Session Tracking
Session Tracking is a way of remembering client data across the multiple requests during a session.
There are 4 techniques used in Session tracking:
-
Hidden Form Field
-
Cookies
-
HttpSession
-
URL Rewriting
1.Hidden Form Field
-
We store the information in the hidden field and get it from another servlet
-
It easy to write
Disadvantages
-
Used only on Textboxes
-
If we see the view-source of html page, the hidden values can visible
-
Not secure
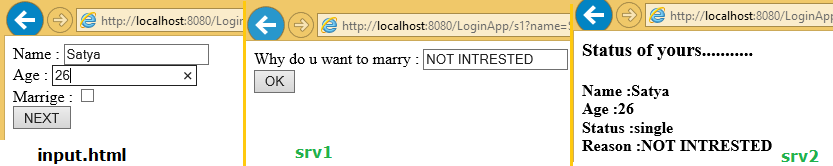
login.html
<form action = "s1" method = "get">
Name : <input type = "text" name = "name"><br>
Age : <input type = "text" name = "age"><br>
Marrige : <input type = "checkbox" name = "mrg" value = "yes"><br>
<input type = "submit" name = "btn" value = "NEXT"> <br>
</form>
public class srv1 extends HttpServlet {
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
String name = req.getParameter("name");
String age = req.getParameter("age");
String mrg = req.getParameter("mrg");
if (mrg == null) {
mrg = "single";
pw.println("<form action = 's2'>");
pw.println("Why do u want to marry :<input type='text' name = 'why'><br>");
pw.println("<input type = 'hidden' name = 'name' value = " + name + ">");
pw.println("<input type = 'hidden' name = 'age' value = " + age + ">");
pw.println("<input type = 'hidden' name = 'mrg' value = " + mrg + ">");
pw.println("<input type = 'submit' name = 'btn' value = 'OK'><br>");
pw.println("</form>");
}
else {
mrg = "married";
pw.println("<form action = 's2'>");
pw.println("How Many Childrens:<input type = 'text' name = 'child'><br>");
pw.println("<input type = 'hidden' name = 'name' value = " + name + ">");
pw.println("<input type = 'hidden' name = 'age' value = " + age + ">");
pw.println("<input type = 'hidden' name = 'mrg' value = " + mrg + ">");
pw.println("<input type = 'submit' name = 'btn' value = 'OK'><br>");
pw.println("</form>");
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------
public class srv2 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
pw.println("<h3> Status of yours...........</h1>");
pw.println("<h4> Name :" + req.getParameter("name"));
pw.println("<br> Age :" + req.getParameter("age"));
pw.println("<br> Status :" + req.getParameter("mrg"));
if (req.getParameter("mrg").equals("single")) {
pw.println("<br> Reason :" + req.getParameter("why"));
}else{
pw.println("<br> No.of Childrents :"+ req.getParameter("child"));
}
}
}
2.Cookies
A cookie is a small piece of information saved in the browser between the multiple client requests.
There are 2 types of cookies in servlets.
-
Non-persistent cookie
-
Persistent cookie

Advantage of Cookies
-
Simplest technique of maintaining the state.
-
Cookies are maintained at client side.
Disadvantage of Cookies
-
It will not work if cookie is disabled from the browser.
-
Only textual information can be set in Cookie object.
public class srv1 extends HttpServlet {
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
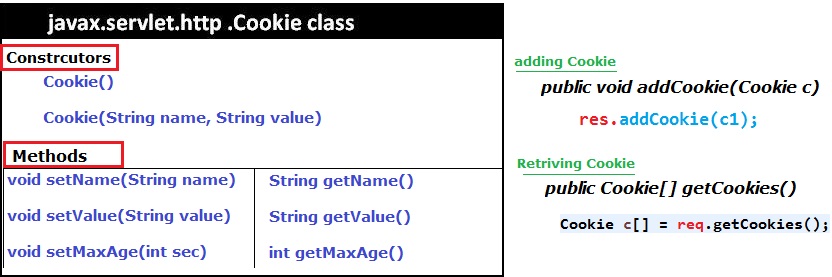
Cookie c1 = new Cookie("name", "Satya");
Cookie c2 = new Cookie("age", "28");
c1.setMaxAge(5000); //max 5 sec alive
res.addCookie(c1);
res.addCookie(c2);
pw.write("<h3>Cookies Added!");
}
}
-----------------------------------------
public class srv2 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
Cookie c[] = req.getCookies();
pw.println("<h4> Cookie Name : Cookie Value </h4>");
for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) {
pw.println(c[i].getName() + " : " + c[i].getValue());
}
}
}

3.Http Session
-
HttpSession Object memory allocates in Server
-
it remembers the client data across the multiple requests in the form of Session Attribute values
-
Every Session object contains SessionID, & stored in browser.
-
Session of a browser can be identified by SessionID.
Constructors
1.public HttpSession getSession():
-
Returns the current session associated with this request
-
If the request does not have a session, creates one.
2.public HttpSession getSession(boolean create
-
Returns the current session associated with this request
-
True request does not have a session, creates new session.
-
False request does not have a session, it wont create new session
Methods
-
public String getId() Returns a string containing the unique identifier value.
-
public long getCreationTime() Returns the time when this session was created
-
public long getLastAccessedTime() Returns the last time the client sent a
-
public void invalidate(): Invalidates this session then unbinds any objects bound to it.
public class srv1 extends HttpServlet {
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
HttpSession ses = req.getSession();
ses.setAttribute("name", "Ravi");
ses.setAttribute("city", "HYD");
pw.write("<h3>Session Added!");
}
}
--------------------------------------
public class srv2 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
HttpSession sess = req.getSession();
pw.write("Name : "+sess.getAttribute("name"));
pw.write("City : "+sess.getAttribute("city"));
}
}
-----------------------------------------
Output : Name : Ravi , City : HYD
4.URL Rewriting
In URL rewriting, we append a token or identifier to the URL of the next Servlet or the next resource.
We can send parameter name/value pairs using the following format:
url?name1=value1&name2=value2&??
Advantage of URL Rewriting
-
It will always work whether cookie is disabled or not (browser independent).
-
Extra form submission is not required on each pages.
Disadvantage of URL Rewriting
-
It will work only with links.
-
It can send only textual information.
-
Not Secure, user can read the information what we are sending
<form action="servlet1">
Name:<input type="text" name="userName"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="go"/>
</form>
public class FirstServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response){
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String n=request.getParameter("userName");
out.print("Welcome "+n);
//appending the username in the query string
out.print("<a href='servlet2?uname="+n+"'>visit</a>");
out.close();
}
}
public class SecondServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
//getting value from the query string
String n=request.getParameter("uname");
out.print("Hello "+n);
out.close();
}
}