Ways to Deploy Application in Apache Tomcat
While working with deployment of Java web applications on Tomcat, you should prepare yourself with a strong grasp about the following stuff:
-
$CATALINA_HOME: is an environment variable points to the directory where you installed Tomcat. For example,c:\Program Files\Apache Software Foundation\Tomcat 7.0on Windows. -
$CATALINA_BASE:is an environment variable points to the directory of a particular instance of Tomcat (if you configure multiple instances of Tomcat). -
Web applications are put under
$CATALINA_HOME\webappsdirectory. -
Document root:is the top-level directory of a web application, where all the resources (JSP pages, HTLM pages, Java classes, images…) that constitute that application are placed. -
Context path:is the name which is relative to the server’s address (i.e http://localhost) and represents the name of the web application. For example, if your web application is put under $CATALINA_HOME\webapps\MyWeb directory, it will be accessed by the URL http://localhost/MyWeb, and its context path is /MyWeb. -
JAR libraries which are shared among web applications are put under
$CATALINA_HOME\libdirectory. -
Application-specific JAR libraries are put under web application’s
WEB-INF\libdirectory.
Deploy method #1: copying Java web application archive file (.war)
Copy the WAR file into $CATALINA_HOME\webapps directory.
Restart the server. Whenever Tomcat is started, it will unpack the WAR file it found in the webapps directory and launch the application in that manner.
Deploy method #2: copying unpacked Java web application directory
Copy the application’s directory from its location into $CATALINA_HOME\webapps directory.
Restart the server, the application is deployed with the context path is name of the directory you copied.
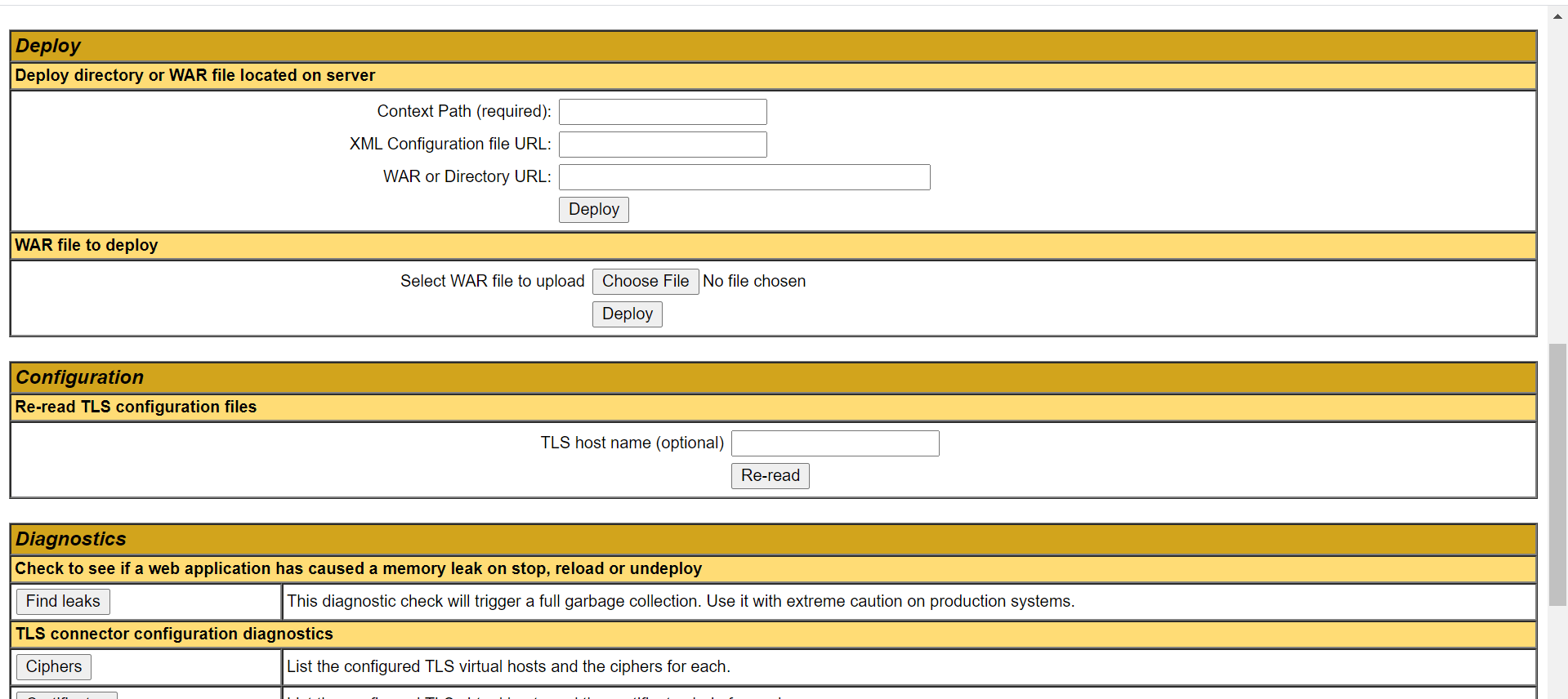
Deploy method #3: using Tomcat’s manager application
Access - http://localhost:8080/manager/html
Upload WAR