1.Introduction
Version Control System (VCS)
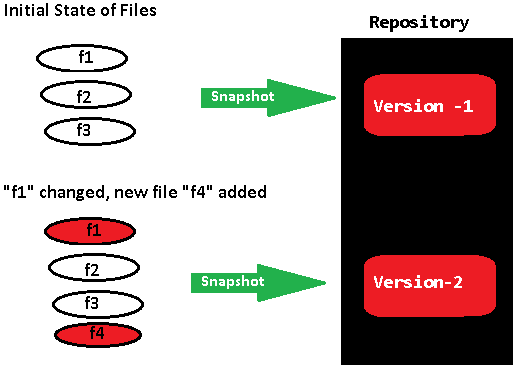
A version control system (VCS) allows you to track the history of a collection of files. It supports creating different versions of this collection. Each version captures a snapshot of the files at a certain point in time and the VCS allows you to switch between these versions. These versions are stored in a specific place, typically called a repository
We have 3 types of version control systems
-
Localized version control systems
-
Centralized version control systems
-
Distributed version control systems
1. Localized version control systems
A localized version control system keeps local copies of the files. This
approach can be as simple as creating a manual copy of the relevant files.
Examples: Revision Control System (RCS) Source Code Control System (SCCS)
2. Centralized version control systems
A centralized version control system provides a server software component which
stores and manages the different versions of the files. A developer can copy
(checkout) a certain version from the central sever onto their individual
computer.
Examples: Subversion (SVN), TFS
Both approaches have the drawback that they have one single point of failure. In a localized version control systems it is the individual computer and in a centralized version control systems it is the server machine
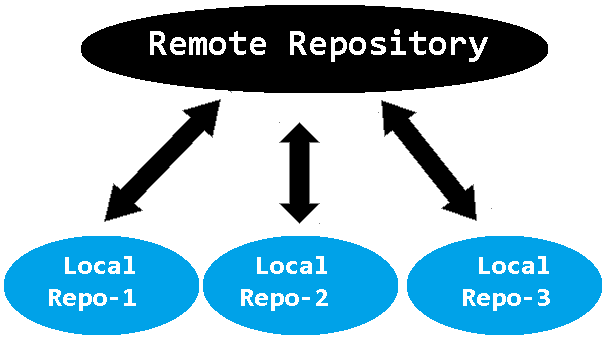
3. Distributed version control systems
In a distributed version control system each user has a complete local copy of a
repository on his individual computer. The user can copy an existing repository.
This copying process is typically called cloning. Every clone contains the
full history of the collection of files and a cloned repository has the same
functionality as the original repository.
Typically, there is a central server for keeping a repository but each cloned repository is a full copy of this repository.
Examples : GIT, BitBucket, GitHub
Introduction to GIT
Git is a distributed version control system, founded in 2005 by Linus Torvald.we can Setup GIT in our machine by downloading it from below links
Git configuration
git config command allows you to configure your Git settings. Git stores all
global configurations in .gitconfig file, which is located in your home
directory
Setting username: This information is used by Git for each commit.
[SmlCodes_Admin]$ git config --global user.name "Small Codes"
Setting email id: This information is used by Git for each commit.
[SmlCodes_Admin]$ git config --global user.email "admin@smlcodes.com"
Git Basic Operations
git init – Create a new repository
Every Git repository is stored in the .git folder of the directory in which the Git repository has been created. This directory contains the complete history of the repository. The .git/config file contains the configuration for the repository.
We use the git init command to create a Git repository in the current directory
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos
$ mkdir LoginDemo
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos
$ cd LoginDemo/
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo
$ git init
Initialized empty Git repository in E:/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo/.git/
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo (master)
$ git status
On branch master
Initial commit
nothing to commit (create/copy files and use "git add" to track)
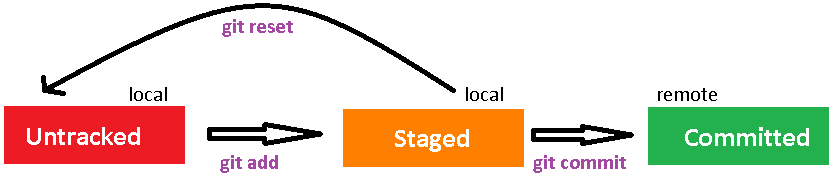
git add – Add a new file to the repo
In LoginDemo repo I want to add 3 files -index.jsp, signup.jsp, login.jsp.
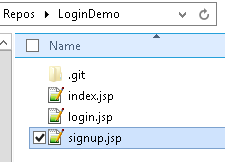
We use git add command to put a snapshot of the file to the staging area.
1.Adding single file to Stage
=========================================
Syntax : git add <file-name>
Example: git add index.php
2.Adding files of same type
=========================================
Syntax : git add -<wildcard>.<extension>"
Example: git add -*.jsp"
3.Adding all files at a time
=========================================
Syntax : git add .
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo (master)
$ git status
On branch master
Initial commit
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
index.jsp
login.jsp
signup.jsp
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo (master)
$ git add .
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo (master)
$ git status
On branch master
Initial commit
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: index.jsp
new file: login.jsp
new file: signup.jsp
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo (master)
$
git commit – commiting changes
git commit command will Stores the current contents of the index in a new commit along with a log message from the user describing the changes.
Syntax : git commit -m "<message>"
git log
git log command will Shows the commit logs.
kaveti_s@HYDPCMCSTS MINGW64 /e/Users/devops/Repos/LoginDemo (master)
$ git log
commit 08032d113ef458a2783da26464d91881449e14a1
Author: Kaveti Vs Satyanarayana <Kaveti_S@ad.infosys.com>
Date: Thu Jul 13 17:56:33 2017 +0530
3.Remote repositories
We created a new empty repository in BitBucket called LoginDemo
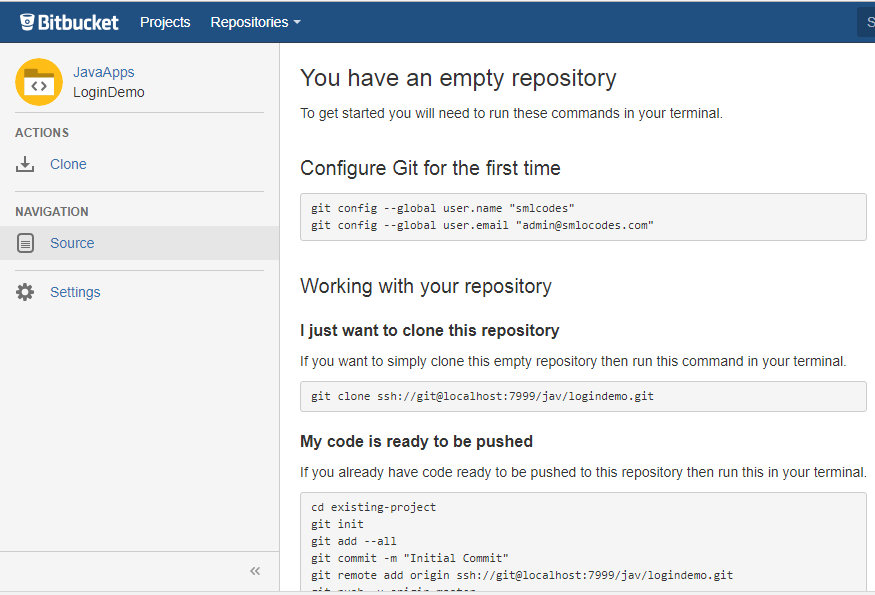
git remote
Now our code is ready in local system, we have to add this into newly created bitbucket repo. For doing this we need use git remote command
kaveti_S@HYDPCM90480L MINGW64 /d/Repo/LoginDemo (master)
$ git remote add origin ssh://git@localhost:7999/jav/logindemo.git
git push
Now we conncted with remote repo. To place these files in Remote repository we use git push command
kaveti_S@HYDPCM90480L MINGW64 /d/Repo/LoginDemo (master)
$ git push -u origin master
Counting objects: 5, done.
Delta compression using up to 4 threads.
Compressing objects: 100% (5/5), done.
Writing objects: 100% (5/5), 800 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done.
Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
To ssh://localhost:7999/jav/logindemo.git
* [new branch] master -> master
Branch master set up to track remote branch master from origin.
Now code is Pushed into remote repository.
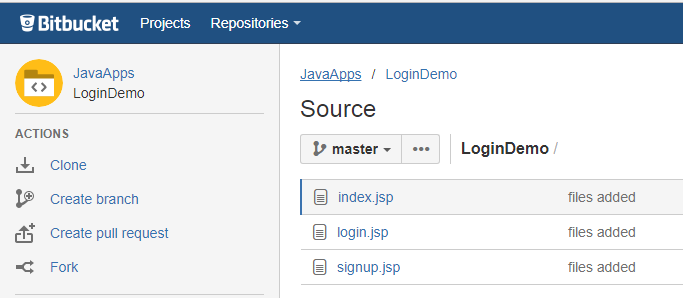
git clone
git clone is used to checkout the remote repository & create a working copy of a local repository.
Syntax: git clone /path/to/repository
kaveti_S@HYDPCM90480L MINGW64 /d/Repo
$ git clone ssh://git@localhost:7999/jav/logindemo.git
Cloning into 'logindemo'...
remote: Counting objects: 5, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (5/5), done.
remote: Total 5 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
Receiving objects: 100% (5/5), done.
git pull
git pull is used for check the changes on our remote repository and pull down if any new changes exist.
Syntax: **git pull origin
kaveti_S@HYDPCM90480L MINGW64 /d/Repo/logindemo (master)
$ git pull origin master
From ssh://localhost:7999/jav/logindemo
* branch master -> FETCH_HEAD
Already up-to-date.
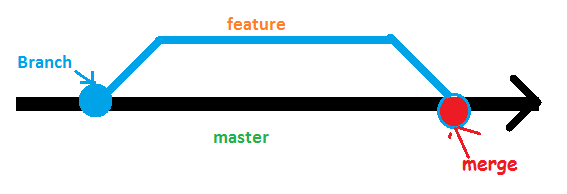
4. Branching
Branches are used to develop features isolated from each other. The master branch is the “default” branch when you create a repository. Use other branches for development and merge them back to the master branch upon completion.