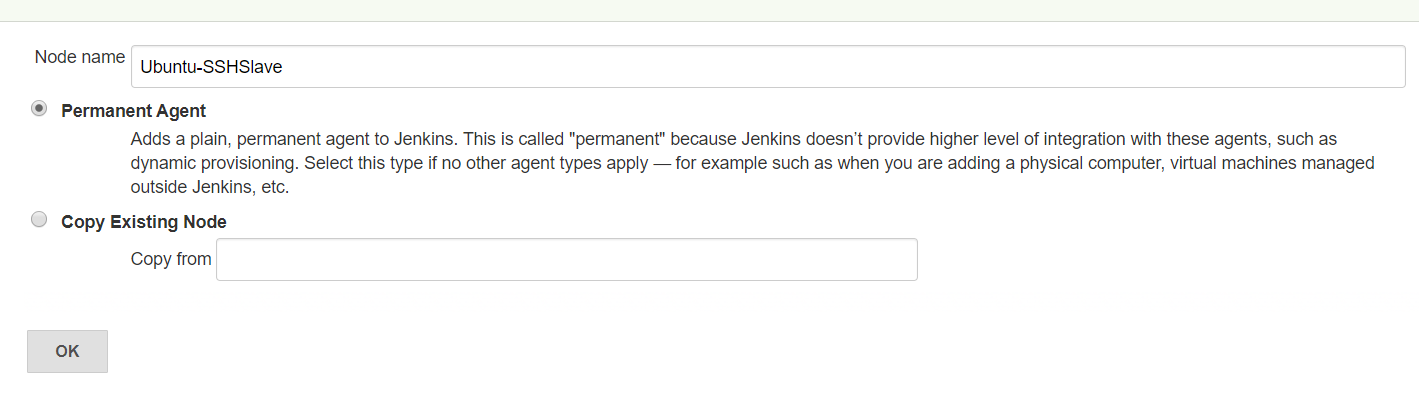
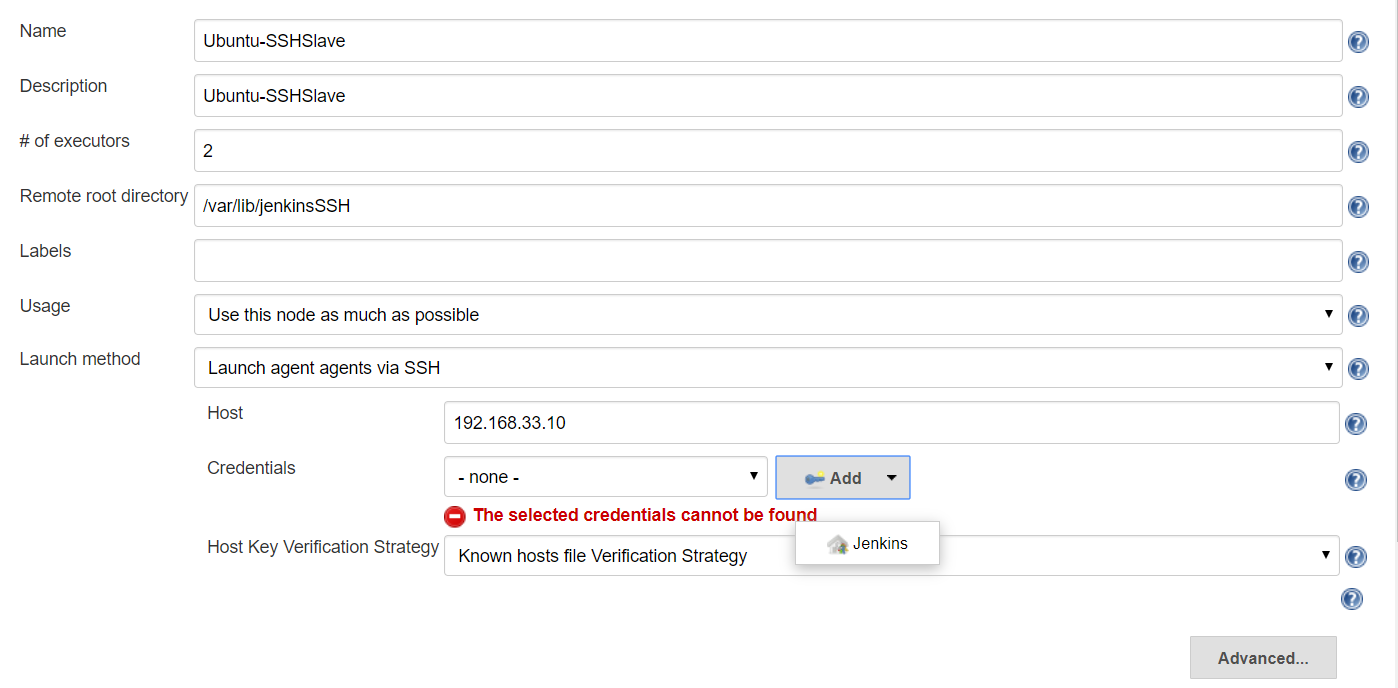
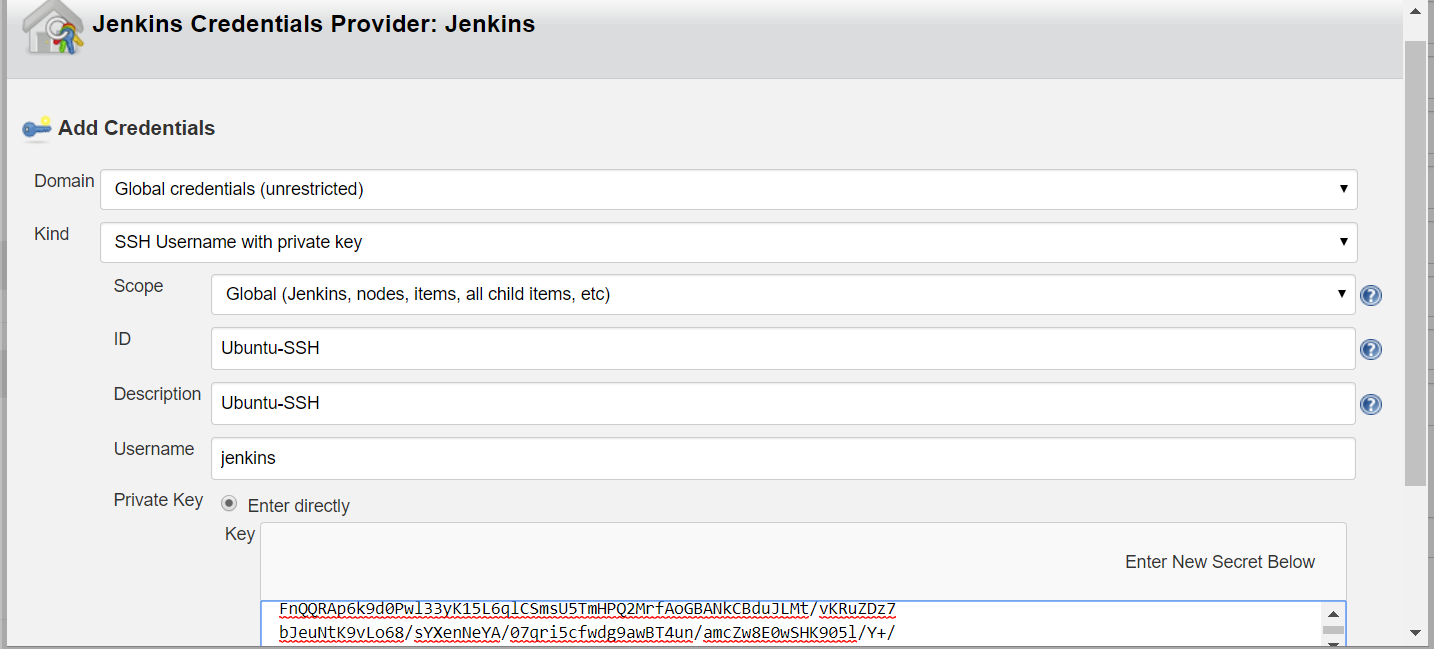
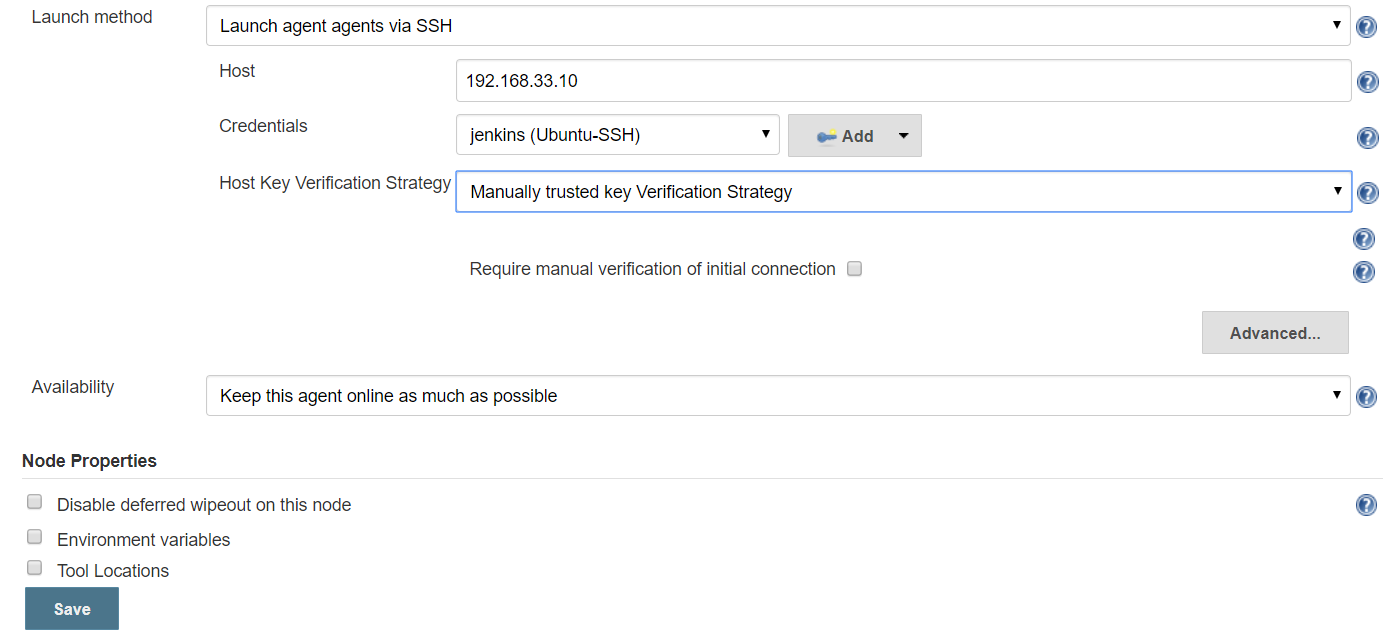
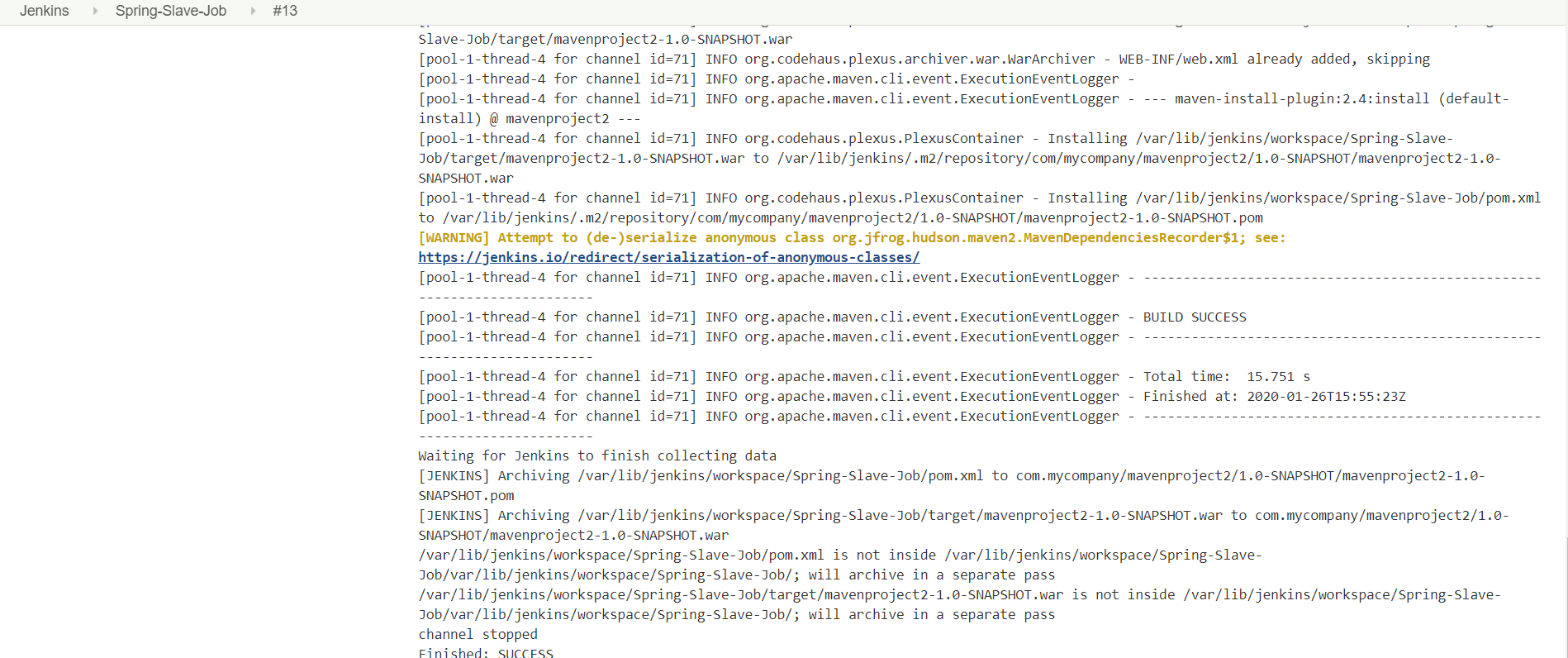
Jenkins – Master Slave Job Configuration
Slave – Configuration
Get JDK, MAVEN, GIT installation paths of Slave node
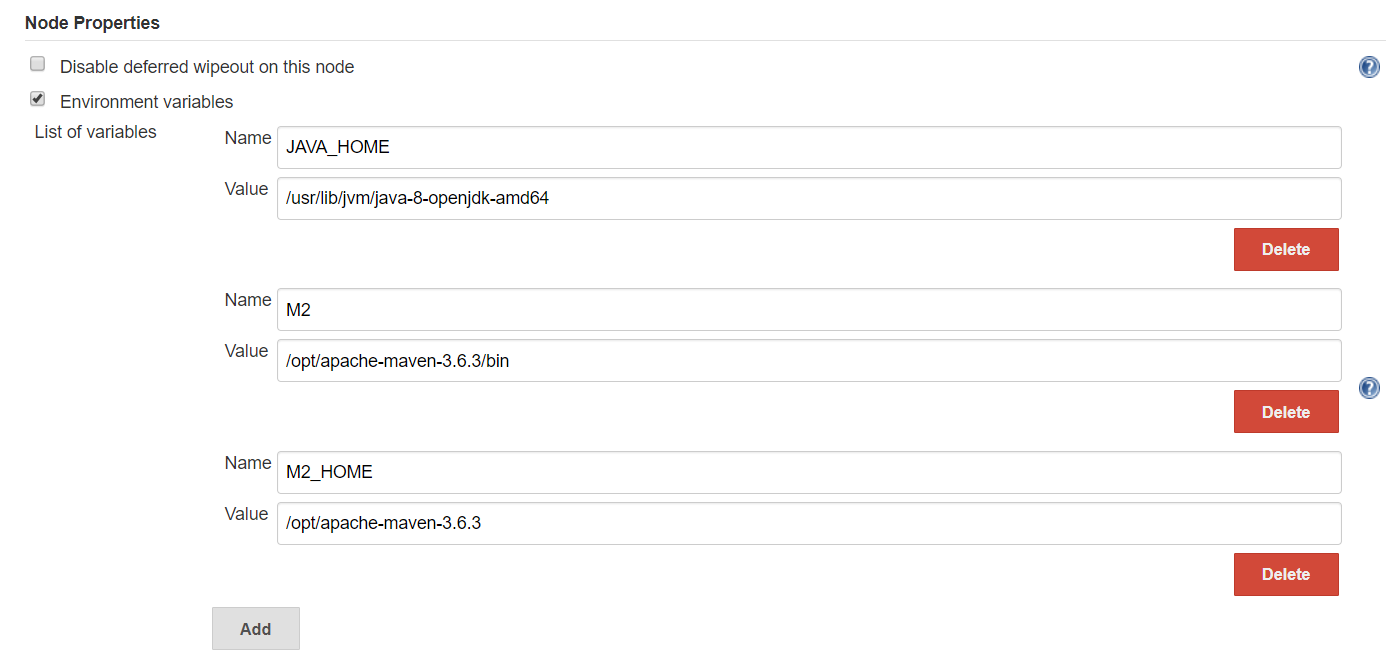
Add Java, Maven paths to Slave nodes.
# JAVA_HOME
/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-openjdk-amd64
# M2
/opt/apache-maven-3.6.3/bin
# M2_HOME
/opt/apache-maven-3.6.3
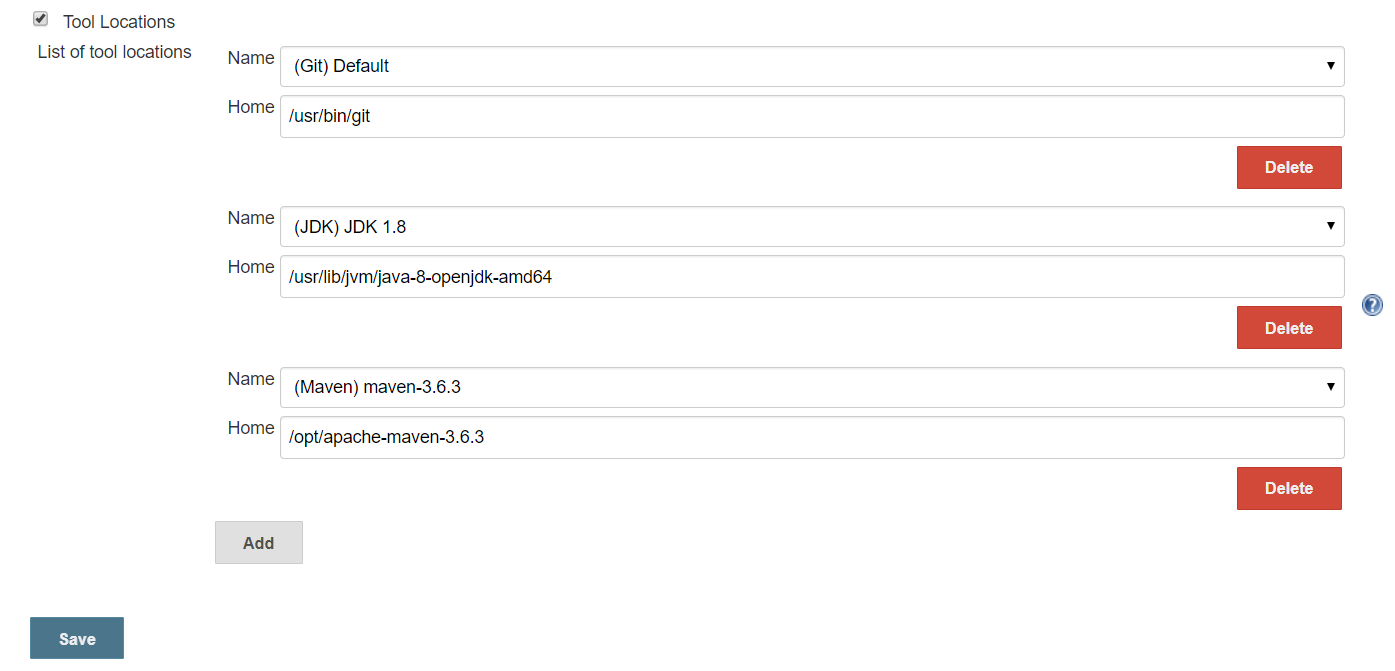
Manage Jenkins >Manage Nodes > Select Node : Ubuntu-Slave > Configure
# Provide Slave Host, Credentials etc
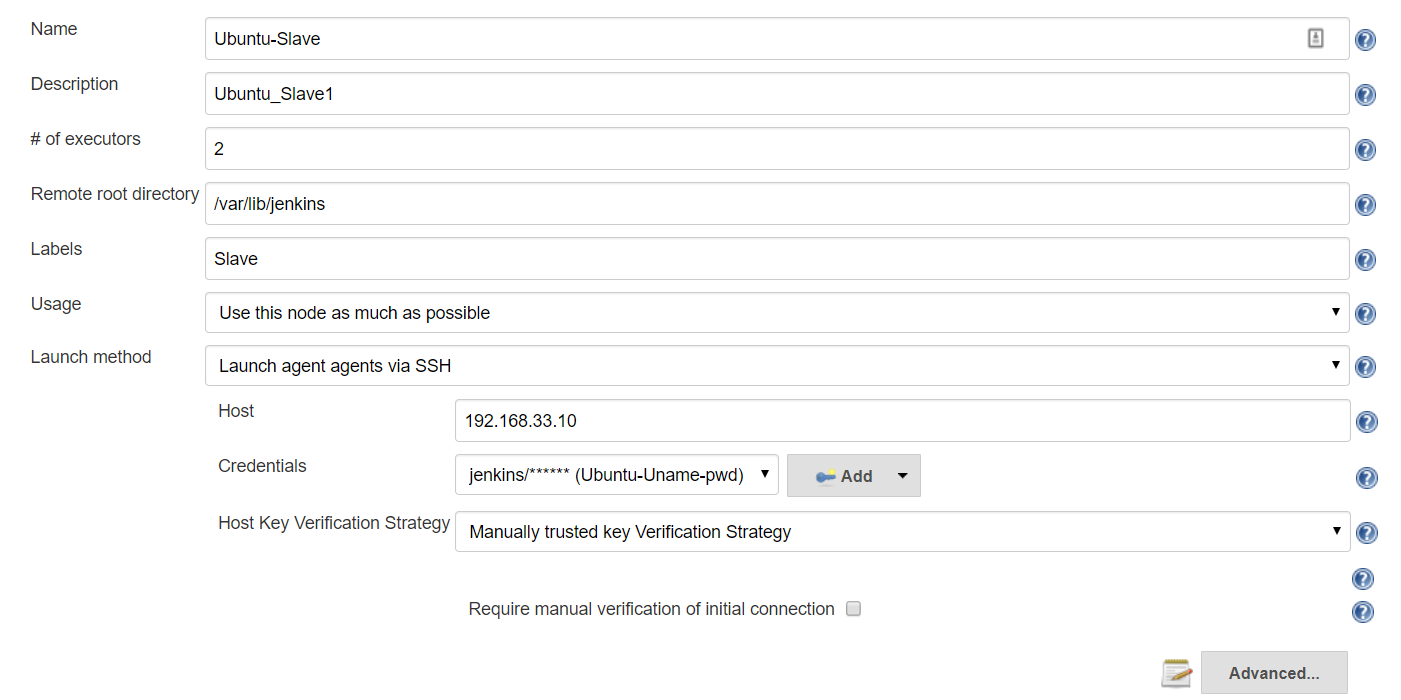
#1 Node Properties > Environment variables
#2 Node Properties > Tool Locations
Master – Configuration
Master must know the Tool Configuration like JDK, Maven used by Nodes.
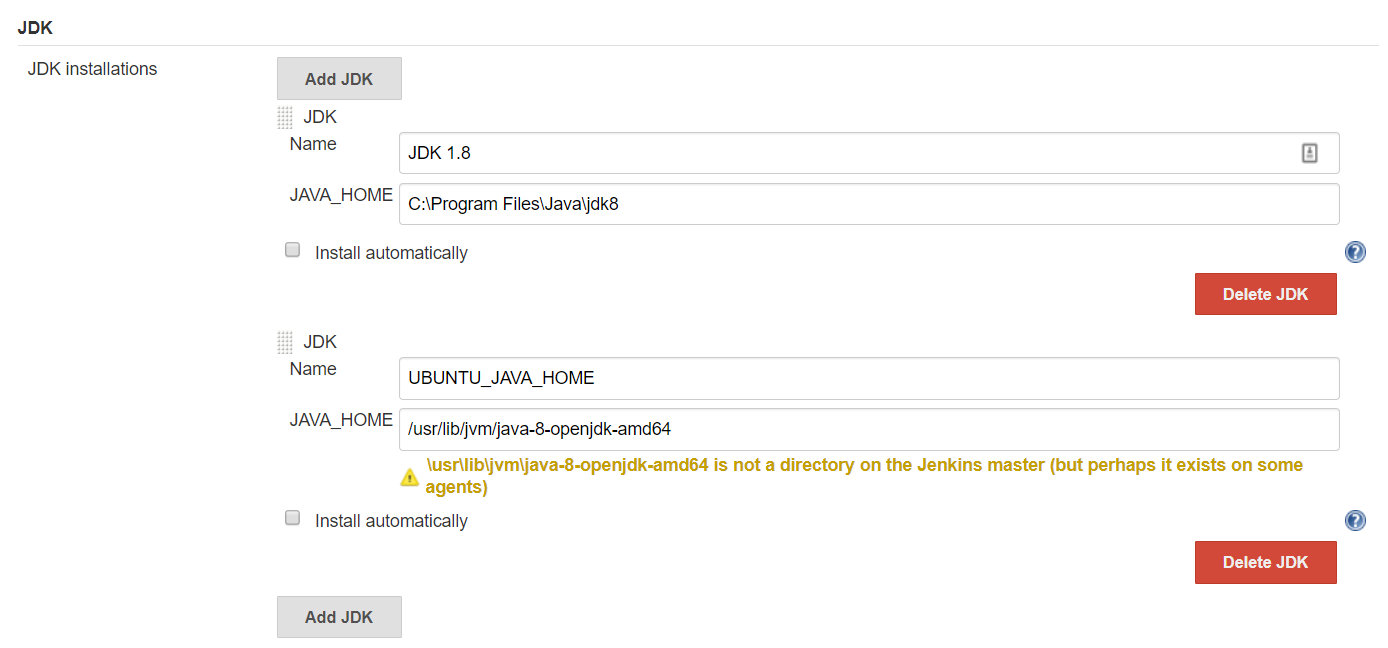
Configure JDK installations
Manage Jenkins > Global Tool Configuration > Configure JDK installations used
by Slave
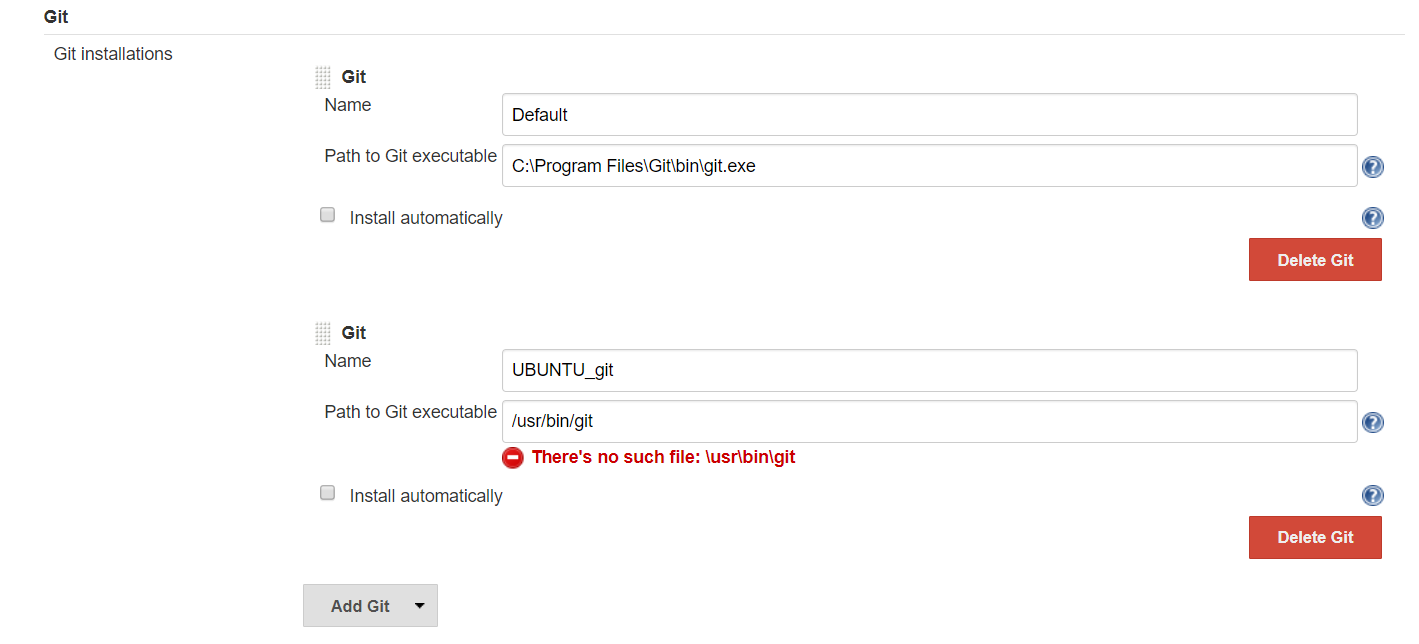
Git installations
Maven installations

Master – Configure Jenkins Job
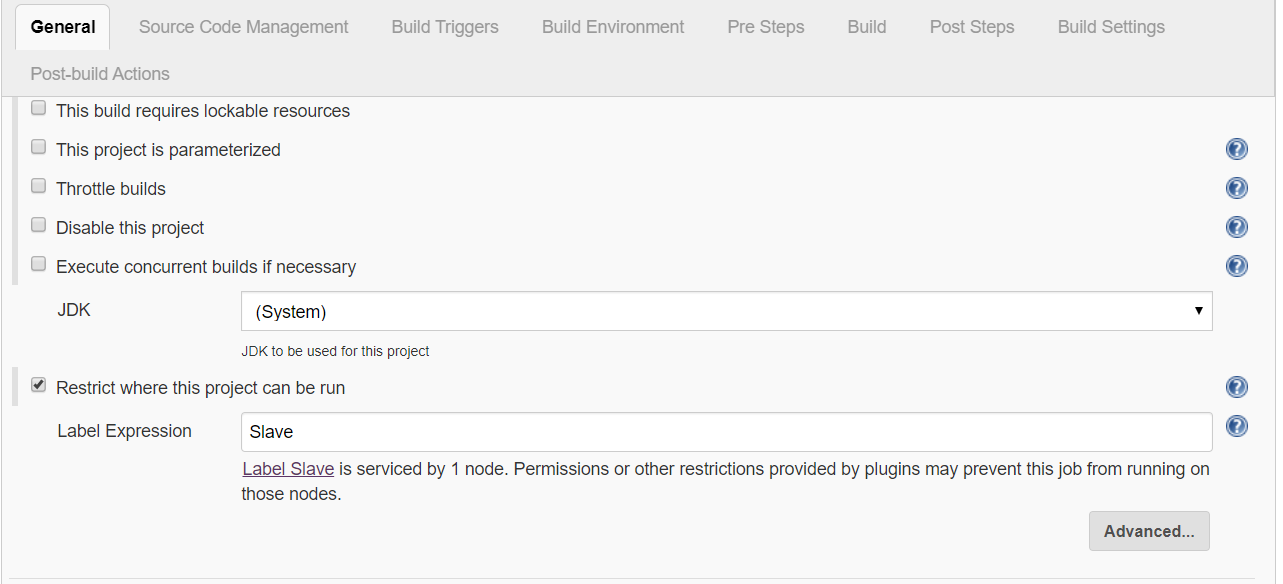
Open any Job > Configure > General >
-
[Tick] Restrict where this project can be run
-
Label : provide Slave label mentioned at the time of Slave creation
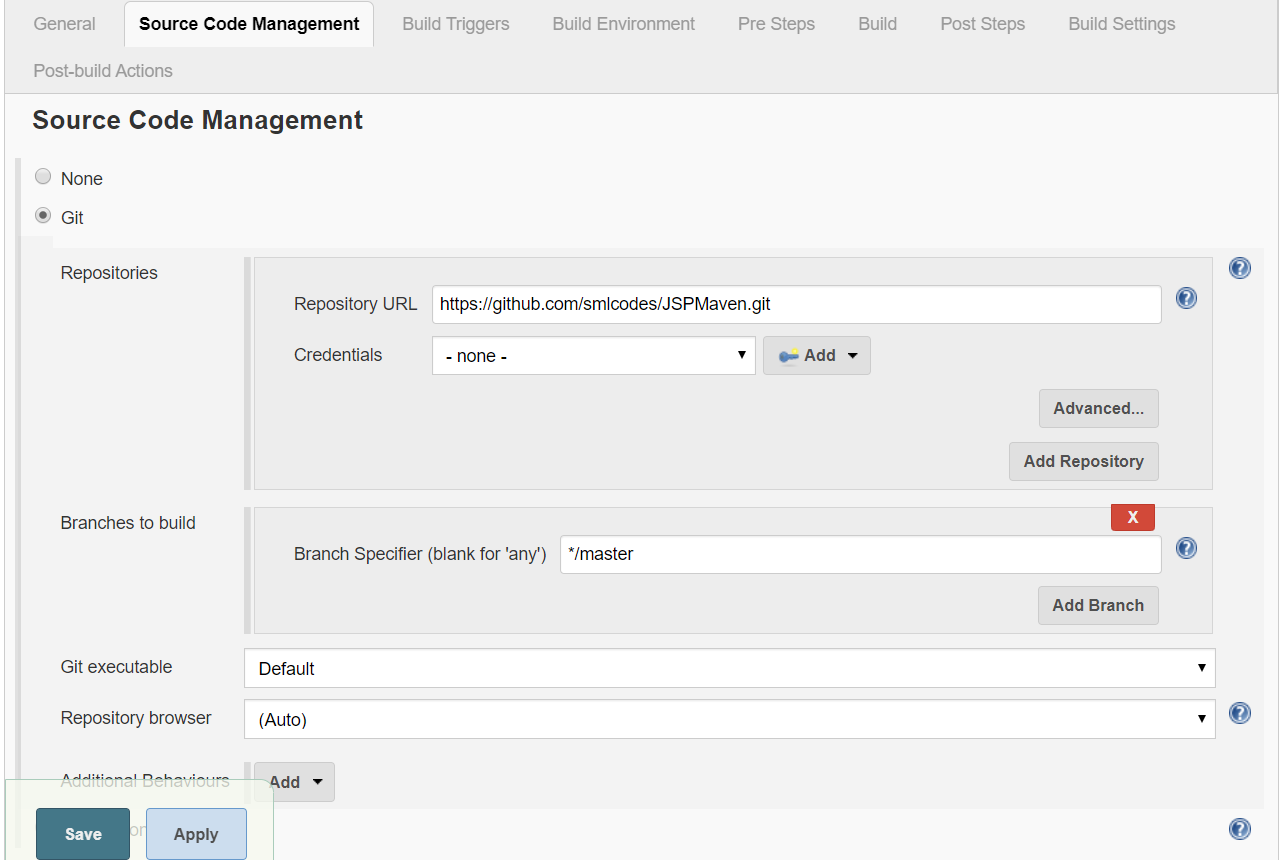
Source Code Management
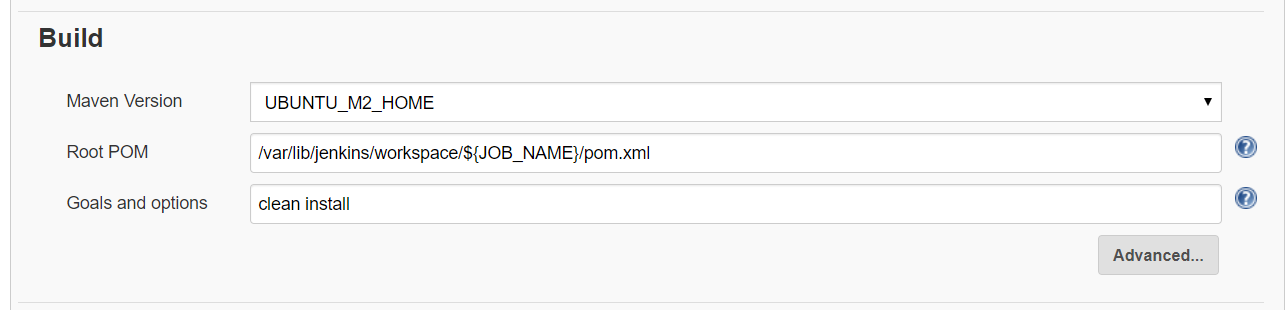
Build Step
location of Build data stored in slave system :
/var/lib/jenkins/workspace/${JOB_NAME}/pom.xml
Save & Build Now