JDBC CURD Operations
executeQuery (String sql) example
We use this method to execute SELECT queries
public class JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection
("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb", "root", "123456");
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM customer");
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1)+""+rs.getString(2)+" "+ rs.getString(3));
}
con.close();
}
}
-----------------------
101 Satya HYD
102 Ravi VIJ
103 RAKESH CHENNEI
104 Surya BANG
executeUpdate (String sql) example
We use this method to NON-SELECT Queries like UPDATE, DELETE, etc
- Returns 1 if success
- Returns 0 if Failure
public class JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
String qry = "UPDATE `customer` SET `name`='Ram' WHERE `cid`=102";
int res = stmt.executeUpdate(qry);
if (res > 0)
System.out.println("Success is :" + res);
else
System.out.println("Failure is :" + res);
con.close();
}
}
---------------------
Success is :1
Failure is :0
Boolean execute() example
We can use execute() method in both SELECT & NON-SELECT queries.
1. SELECT
It returns TRUE on SELECT queres we can get ResultSet by calling below method
ResultSet rs = statement.getResultSet ()
2. NON-SELECT
It returns FALSE on NON-SELECT queres. we can get Int value by calling below
method
int i = statement.getUpdateCount();
public class JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
// String qry = "SELECT * FROM customer";
String qry = "UPDATE `customer` SET `name`='Ram' WHERE `cid`=102";
boolean flag = stmt.execute(qry);
if (flag == true) {
System.out.println("SELECT QUERY\n --------");
ResultSet rs = stmt.getResultSet();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString(1) + ":" + rs.getString(2));
}
}
else {
System.out.println("NON-SELECT QUERY\n --------");
int i = stmt.getUpdateCount();
System.out.println("Result is : " + i);
}
}
}
SELECT QUERY
--------
101:Satya
102:Ram
103:RAKESH
104:Surya
NON-SELECT QUERY
--------
Result is : 1
executeBatch(String sql) example
public class BatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
Statement st = con.createStatement();
st.addBatch("insert into student values(81, 'Syam', 'mtm')");
st.addBatch("insert into student values(11, 'ram', 'mum')");
st.addBatch("insert into student values(14, 'bam', 'kuk')");
st.addBatch("insert into student values(44, 'pram', 'secu')");
int rs[] = st.executeBatch();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rs.length; i++) {
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println(sum + "Record are UPDATED using BATCH");
}
}
Scrollabe Resultset(String sql) example
By Default ResultSet Object is not SCROLLABLE & NOT UPDATABLE.to make ResultSet Object to move both Directions we need to configure TYPE & MODE Values
Possible TYPE Values
- ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE (Update Possible)
- ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE (Default)
Possible MODE Values
- ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY (Update Possible)
- ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE (Default)
Methods applicable on Scrolable ResultSet Object
-
int getRow() Returns ROW INDEX
-
boolean first() Keep CURSOR at 1st Record
-
boolean last() Keep CURSOR at LAST Record
-
boolean next() Moves Cursor to Forward
-
boolean previous() Moves Cursor to Backword
-
boolean absolute(int +/-) Moves Cursor to given Index on ResultSet
-
boolean relative(int +/-) Moves Cursor to given Index, based on current Row
public class JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456"); Statement st = con.createStatement
(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from customer");
System.out.println("From Using Next\n------");
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2));
}
System.out.println("\nFrom Using Previous ");
while (rs.previous()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2));
}
System.out.println("randomly................... ");
rs.first();
System.out.println(rs.getRow()+"First:"+rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2));
rs.last();
System.out.println(rs.getRow()+"Last: "+rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2));
rs.absolute(4);//from starting point to 4 records
System.out.println(rs.getRow()+"Absolute:"+rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2));
rs.relative(-2); //from here to 2 points back
System.out.println(rs.getRow()+"relative:"+rs.getString(1)+":"+rs.getString(2));
}
}
From Using Next
------
101:Satya
102:Ram
103:RAKESH
104:Surya
From Using Previous
104:Surya
103:RAKESH
102:Ram
101:Satya
randomly...................
1First: 101:Satya
4Last: 104:Surya
4Absolute Record : 104:Surya
2relative Record : 102:Ram
In above example we used on for SCROLLING resultset on both ditections using
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY.
If we want perform UPDATE operations & SCROLLING also, we have to use
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE
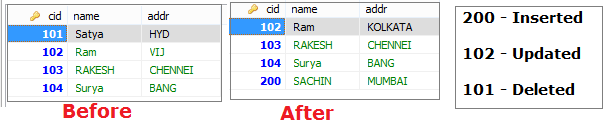
Steps to Perform Insert/ UPDATE /Delete Operations on ResultSet
1. Select the Records
while (rs.next())
{
System.out.println(rs.getRow()+""+rs.getString(1)+","+ rs.getString(2));
}
2. Perform INSERT Operation
System.out.println("1.INSERT OPERATION\n-----");
rs.moveToInsertRow(); // creates Empty Record
rs.updateInt(1, 200);
rs.updateString(2, "SACHIN");
rs.updateString(3, "MUMBAI");
rs.insertRow(); // Inserts Row
3. Perform UPDATE Operation
System.out.println("\n2.UPDATE OPERATION\n-----");
rs.absolute(2); // move to row to update
rs.updateString(3, "KOLKATA");
rs.updateRow();
4. Perform DELETE Operation
System.out.println("\n3.DELTE OPERATION\n-----");
rs.absolute(1); // move to row to DELETE
rs.deleteRow();
Example
public class JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb";
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
Statement st = con.createStatement
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from customer");
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getRow() + "->" + rs.getString(1) + "," + rs.getString(2));
}
System.out.println("1.INSERT OPERATION\n-----");
rs.moveToInsertRow(); // creates Empty Record
rs.updateInt(1, 200);
rs.updateString(2, "SACHIN");
rs.updateString(3, "MUMBAI");
rs.insertRow(); // Inserts Row
System.out.println("\n2.UPDATE OPERATION\n-----");
rs.absolute(2); // move to row to update
rs.updateString(3, "KOLKATA");
rs.updateRow();
System.out.println("\n3.DELTE OPERATION\n-----");
rs.absolute(1); // move to row to DELETE
rs.deleteRow();
}
}