SOAP -Simple Object Access Protocol
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) is a standard protocol specification for message exchange based on XML. Communication between the web service and client happens using XML messages.
A simple web service architecture has two components.
- Client
- Service provider
To communicate clinet with service provider clinet must know about following things
- Location of WebServices Server
- Functions available, signature and return types of function.
- Communication protocol
- Input output formats
Service provider will create a standard XML file which will have all above information. So if this XML file is given to client, then client will be able to access web service. This XML file is called -WSDL”.
WSDL (Web Services Description Language):
WSDL stands for Web Service Description Language. It is an XML file that describes the technical details of how to implement a web service, more specifically the URI, port, method names, arguments, and data types. Since WSDL is XML, it is both human-readable and machine-consumable.
Using this WSDL file we can understand things like,
-
Port / Endpoint – URL of the web service
-
Input message format
-
Output message format
-
Security protocol that needs to be followed
-
Which protocol the webservice uses?
How to access web service:
There are two ways to access web service
-
If Service provider knows client
-
If Service provider register its WSDL to UDDI and client can access it from UDDI
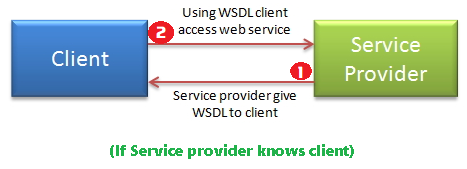
1.If Service provider knows client
If Service provider knows client, then it will provide its wsdl to client and client will be able to access web service.
2.If Service provider register its WSDL to UDDI and client can access it from
UDDI:
Service provider register its WSDL to UDDI and client can access it from
UDDI:
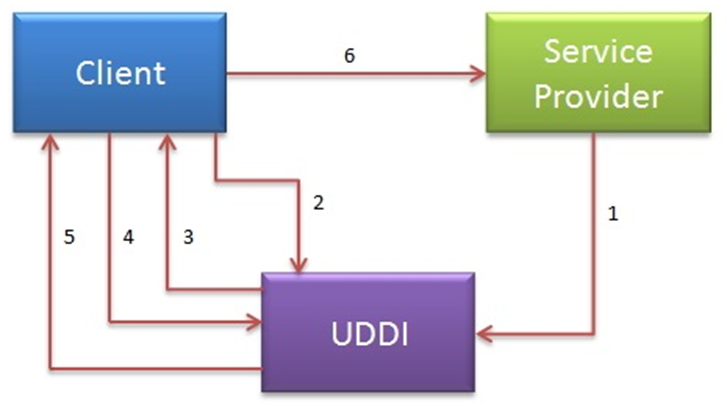
UDDI stands for Universal Description, Discovery and Integration.It is a directory service. Web services can register with a UDDI and make themselves available through it for discovery. So following steps are involved.
-
Service provider registers with UDDI.
-
Client searches for service in UDDI.
-
UDDI returns all service providers offering that service.
-
Client chooses service provider
-
UDDI returns WSDL of chosen service provider.
-
Using WSDL of service provider, client accesses web service
UDDI:
-
UDDI is an XML-based standard for describing, publishing, and finding web services.
-
UDDI is a specification for a distributed registry of web services
A business or a company can register three types of information into a UDDI registry. This information is contained in three elements of UDDI.
These three elements are:
-
White Pages: Basic information about the company and its business
-
Yellow Pages: contain more details about the company
-
Green Pages: contains technical information about a web service (url locations etc)