SpringBoot – SpringBoot +MySQL + Docker Example
Consider a scenario - You have just joined a new organization as a developer. You will now have to setup the project with the assistance of a fellow developer. He suggests you follow certain steps for setting up the required environment and then start the project deployable like a WAR. You do the same but keep getting some or other issues regarding environment configuration. May be even your fellow developer has forgot some configuration property he might have set.
Other similar scenario of this dependency hell are - The application is running on my dev machine but not in production. Dont know what issue is. There is also other scenarios like Matrix of Hell. But this is mostly related to DEVOPS people.
Docker to the rescue. Docker is a tool designed to make it easier to create, deploy, and run applications by using containers.
Containers allow a developer to package up an application with all of the parts it needs, such as libraries and other dependencies, and ship it all out as one package. Create self-contained development environments inside Docker containers. So, we share an environment already configured.
An image is a lightweight, stand-alone, executable package that includes
everything needed to run a piece of software, including the code, a runtime,
libraries, environment variables, and config files. 
So, an existing fellow developer will create an image of his environment and share it with the new developer. The new developer will just have to run the image as a docker container.
A container is a runtime instance of an image what the image becomes in memory when actually executed. It runs completely isolated from the host environment by default, only accessing host files and ports if configured to do so. So the following scenarios we can consider the use of docker for Java Developers-
-
Sharing development workspace, with preconfigured development environment.
-
Continuous integration is one of the most popular use cases for Docker. Teams looking build and deploy their applications quickly use Docker, combined with ecosystem tools like Jenkins, to drive apps from dev, testing staging and into production without having to change any code.
-
Running UAT’s using Docker
Deploying SpringBoot+MySQL using Dockerfile
We have following Code, after maven build it creates jar file.
(SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar)
https://github.com/smlcodes/Books-Sync-Gitlab/tree/main/Codes/SpringBoot-Thymeleaf
we have inbuilt apache tomcat in SpringBoot. So Apache tomcat container not required.
Create Dockerfile inside root directory SpringBoot-Thymeleaf
FROM openjdk:8
ADD target/SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
EXPOSE 8089
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar"]
Here
-
Use openJDK 8
-
Add the SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar from target directory
-
Use port 8089 to run the application
-
Execute SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar -jar command
Build Doker image by using docker build -t <name> from the directory where Dockerfile is placed.
docker build -t springboot-thymeleaf .
Docker will create the image of our application& tagged it as
SpringBoot-Thymeleaf
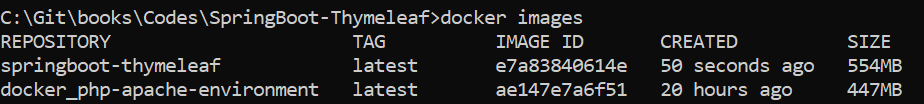
Once the image is built, use the following command to view the list of images:
docker images
Create MySQL DB Container image
pull MySQL image from Docker Hub.
docker pull mysql:latest
Run MySQL Docker container
C:\Git\books\Codes\SpringBoot-Thymeleaf>
-d
-p 6033:3306
--name=docker-mysql
--env="MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root"
--env="MYSQL_PASSWORD=root"
--env="MYSQL_DATABASE=webapp"
mysql
Similarly Start Sprint Boot application in the same manner using the following command.
docker run -t --link springboot-mysql:mysql -p 10222:10222 springboot-thymeleaf
Deploying SpringBoot+MySQL using Docker Compose
In above example we use CLI commands to run a database, and Spring Boot applications. We used Dockerfile to set up the environment and run the application by running containers separately and then building a link between them.
But for multiple container applications we can use the docker-compose tool. Docker CLI can manage a single container, but docker-compose can manage multiple containers and define the dependent services.
If we want to run services with the docker-compose tool, we have to follow these steps that are also defined in Docker documentation.
-
We need to define the application environment with a Dockerfile, so it can be reproduced anywhere.
-
We need to define the services that make up the application in
docker-compose.ymlso they can be run together in an isolated environment. -
Run docker-compose commands to run/stop the container or deploy/undeploy the application.
We need a docker-compose.yml file to write the services. In a Dockerfile, we
defined the environment of the application, and in docker-compose file we
write down the other properties of services, like which service will run on
which port, which service will be dependent on other services, which port will
be forwarded to other port for public access, define network, cluster
applications, etc.
Dockerfile
FROM openjdk:8
ADD target/SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
EXPOSE 8089
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "SpringBoot-Thymeleaf-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar"]
And the docker-compose.yml file looks like this:
version: '3'
services:
docker-mysql:
restart: always
container_name: springboot-mysql
image: mysql
environment:
MYSQL_DATABASE: webapp
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
MYSQL_ROOT_HOST: '%'
volumes:
- './sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d'
ports:
- '3306:3306'
healthcheck:
test: /usr/bin/mysql --user=root --password=root--execute "SHOW DATABASES;"
interval: 2s
timeout: 20s
retries: 10
springboot-thymeleaf:
restart: on-failure
build: ./
expose:
- '10222'
ports:
- '10222:10222'
environment:
WAIT_HOSTS: 'mysql:3306'
depends_on:
- docker-mysql
We will go to the project root directory. To run the application, we will use following commands:
-
docker-compose up— This will execute Dockerfile commands and will run services defined in the docker-compose file. -
docker-compose down— This will stop and remove all containers that were running by docker-compose file. -
docker-compose up --build— If we do an update on the Dockerfile, the war/jar file, or the docker-compose file.