JAX-WS RPC Style
-
RPC style web services use method name and parameters to generate XML structure.
-
The generated WSDL is difficult to be validated against schema.
-
In RPC style, SOAP message is sent as many elements.
-
RPC style message is tightly coupled.
-
In RPC style, SOAP message keeps the operation name.
-
In RPC style, parameters are sent as discrete values.
Steps to create JAX-WS RPC Style Example
1. JAX-WS Web Service End Point files
-
Create a Web Service Endpoint Interface with @SOAPBinding(style = Style.RPC)
-
Create a Web Service Endpoint Implementation
-
Create an Endpoint Publisher
-
Test generated WSDL. Ex: http://localhost:8080/ws/hello?wsdl
2. Web Service Client files
Java Web Service Client
-
In general words, -web service endpoint” is a service which published outside for user to access;
-
where -web service client” is the party who access the published service.
Example : Hello World using JAX-WS RPC Style
1. JAX-WS Web Service End Point files
*************************************************
1. Create a Web Service Endpoint Interface
*************************************************
package endpoint;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding;
import javax.jws.soap.SOAPBinding.Style;
//Service Endpoint Interface
@WebService
@SOAPBinding(style = Style.RPC)
public interface HelloWorld{
@WebMethod
String getHelloWorldMsg(String msg);
}
*************************************************
2. Create a Web Service Endpoint Implementation
*************************************************
package endpoint;
import javax.jws.WebService;
//Service Implementation
@WebService(endpointInterface = "endpoint.HelloWorld")
public class HelloWorldImpl implements HelloWorld{
@Override
public String getHelloWorldMsg(String msg) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "Your Message from WebService is : "+msg;
}
}
********************************************
3. Create an Endpoint Publisher
********************************************
package endpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
//Endpoint publisher
public class HelloWorldPublisher{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:7777/ws/hello", new HelloWorldImpl());
System.out.println("WSDL Published !!");
}
}
4. Test generated WSDL
Run HelloWorldPublisher as Java Application & access url: http://localhost:7777/ws/hello?wsdl
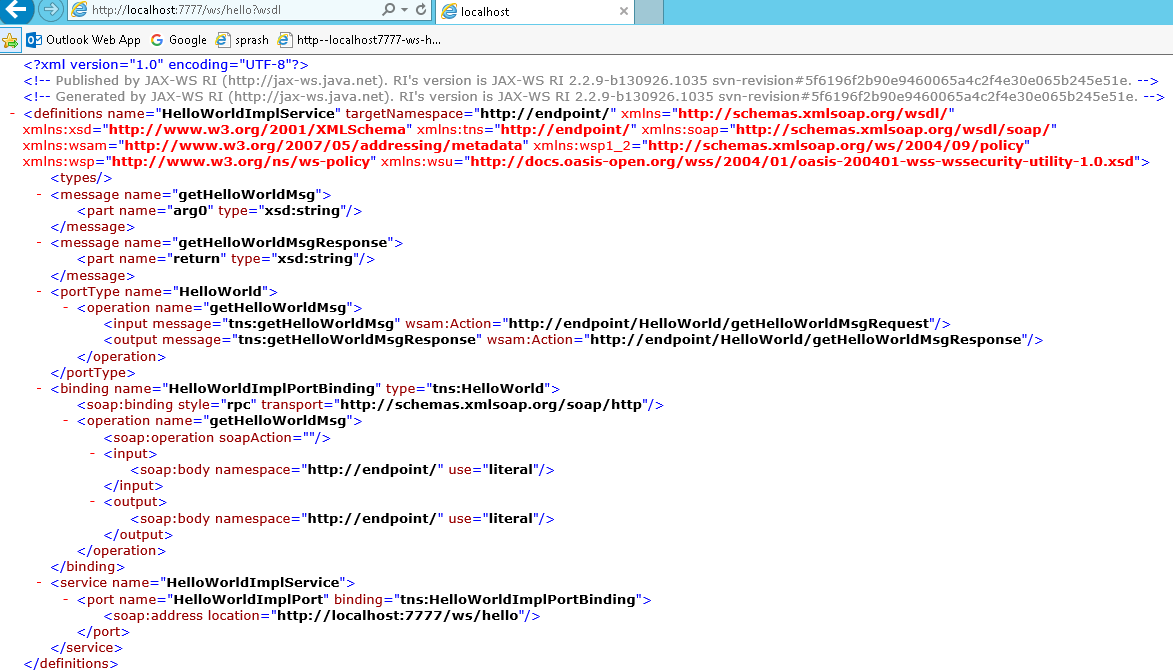
http://endpoint/” uses package name of Service endpoint publisher
the main components of WSDL documents are as below.
WSDL Explanation
1.first Message part contains service method name & parameter list
<message name="getHelloWorldMsg">
<part name="arg0" type="xsd:string"/>
</message>
2.Second Meaage part contains autogenerated Response method & return type
<message name="getHelloWorldMsgResponse">
<part name="return" type="xsd:string"/>
</message>
3.PortType information is about ServiceEndpoint interface & input,output action urls
<portType name="HelloWorld">
<operation name="getHelloWorldMsg">
<input message="tns:getHelloWorldMsg" wsam:Action="http://endpoint/HelloWorld/getHelloWorldMsgRequest"/>
<output message="tns:getHelloWorldMsgResponse" wsam:Action="http://endpoint/HelloWorld/getHelloWorldMsgResponse"/>
</operation>
</portType>
Here http://endpoint it will take package name as automatically if we won’t provide anything
4.Binding will generate automatically by taking RPC Style/ Document Style

5.Service tag contains service details & WSDL document location
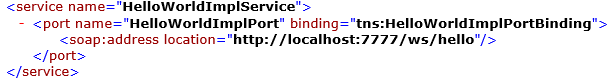
2. Web Service Client file
Follow below steps to write Webservice client
- Create URL object by passing WSDL document location
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:7777/ws/hello?wsdl"); - Create QName by passing service URI, Service name as arguments
QName qname = new QName("http://endpoint/", "HelloWorldImplService"); - Create Service Object by calling create (-,-) by passing URL,QName as
arguments. Service objects provide the client view of a Web service. ports
available on a service can be enumerated using the getPorts method
Service service = Service.create(url, qname); HelloWorld hello = service.getPort(HelloWorld.class);
package client;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import endpoint.HelloWorld;
public class HelloWorldClient{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:7777/ws/hello?wsdl");
//1st argument service URI, refer to wsdl document above
//2nd argument is service name, refer to wsdl document above
QName qname = new QName("http://endpoint/", "HelloWorldImplService");
Service service = Service.create(url, qname);
HelloWorld hello = service.getPort(HelloWorld.class);
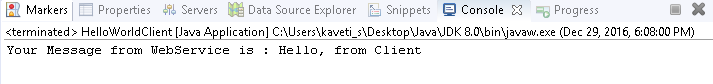
System.out.println(hello.getHelloWorldMsg("Hello, from Client"));
}
}
By running Clinet application we will get output as below