Docker – Creating Docker Image for Lamp Stack (Apache+MySQL+PHP)
After you have downloaded and installed the Docker demon, open the Docker engine and make sure the engine is running.
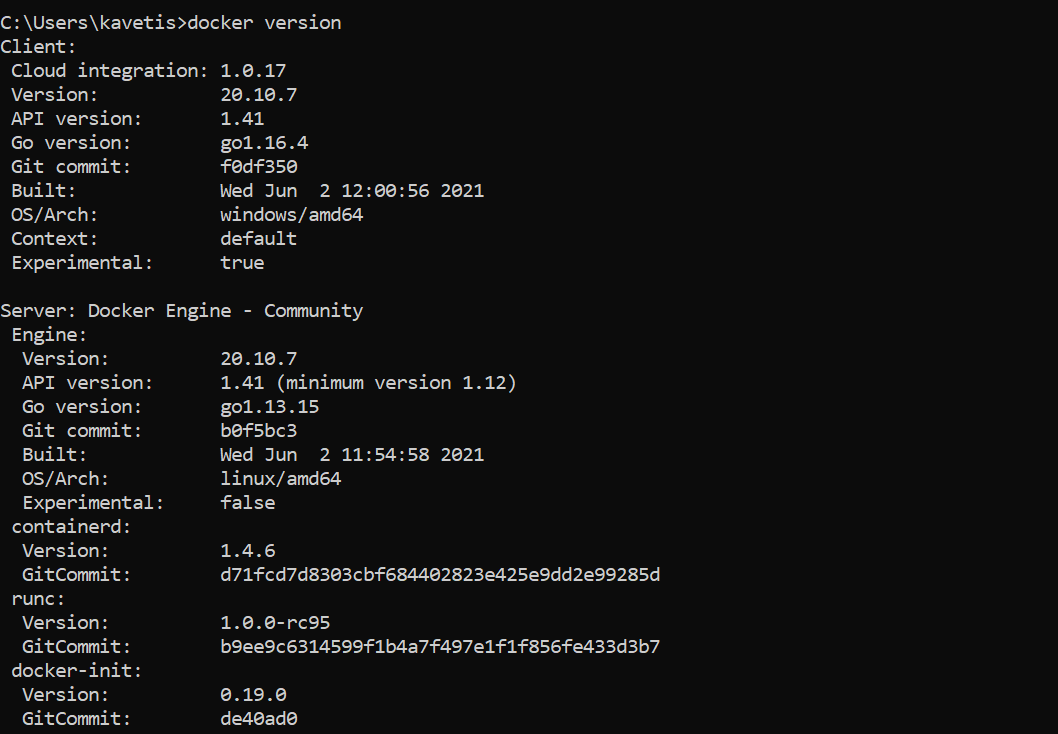
Open a command line verify if Docker is correctly installed on your computer.
docker version
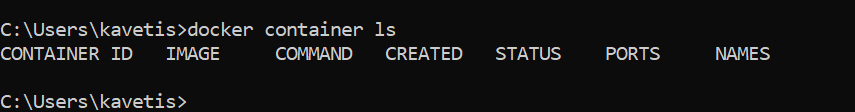
We are starting from scratch; make sure you have no containers and images running in your Docker engine.
Run docker container ls to check any available container.
To remove a Docker container, run docker container rm <container's name>. And
make sure no container is running.
docker-compose.yml
Docker compose file contains following hierarchy.
Docker version
Services
|
<Service-Name>
<Image Details>
Docker version you want to use, the services you want to provide, and the containers you want to run.
Apache Server Container
Add Apache server instance
version: '3.8'
services:
php-apache-environment:
container_name: php-apache
image: php:8.0-apache
volumes:
- ./php/src:/var/www/html/
ports:
- 8000:80
-
version: ‘3.8’ - Docker version
-
container_name - just a random name that you would like to name your PHP container.
-
image - this the official PHP image, the version of PHP Apache you want to use.
-
volumes - Root/home directory of the server
-
ports - This means that we are setting up an Apache server to expose port 80. Port 8000 reaches out to the PHP scripts and executes them in a browser from within Docker containers.
Let’s test it out. Go ahead and run docker-compose up. That’s going to pull all the information, download the Apache server, build the image, and run the container.
C:\Git\books\Codes\Docker>
Creating network "docker_default" with the default driver
Pulling php-apache-environment (php:8.0-apache)...
Digest: sha256:1a69e0b19f5e2d006bec4d985e678733bf452ce76bf558d15534a6ca1b73e089
Status: Downloaded newer image for php:8.0-apache
Creating php-apache ... done
If you open the Docker desktop engine, the container should be up and running.
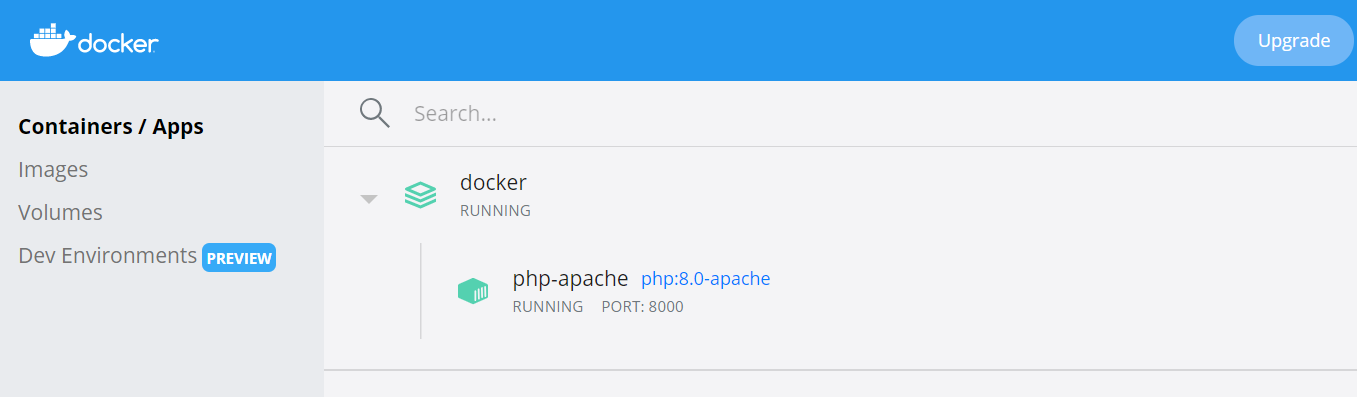
open your defined local host post in the browser,
http://localhost:8000/.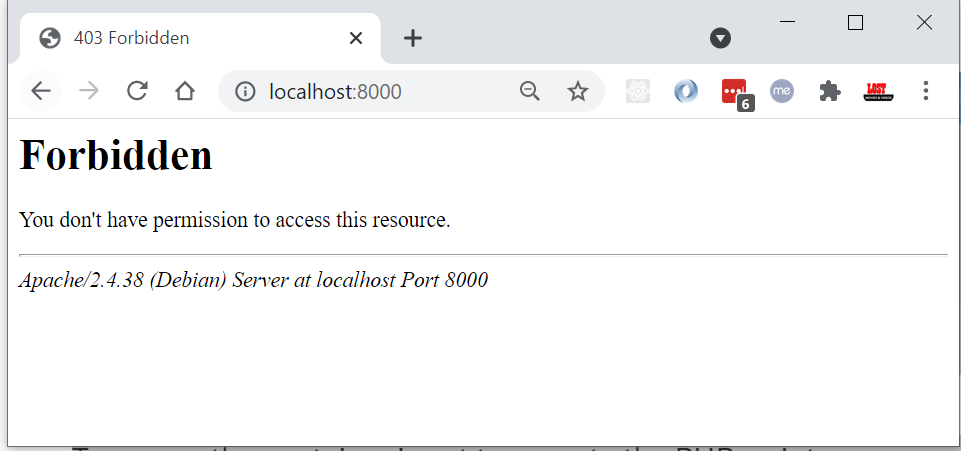
Docker will create php/src directory on the same folder where
docker-compose.yml is there.
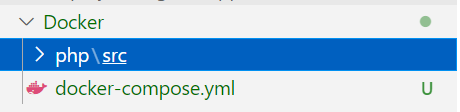
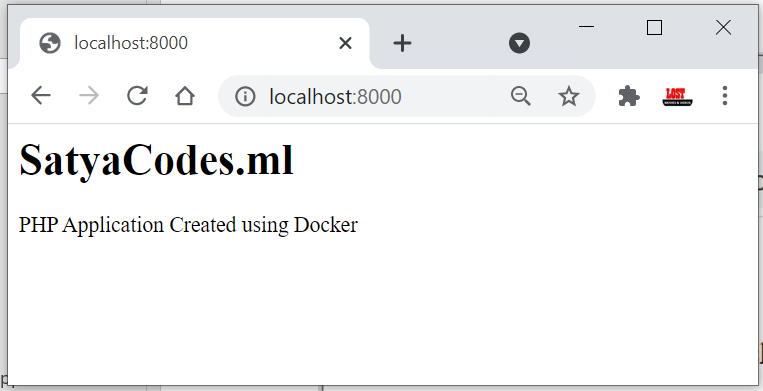
If you want write any PHP code, please place inside php/src folder. Lets
create index.php
<?php
echo "<h1>SatyaCodes.ml</h1>";
echo "PHP Application Created using Docker";
?>
Refresh Browser
MySQL database container
You would probably want to set up a database to interact with your website. We will create another service to provide MySQL support inside the PHP container.
Now we need to build this custom image inside php-apache service in
the docker-compose.yml file. PHP Apache also depends on the db service to
connect to MySQL. We need to configure it by specifying a depends_on
environment.
This is how your docker-compose.yml file should look like.
version: '3.8'
services:
php-apache-environment:
container_name: php-apache
build:
context: ./php
dockerfile: Dockerfile
depends_on:
- db
volumes:
- ./php/src:/var/www/html/
ports:
- 8000:80
db:
container_name: db
image: mysql
restart: always
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
MYSQL_DATABASE: MYSQL_DATABASE
MYSQL_USER: MYSQL_USER
MYSQL_PASSWORD: MYSQL_PASSWORD
ports:
- "9906:3306"
We need to add some MySQL support tools inside the PHP container for the two services (db and php-apache) to work correctly. This tool includes mysqli.
Inside your project directory, head to the /php folder, create a Docker file,
name it Dockerfile and add the following PHP configurations.
FROM
RUN docker-php-ext-install mysqli && docker-php-ext-enable mysqli
RUN apt-get update && apt-get upgrade -y
Here we have created a custom PHP Apache image and an environment that will install mysqli, a PHP extension that will connect the PHP Apache to the MySQL server.
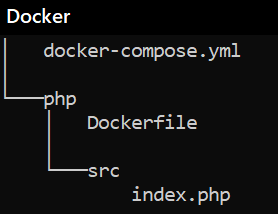
Now folder structure be like,
Run docker-compose up to pull and set up the MySQL environment. MySQL will be
added to the container.
C:\Git\books\Codes\Docker>
Pulling db (mysql:)...
latest: Pulling from library/mysql
/mysqld.sock' port: 3306 MySQL Community Server – GP
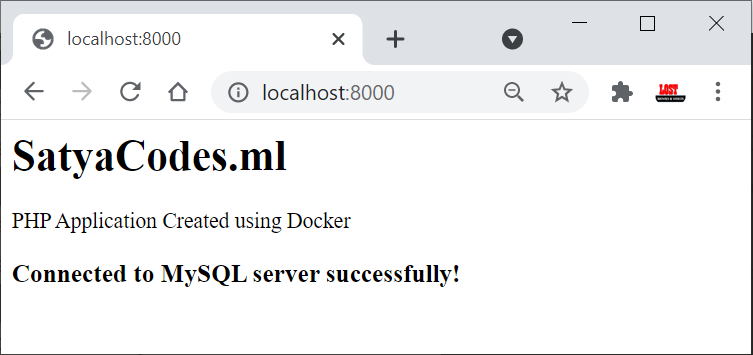
To test MySQL db connection, Update index.php with below code.
<?php
echo "<h1>SatyaCodes.ml</h1>";
echo "PHP Application Created using Docker";
$host = 'db';
// Database use name
$user = 'MYSQL_USER';
//database user password
$pass = 'MYSQL_PASSWORD';
// check the MySQL connection status
$conn = new mysqli($host, $user, $pass);
if ($conn->connect_error) {
die("<h3>Connection failed: </h3>" . $conn->connect_error);
} else {
echo "<h3>Connected to MySQL server successfully!</h3>";
}
PhpMyadmin Container
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
ports:
- '8080:80'
restart: always
environment:
PMA_HOST: db
depends_on:
- db
Run docker-compose up. Open http://localhost:8080/ to access the PHPMyAdmin.
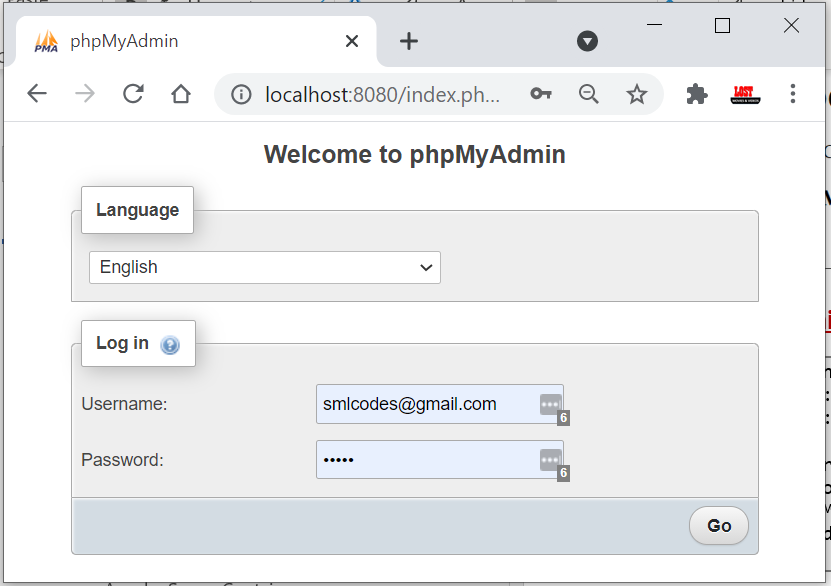
To login to the Phpmyadmin panel, use username as root and password as
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD. The password was already set in the MySQL environment
variables (MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD)
Update index.php to get some sample data from MySQL
//SQL
create table `users` (
id int not null auto_increment,
username text not null,
password text not null,
primary key (id)
);
insert into `users` (username, password) values
("admin","password"),
("Alice","this is my password"),
("Job","12345678");
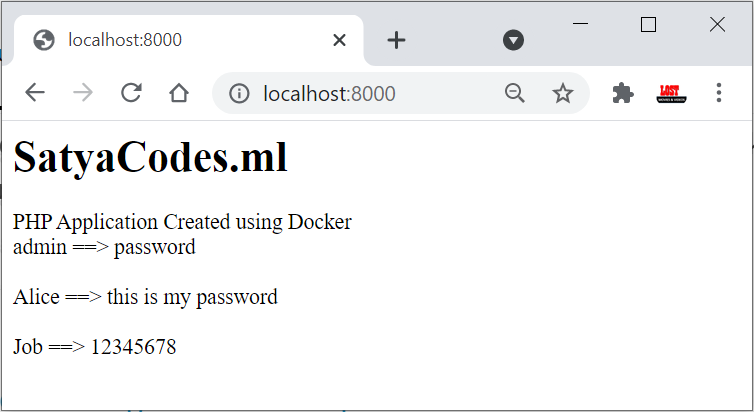
// index.php
<?php
echo "<h1>SatyaCodes.ml</h1>";
echo "PHP Application Created using Docker";
$host = 'db';
$user = 'MYSQL_USER';
$pass = 'MYSQL_PASSWORD';
$mydatabase = 'MYSQL_DATABASE';
$conn = new mysqli($host, $user, $pass, $mydatabase);
$sql = 'SELECT * FROM users';
if ($result = $conn->query($sql)) {
while ($data = $result->fetch_object()) {
$users[] = $data;
}
}
foreach ($users as $user) {
echo "<br>";
echo $user->username . " ==> " . $user->password;
echo "<br>";
}
?>