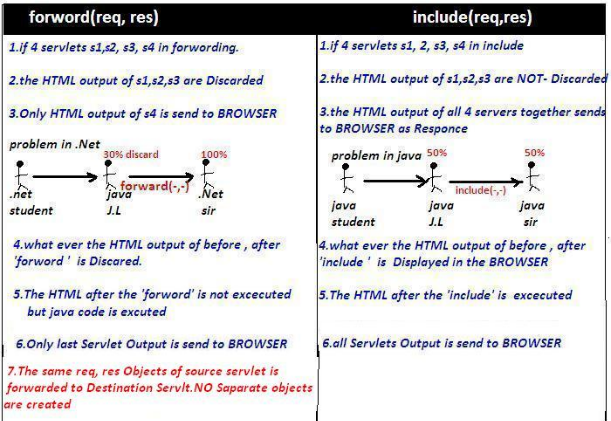
Servlet Chaining
Servlet chaining is used to achieve Communication between servlets. To perform this we have to use RequestDisptcher interface. following are the possible ways to achieve Servlet Chaining
-
rd. forward(req, res)
-
rd. include (req, res)
-
res.sendRedirect(/url)
RequestDisptcher Interface
The RequestDispatcher interface provides the facility of dispatching the request to another resource it may be html, servlet or jsp. We have 2 main methods in this RequestDisptcher
-
public void forward(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res)
-
public void include (ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res)
How to get RequestDisptcher Object
We have 3 ways to get RequestDisptcher object
1.using Request object
RequestDispatcher rd = request.getRequestDispatcher("/url or servletname");
rd.forward(req, res);
rd.include(req, res);
If we use request object, the webresource programs are must be in same web application
2.using ServletContext object with getRequestDispatcher(-url”) method
RequestDispatcher rd = context.getRequestDispatcher("/url or servletname");
rd.forward(req, res);
rd.include(req, res);
If we use Context object, the webresource programs are may in same/different web applictions
3.using ServletContext object with getNamedDispatcher(-servletname”) method
RequestDispatcher rd = context. getNamedDispatcher("serv1");
rd.forward(req, res);
rd.include(req, res);
-
/URL if we are placing .html, .jsp type of files we have to add ‘/’ in path
-
Servletname if we are using logical names of servlet/jsp like serv1, serv2 etc, then we must not to add ‘/’ in path
Servlet chaining in Same Server
We can use forward(), include() methods to perform chaining between two servlets which are resides in same web application or different web applications of same server
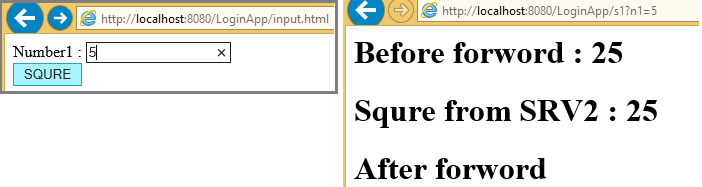
Forword() example
Input.html
<form action="s1" method="GET">
Number1 : <input type="text" name="n1"><br>
<input type="submit" value="SQURE">
</form>
Web.xml
<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>s1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>demo.srv1</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>s2</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>demo.srv2</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>s1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/s1</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>s2</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/s2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
srv1.java
public class srv1 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletConfig cg = getServletConfig();
ServletContext sc = cg.getServletContext();
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
String s1 = req.getParameter("n1");
int a = Integer.parseInt(s1);
int b = a * a;
pw.println("<h1>Before forword : " + b + "</h1>");
RequestDispatcher rd = sc.getRequestDispatcher("/s2");
rd.forward(req, res); // (1)
pw.println("<h1> After forword</h1>");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, res);
}
}
srv2.java
public class srv2 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
String s1 = req.getParameter("n1");
int a = Integer.parseInt(s1);
int b = a * a;
pw.println("<h1>Squre from SRV2 : " + b + "</h1>");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, res);
}
}

In above (1), if we just replace with include(req, res) as below it include serv1 result also
RequestDispatcher rd = sc.getRequestDispatcher("/s2");
rd.include(req, res);
Servlet chaining in Different Server
We can use res.sendRedirect(url) method to perform chaining between two servlets
which are running on different servers

public class srv3 extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter pw = res.getWriter();
pw.println("<h1>Before sendReditrect</h1>");
res.sendRedirect("http://www.google.com");
pw.println("<h1>After sendReditrect</h1>");
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, res);
}
}
| forward() method | sendRedirect() method |
|---|---|
| The forward() method works at server side. | The sendRedirect() method works at client side. |
| It sends the same request and response objects to another servlet. | It always sends a new request. |
| It can work within the server only. | It can be used within and outside the server. |